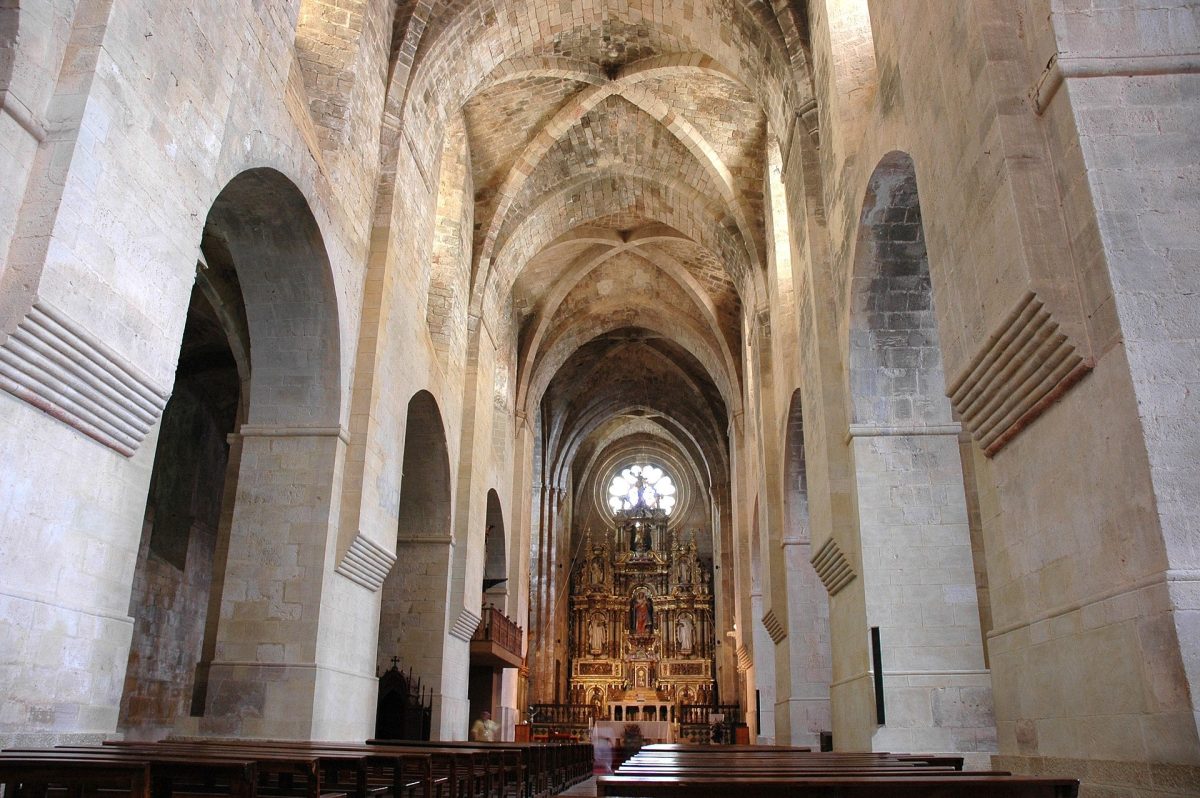
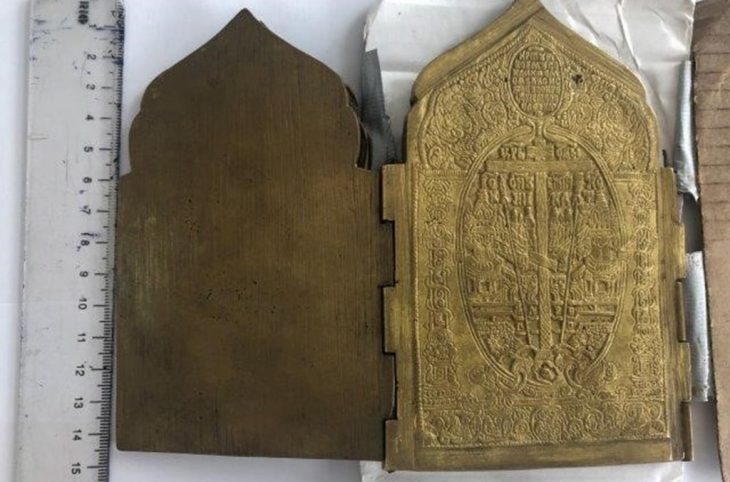
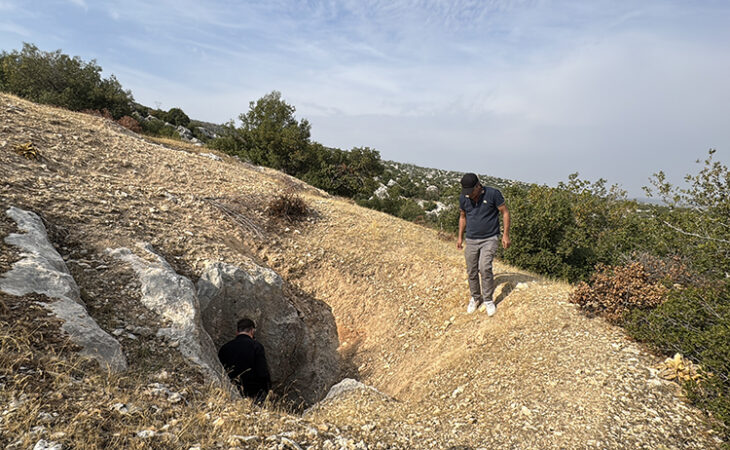
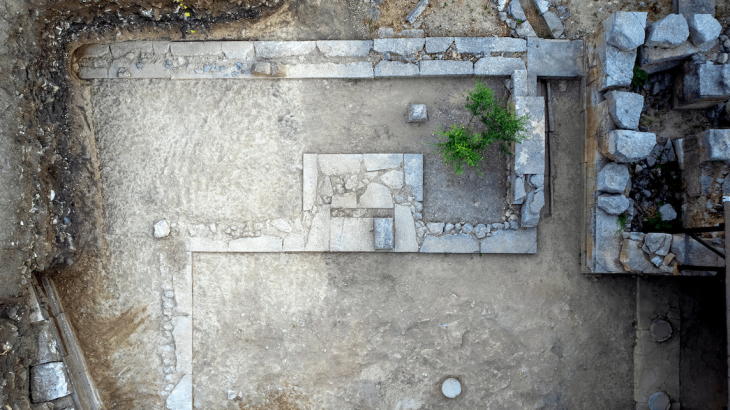
A team of archaeologists and anthropologists found the human remains of a dozen members of the Catalan nobility dating back to the 13th and 14th centuries at the Royal Monastery of Santes Creus, a Catalan cultural heritage site in northeastern Spain.
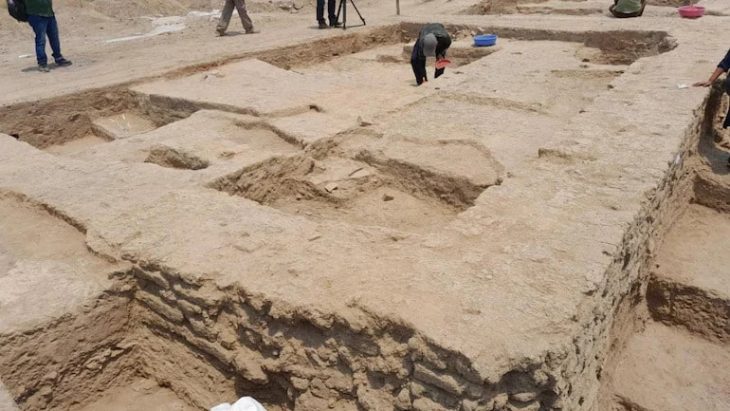
The discovery was made after the restoration of the ancient Gothic cloister began in April of 2023 and six sarcophagi were opened.
In a press release, the autonomous community of Catalonia’s Department of Culture, the not-for-profit “La Caixa” banking foundation, and a team of researchers announced their “exceptional discovery” at the Gothic cloister of the Royal Monastery of Santes Creus in Tarragona.
The restoration of the Gothic cloister in the municipality of Aiguamúrcia has been ongoing, but the release states that the finding of the intact royal burials was “totally unexpected,” revealing an unusual funerary complex.
The team called the find “exceptional” as it shows a chronological and social class uniformity as well all the diversity of cases, the good state of preservation of bones and bone tissue, and textile remains.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Prior to opening the tombs, experts suspected that they had already been looted, based on existing documentation.
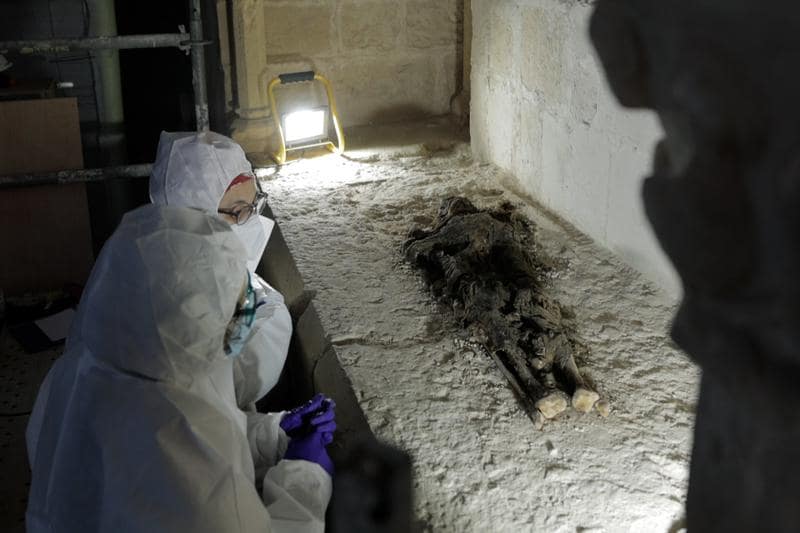

According to the archaeologist Josep Maria Vila, the find was surprising, because “in principle, there shouldn’t be human remains in such good condition inside the sarcophagi, because they should have been looted.”
However, Vila pointed out that the human remains inside the coffins were preserved without being desecrated, adding that it is the first time such a find has been made in Catalonia:
“In no other site we have excavated have we found so many remains in such good condition,” he said, adding that the burial site at Santes Creus was left “as the monks had left it.”
According to a press release from the Catalan Ministry of Culture, the royals were buried in Santes Creus after King James II (also known as James the Just or James of Aragon) and his second wife Blanca d’Anjou to turn the monastery into ‘a pantheon of Catalan royalty’. From 1291 to 1327, James served as King of Aragon and Valencia, as well as Count of Barcelona, among other titles.

At the Royal Monastery of Santes Creus, restoration work started in April of last year. Their goals included restoring the monastery’s famous tombs and waterproofing the roof. They discovered six stone sarcophagi buried in one of the walls during this process. This room, called the cloister, is well known for housing the massive, elaborately built stone coffins that mark the resting places of many noble families from the 1300s.
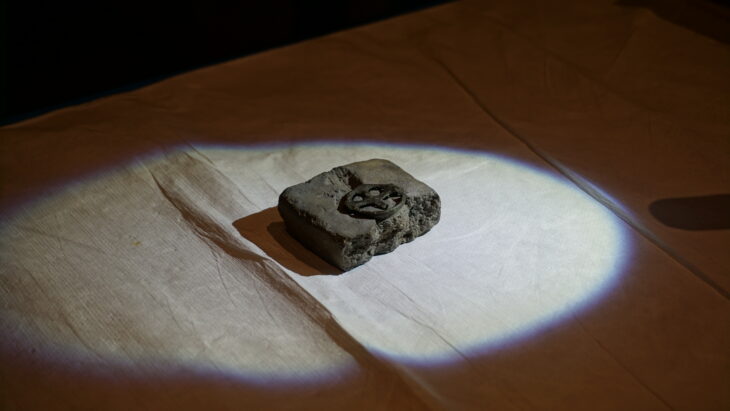
The sarcophagi within the monastery are adorned with heraldic symbols, aiding in the identification of the nobles entombed within as members of the Cervelló, Cervera, Queralt, Puigvert, and Montcada families.
Human tissue and textile fabric samples were carefully extracted from the tombs. These samples are expected to provide invaluable insights into various aspects of the individuals’ lives, including their identities, dietary habits, potential illnesses, living conditions, burial practices, and rituals.
When taken as a whole, the investigations may clarify the funerary customs and burial practices of the Catalan nobility in the Middle Ages.
Cover Photo: Commons