Researchers have successfully extracted ancient DNA from a 2,900-year-old clay brick, uncovering a wealth of information about the plant life cultivated during that era.
While offering an invaluable look into the past, this monumental research also opens the door for similar studies on clay material from various sites and time periods.
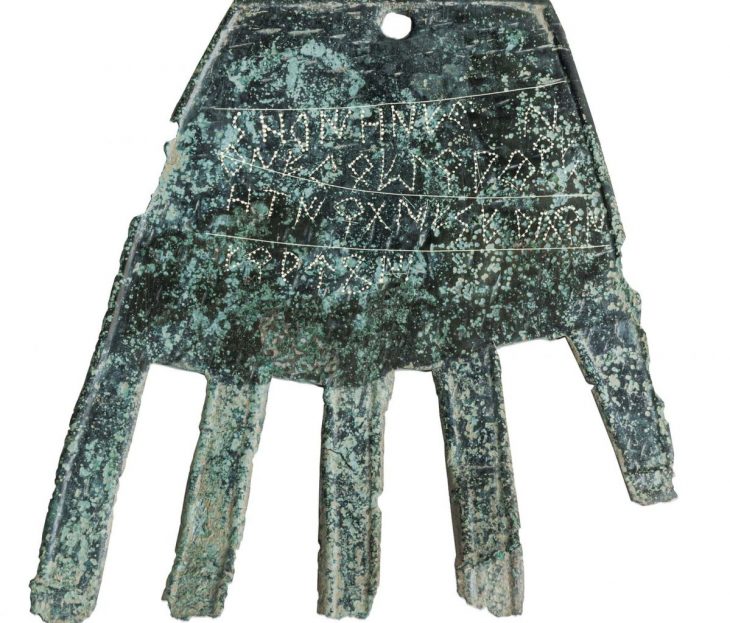
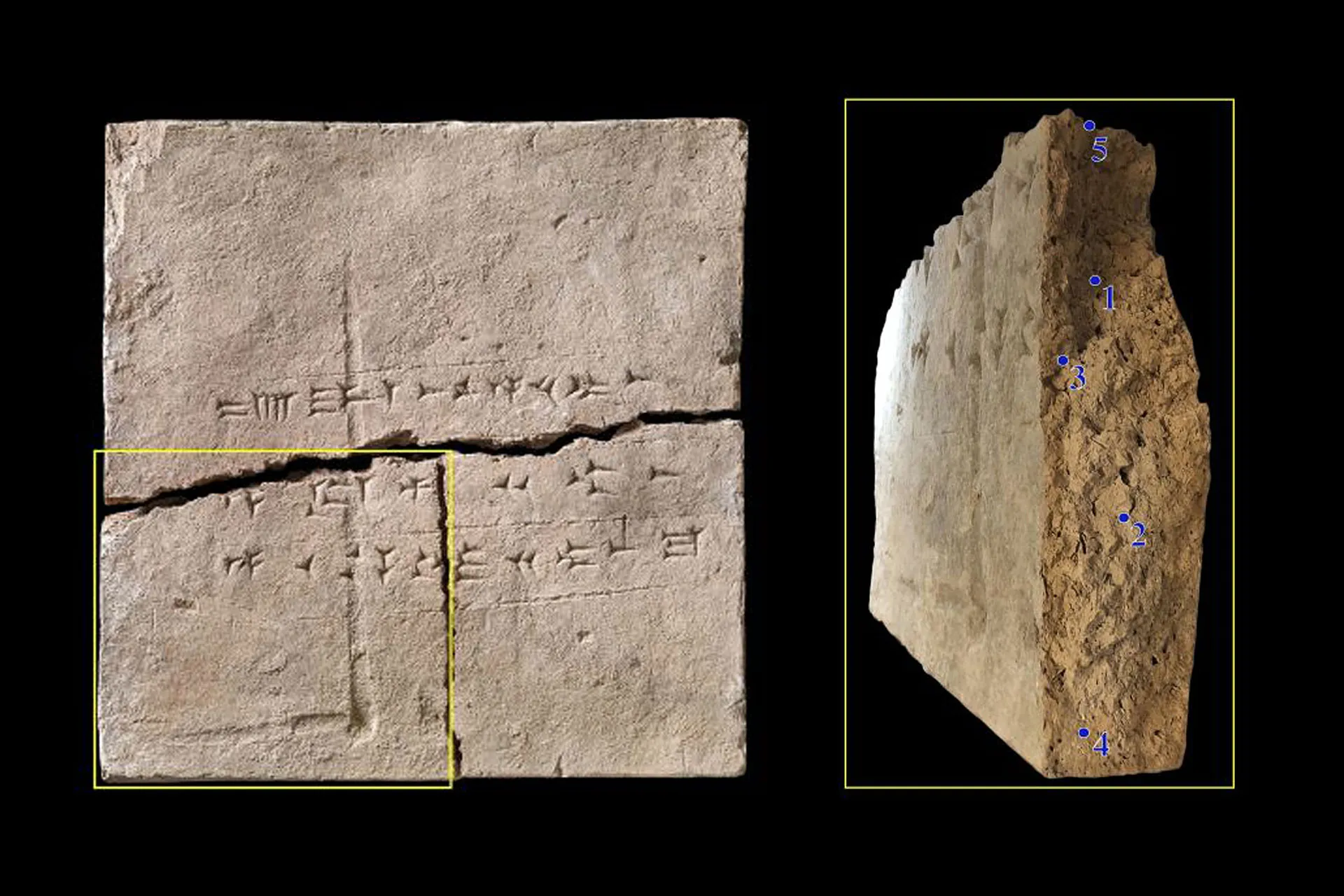
The clay brick analyzed for the study is currently housed at the National Museum of Denmark. It originates from the palace of Neo-Assyrian king Ashurnasirpal II, in the ancient city of Kalhu, now known as the North-West palace in Nimrud, modern-day northern Iraq.
Known today as the North-West Palace in Nimrud (modern-day northern Iraq), its construction began around 879 BCE. The brick has a cuneiform inscription (written in the now-extinct Semitic language Akkadian) stating that it is ‘The property of the palace of Ashurnasirpal, king of Assyria.’ This makes it possible to date the brick precisely to within a decade (879 BCE to 869 BCE).
During a digitalization project at the Museum in 2020, the group of researchers were able to obtain samples from the inner core of the brick – meaning that there was a low risk of DNA contamination since the brick was created. The team extracted DNA from the samples by adapting a protocol previously used for other porous materials, such as bone.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
After the extracted DNA had been sequenced, the researchers identified 34 distinct taxonomic groups of plants. The plant families with the most abundant sequences were Brassicaceae (cabbage) and Ericaceae (heather). Other represented families were Betulaceae (birch), Lauraceae (laurels), Selineae (umbellifiers), and Triticeae (cultivated grasses).
With the interdisciplinary team comprising assyriologists, archaeologists, biologists, and geneticists, they were able to compare their findings with modern-day botanical records from Iraq as well as ancient Assyrian plant descriptions.
The brick would have been made primarily of mud collected near the local Tigris river, mixed with material such as chaff or straw, or animal dung. It would have been shaped in a mould before being inscribed with cuneiform script, then left in the sun to dry. The fact that the brick was never burned, but left to dry naturally, would have helped to preserve the genetic material trapped within the clay.
Dr Sophie Lund Rasmussen (Wildlife Conservation Research Unit, Department of Biology, University of Oxford), joint first author of the paper, said: ‘We were absolutely thrilled to discover that ancient DNA, effectively protected from contamination inside a mass of clay, can successfully be extracted from a 2,900-year-old brick. This research project is a perfect example of the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in science, as the diverse expertise included in this study provided a holistic approach to the investigation of this material and the results it yielded.’
In addition to the fascinating insight this individual brick revealed, the research serves as a proof of concept and method which could be applied to many other archaeological sources of clay from different places and time periods around the world, to identify past flora and fauna. Clay materials are nearly always present in any archaeological site around the world, and their context means they can often be dated with high precision.
This study only described the plant DNA extracted, as these were the most prevalent and best-preserved specimens. However, depending on the sample, all taxa could potentially be identified, including vertebrates and invertebrates. The ability to provide accurate descriptions of ancient biodiversity would be a valuable tool to better understand and quantify present-day biodiversity loss, and to gain a deeper understanding of ancient and lost civilisations.
‘Because of the inscription on the brick, we can allocate the clay to a relatively specific period of time in a particular region, which means the brick serves as a biodiversity time-capsule of information regarding a single site and its surroundings. In this case, it provides researchers with a unique access to the ancient Assyrians’ said Dr Troels Arbøll, joint first author of the paper and junior research fellow at the Faculty of Asian and Middle Eastern Studies, University of Oxford, when the study was conducted.
The study ‘Revealing the secrets of a 2900‑year‑old clay brick, discovering a time capsule of ancient DNA’ has been published in Nature Scientific Reports.
Cover Photo: Troels Pank Arbøll.