A new natural technique for cleaning and preserving priceless ancient Egyptian papyrus that are in danger from bacteria and fungi has been discovered by researchers. This new technique employs wasabi – yes, the pungent green paste accompanying your sushi – to combat the relentless threat of fungal damage on these precious historical documents.
The study, led by Hanadi Saada and her team, investigated the effectiveness of wasabi vapors in eliminating microbial growth that deteriorates papyrus artifacts, which have historical and cultural significance, particularly in ancient Egypt.
The techniques used up until now to clean and sanitize the papyri presented certain difficulties. Chemicals were employed that, while effectively eliminating microbes, sometimes damaged the papyrus fiber or altered the pigments of the illustrations. Other physical methods, such as ultraviolet rays or heat, did not always ensure the complete removal of biological agents without causing collateral damage. This is where wasabi comes into play.
The Grand Egyptian Museum’s team has devised a ‘green’ solution that promises to protect these ancient texts without jeopardizing their integrity by generating vapors from wasabi paste.
Scientists simulated microbiological contamination on samples of papyrus with different pigments, including red, yellow, and blue.
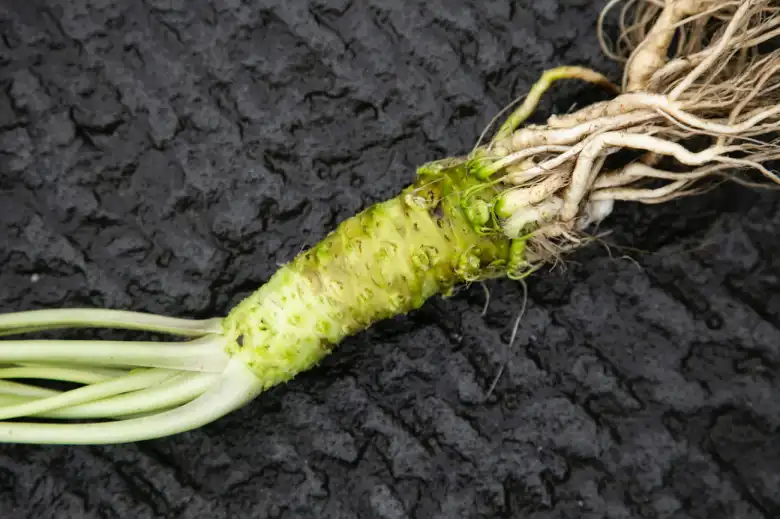

In this experiment, treatment with wasabi vapors for 72 hours eradicated microbial growth in both painted and non-painted papyrus samples with a 100% inhibition efficiency. Notably, the treatment improved the tensile strength of the papyri by 26% without causing any noticeable change to the color or surface morphology of the artifacts. Furthermore, FT-IR and EDX analyses indicated negligible chemical changes, underscoring the non-invasive nature of the treatment.
In addition to providing a safer, more environmentally friendly option for preserving archaeological papyri, this cutting-edge technique guarantees the longevity of these priceless relics without sacrificing their integrity. The results of the study point to a dramatic shift in favor of environmentally friendly conservation techniques and highlight the significance of sustainable methods for the preservation of cultural heritage and archaeology.
The results of this study could have an impact on preservation methods for a variety of organic archaeological materials, going beyond papyri conservation. The archaeological community is keeping a close eye on the research in the hopes that this environmentally friendly solution will usher in a new era for the preservation of our world’s cultural heritage.
The study was published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2024.105936
Cover Photo: The Book of the Dead of Hunefer, sheet 3.