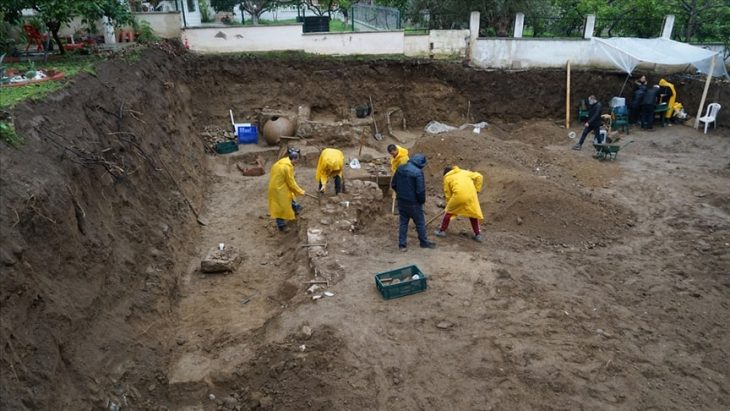
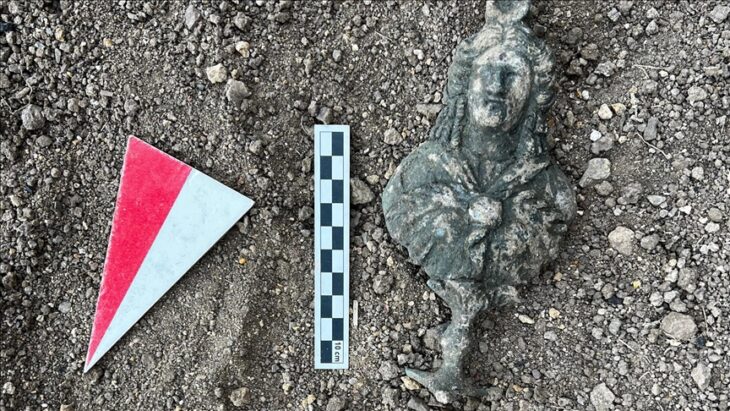
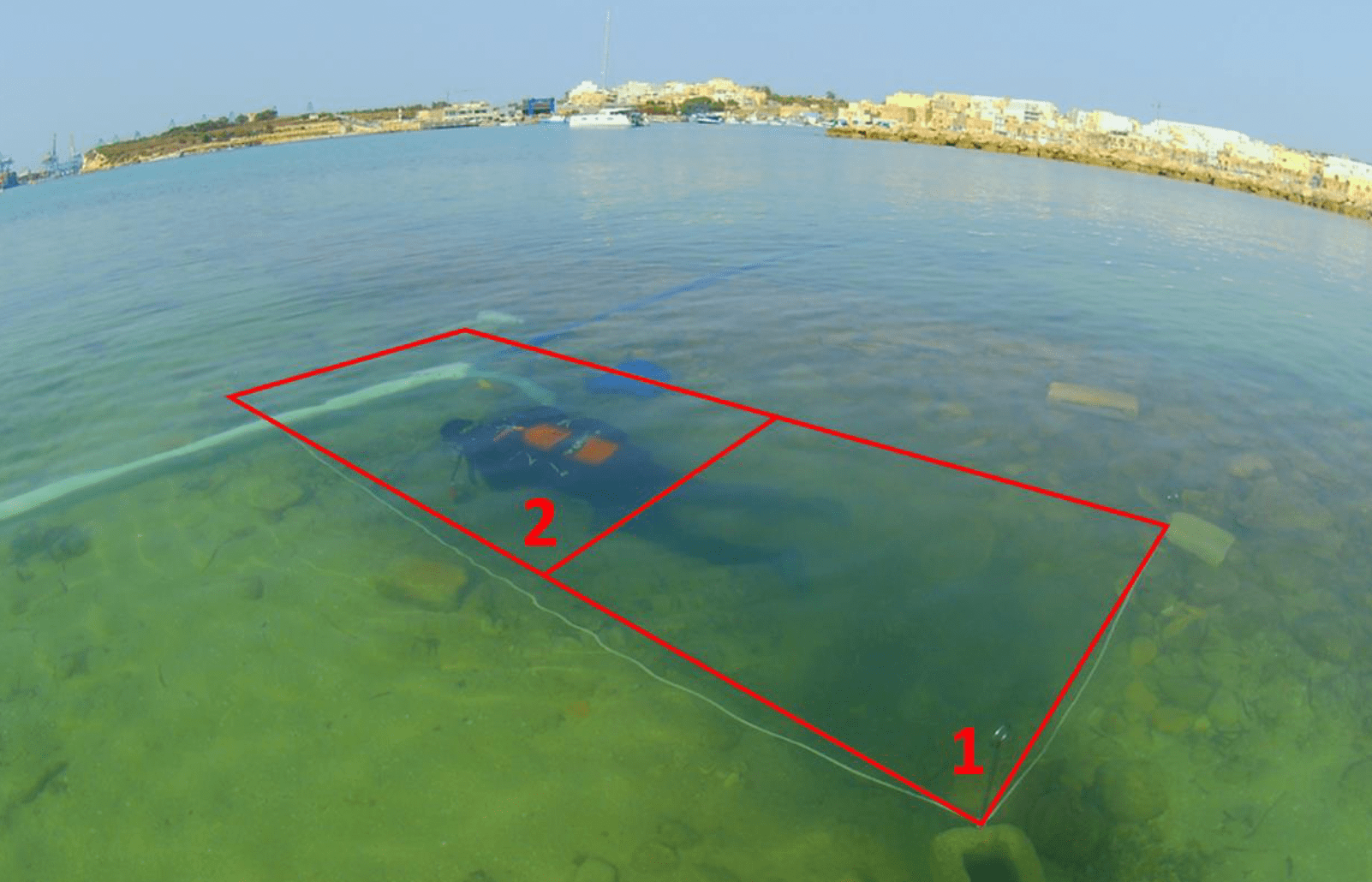
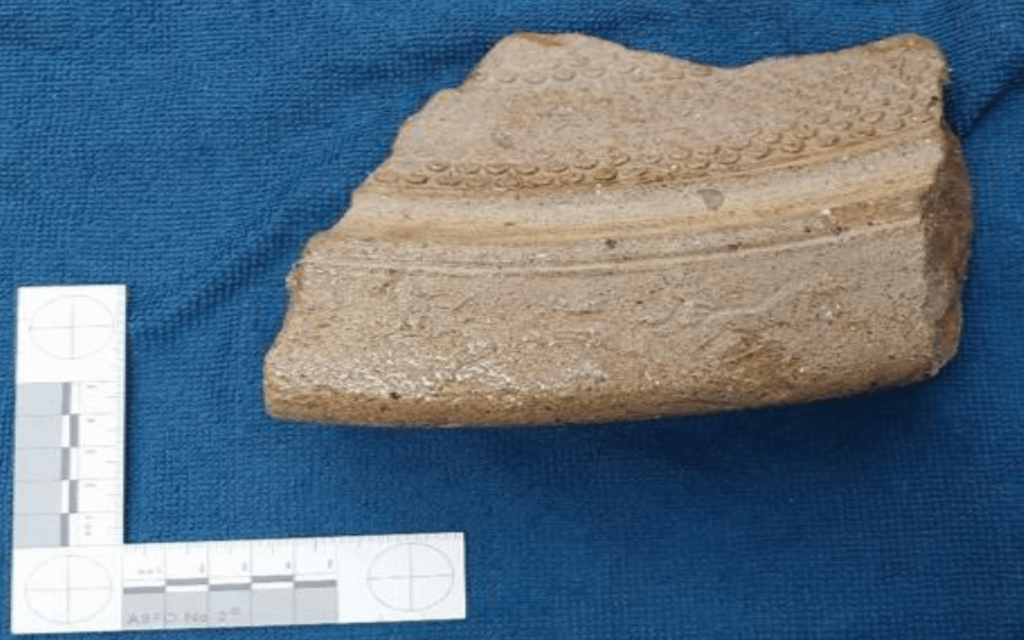
Archaeological investigations, initiated by a proposal to build a 130-meter-long boulder revetment along the shore of Ballut ta’ Marsaxlokk to protect the habitat from sea erosion in the south-eastern region of Malta, have yielded 64 individual artifacts, including an important fragment of a louterion.
The term ‘louterion’ (coming from a word meaning ‘wash’) is a vessel used for holding water for bathing or washing, usually mounted on a pedestal, and used in both domestic and sacred or ritual settings.
Louteria are typical of the Greek Late Archaic period, which occurred in the 6th and 5th centuries BCE. However, non-Greek indigenous cultures in the Central Mediterranean also modified louteria to suit their requirements.
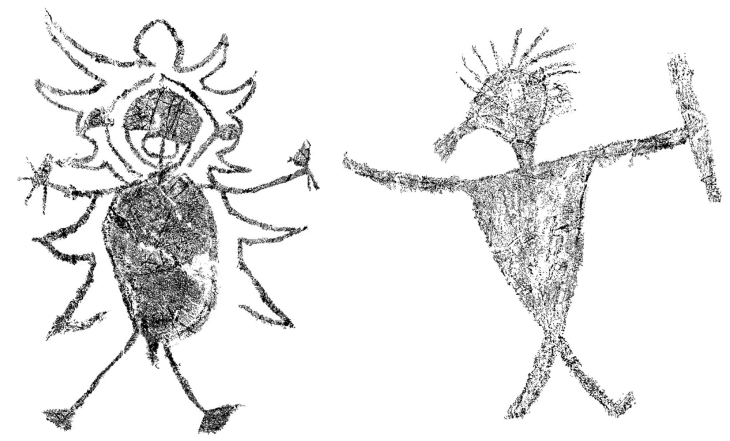
The louterion fragment was recovered from the seabed in a trench about 45 cm deep. The basin fragment, originally part of an object 70cm in diameter, features elaborate decorations, and the image of horse-drawn chariots can be discerned around its rim. Usually similar examples from Sicily date to the 6th and 5th centuries BCE.
Rarely discovered, louteria with images of horses pulling chariots have been discovered in Etruscan and Greek contexts, such as Athens, Corinth, and Greek colonies in Sicily and southern Italy. These basins are used in ritual settings and are frequently decorated with intricate scenes of chariots, which represent victory or divine favor. Louteria were commonly used in purification rituals, both in domestic settings and temples.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Given their apparent significance in a range of religious, domestic, and ceremonial contexts, these artifacts are important resources for learning about ancient societies.
At least 64 distinct objects have been inventoried thus far, despite the fact that the archaeological report is still in its preliminary stages and the artifacts are still being examined. The majority of the finds are ceramics, although metal, stone, and bones from marine and fauna have also been found.
The concentration of a significant amount of material in a small area indicates that the site is extremely archaeologically sensitive and must be protected and investigated further, according to the Superintendence for Cultural Heritage Malta (SCH).
The depth at which the artifacts were found suggests that they were thrown into the water at the location where they were discovered.
Additionally, two trenches were dug down to average depths of 50 and 125 cm, respectively, below the seafloor. According to the excavations, one of the trenches was built with meticulously stacked limestone rubble. The building predates the artifacts discovered beneath it, but more research is needed because it is currently difficult to date the building precisely.
The Superintendence of Cultural Heritage will continue to investigate the area, primarily underwater, in the coming months to address various research questions arising from this initial investigation
Cover Image: Underwater investigations at Il-Ballut in Marsaxlokk Malta