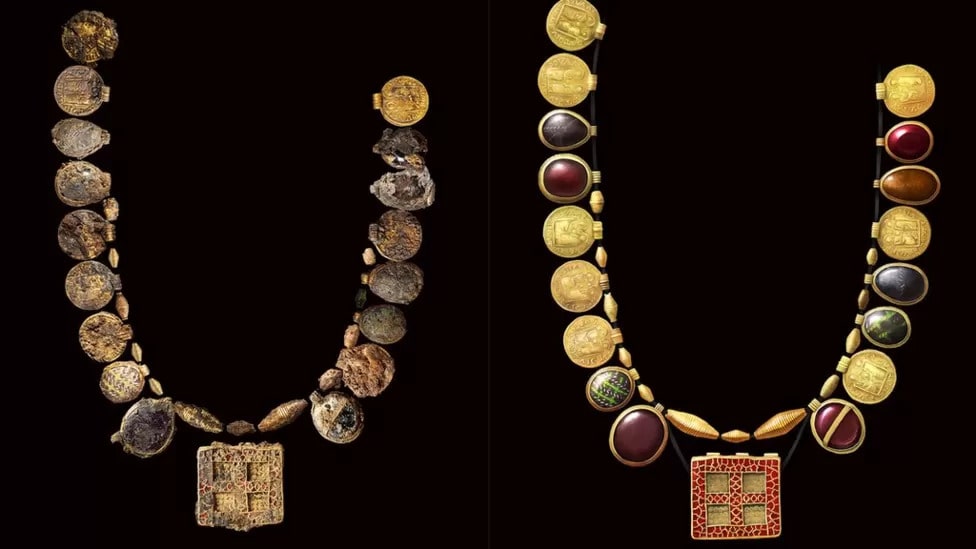
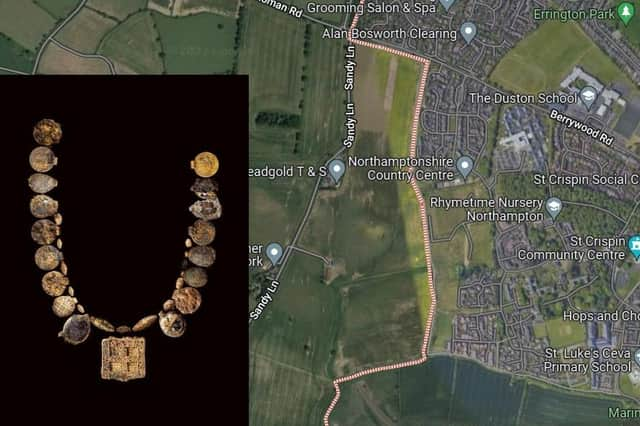
Museum of London Archaeology (MOLA) archaeologists have found a “once-in-a-lifetime” 1,300-year-old gold and gemstone necklace dating back to 630-670 AD and described as the richest of its type ever uncovered in a village near Northampton, Britain.
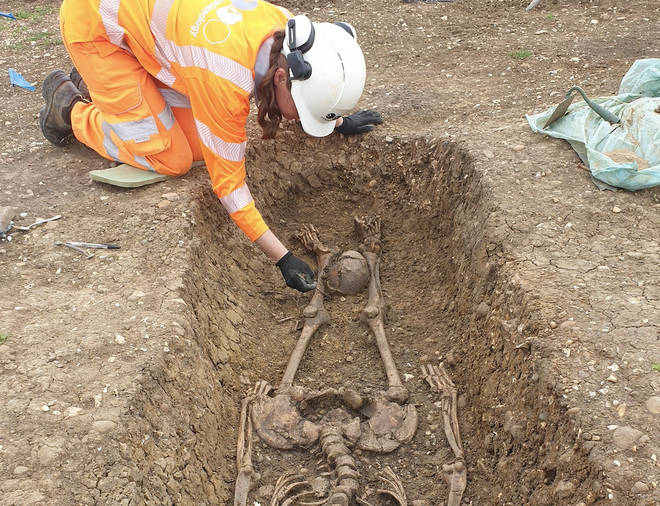
Archaeologists say they found the necklace during excavation works ahead of a housing development on land between Harpole and Duston. The jewelry has at least 30 pendants and beads made of Roman coins, gold, garnets, glass, and semi-precious stones.
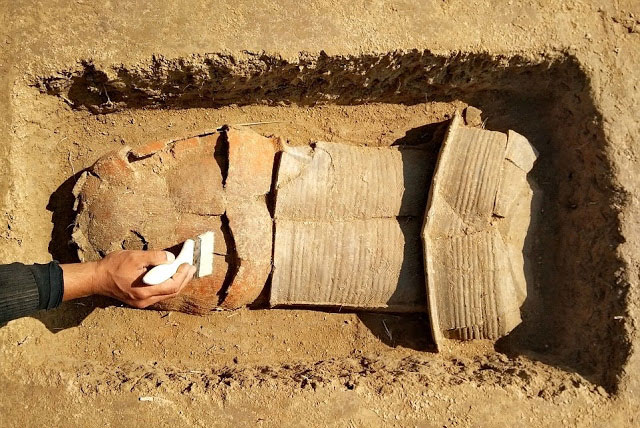
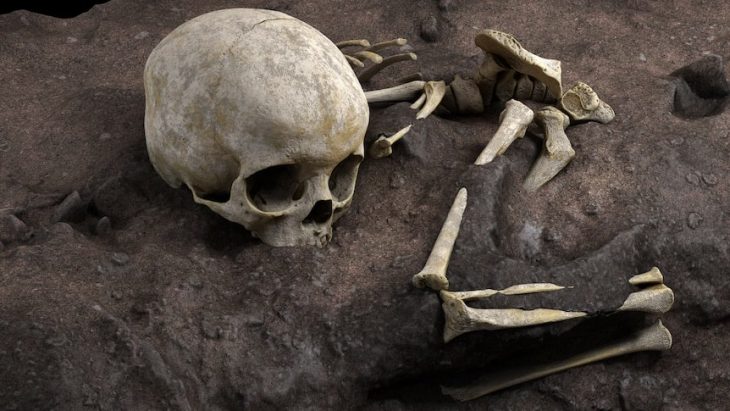
The 1,300-year-old jewelry was discovered in a grave that was believed to belong to a high-status woman, possibly royalty.
The largest and most intricate component of the necklace is a rectangular pendant with a cross motif that serves as its focal point. Mola experts think this piece, which is made of red garnets set in gold, was once only half of a hinged clasp before it was reused. The burial also contained two decorated pots and a shallow copper dish.
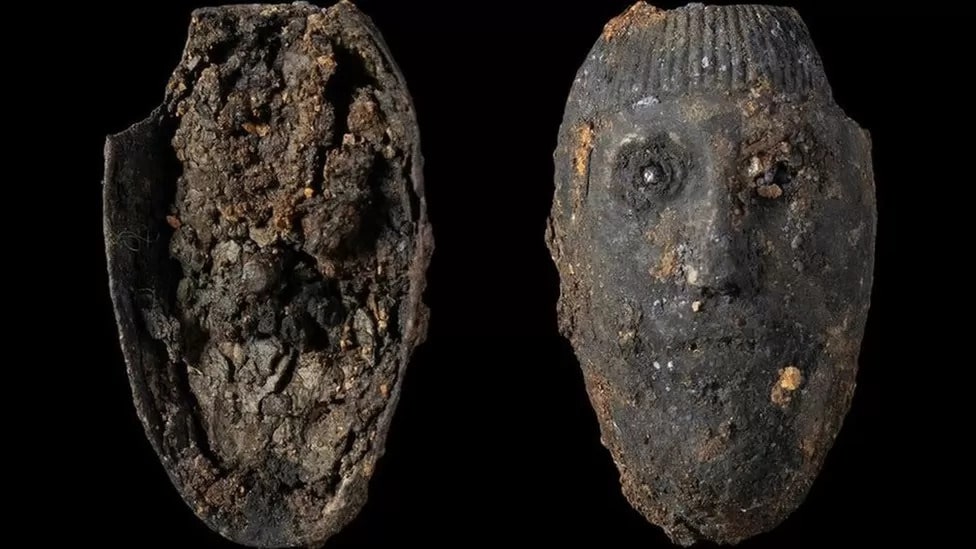
X-rays of soil blocks lifted from the grave, however, revealed an elaborately decorated cross with highly unusual depictions of human faces cast in silver. Mola conservators believe the large and ornate piece indicates the woman was an early Christian leader.
Apart from minute pieces of tooth enamel, according to experts, the skeleton had completely decomposed. However, the combination of grave finds suggested it belonged to a very pious high-status woman, possibly royalty or an abbess.

A few similar necklaces from this era have previously been discovered in other parts of England, but none are as ornate as the “Harpole treasure,” according to experts. The Desborough necklace, discovered in Northamptonshire in 1876 and now housed in the British Museum, is the closest parallel.
In January, BBC Two’s Digging for Britain will feature the discoveries, with Prof. Alice Roberts getting an exclusive look at the artifacts and going into more detail about the ongoing conservation and analysis.
The discoveries are still being examined and conserved by conservators; they will then be given to the Northamptonshire Archaeology Resource Centre.
















