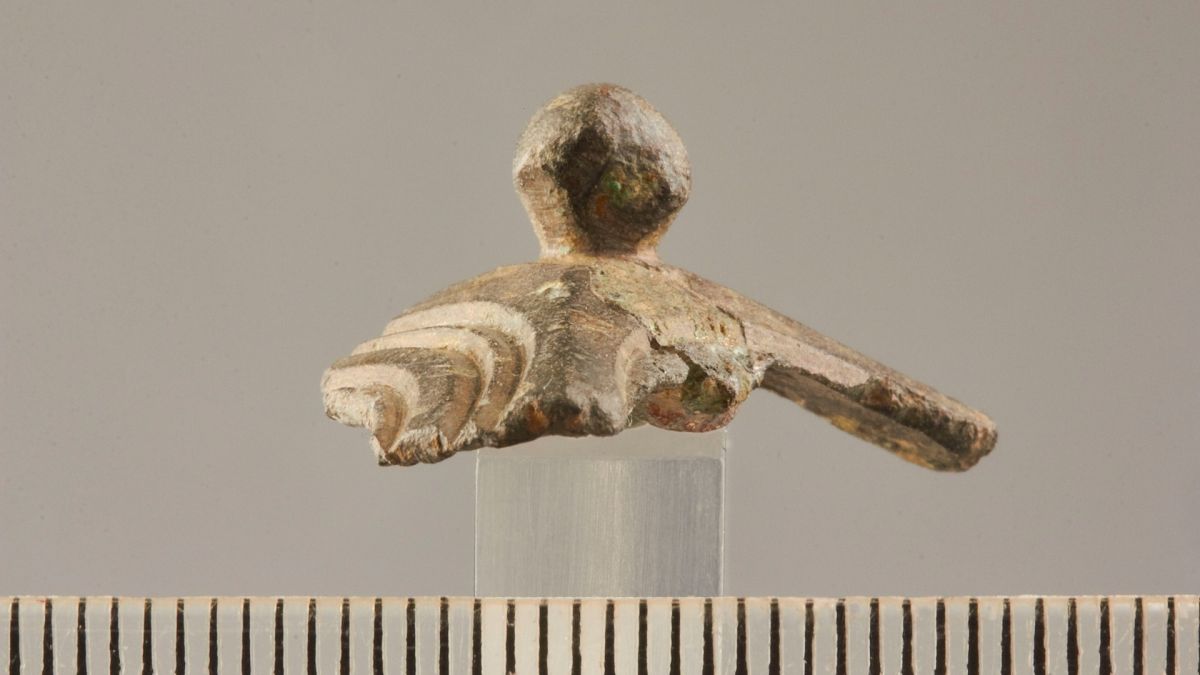
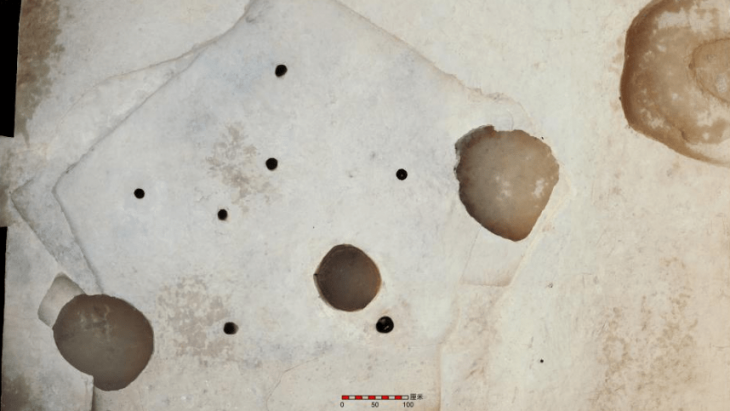
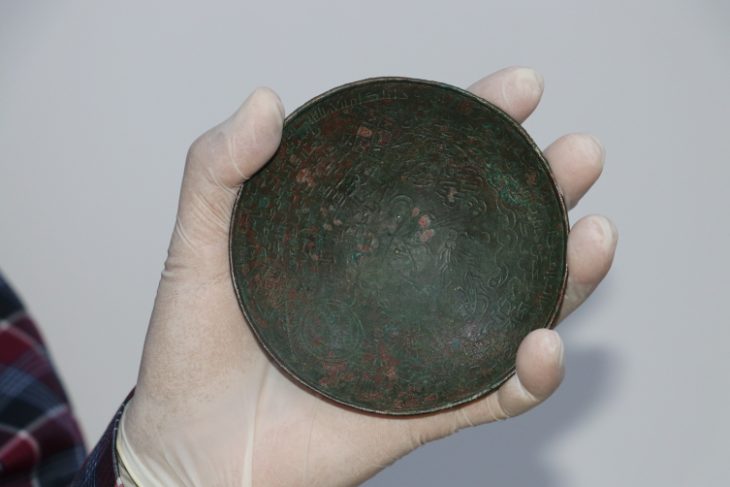
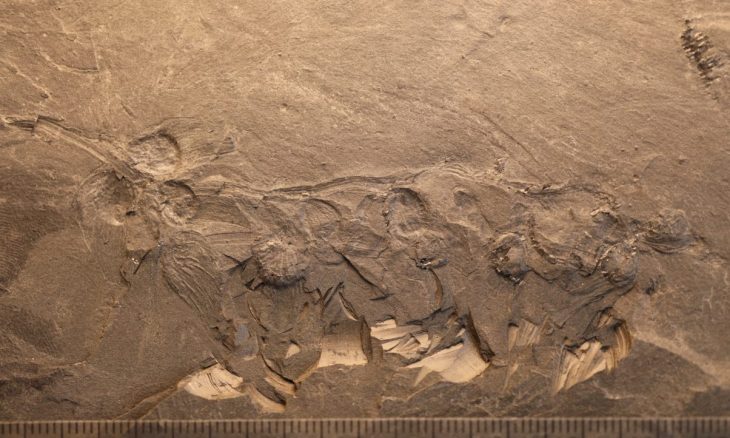
A metal detectorist in Belgium discovered a piece of a mysterious bronze artifact known as a Roman dodecahedron, which is thought to be over 1,600 years old.
Patrick Schuermans, a hobby archaeologist, was scanning the ground in Kortessem with a metal detector when he stumbled upon an unusual fragment, according to a news release from the Flanders Heritage Agency.
Dodecahedrons are hollow 12-sided geometric shapes with small knobs at their corners and holes of varying diameters on each pentagonal face. They have perplexed researchers for centuries, owing to the fact that the polygonal object does not appear in Roman writings or drawings.
Around 120 Roman dodecahedrons have been found since the 18th century, mostly in Great Britain, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Germany, Austria, and Switzerland. The first Roman dodecahedron to be discovered in modern times was discovered in England.
The known complete specimens differ in detail in appearance, and they also vary in size and weight. Most are between 4.5 and 8.5 centimeters in size.
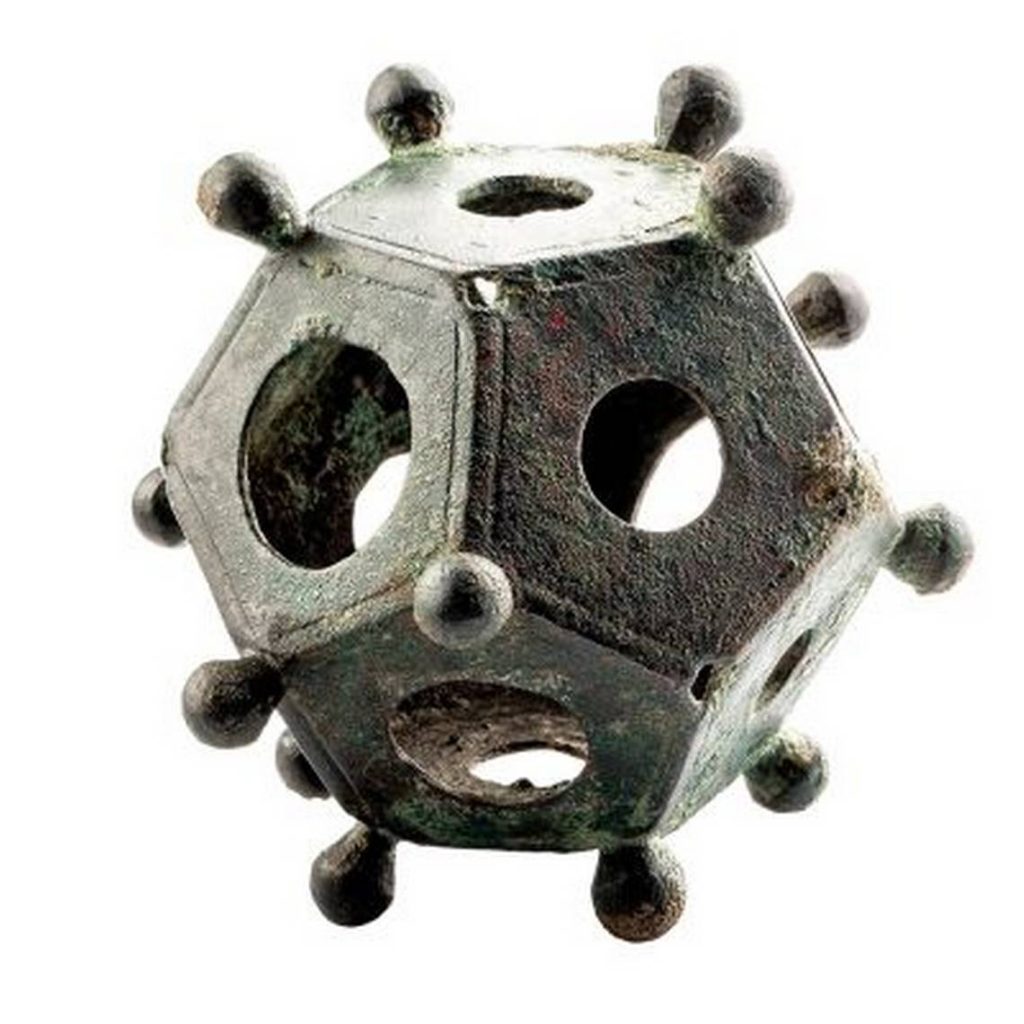

These items are sometimes referred to as Gallo-Roman dodecahedrons since most of the dodecahedrons were found in these areas in parts that coincided with the Celtic civilization.
However, archaeologists aren’t completely sure. But what is this quirky object for? Is it a weapon? A tool? Or something else entirely? Measuring instruments?
However, there is growing evidence that dodecahedrons were not practical objects such as measuring instruments. The known specimens are too dissimilar in size and detail for that.
According to Onroerend Erfgoed’s archaeologists, their significance should be sought in the magical-religious sphere. This may help to explain why grave finds frequently include dodecahedrons.
Schuermans donated the object to the Gallo-Roman Museum of Tongeren after reporting his discovery to the Flanders Heritage Agency.
The Flemish agency believes the whole dodecahedron could have been over two inches wide and was possibly broken during a ritual. But archaeologists are most enthusiastic about what the find means for research into Ancient Roman history. “Thanks to the correct working method of the metal detectorist, archaeologists know for the first time the exact location of a Roman dodecahedron in Flanders,” the agency wrote in a statement, adding that it plans to monitor the area where Schuermans uncovered the fragment in case of future discoveries.
Cover Photo: The fragment found in a field near the town of Kortessem in Flanders is clearly part of a Roman dodecahedron. Photo: Kris Vandevorst/Flanders Heritage Agency