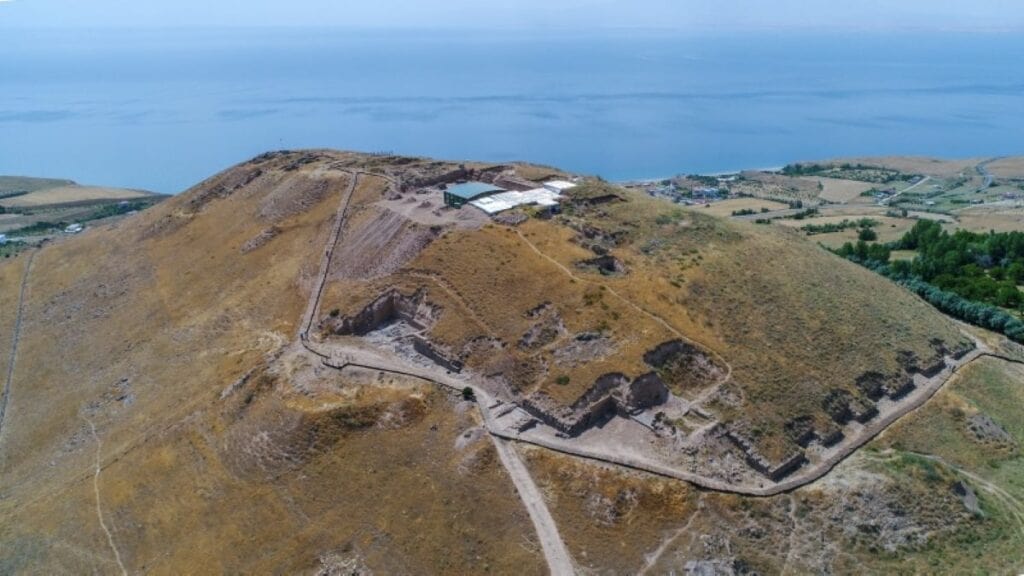
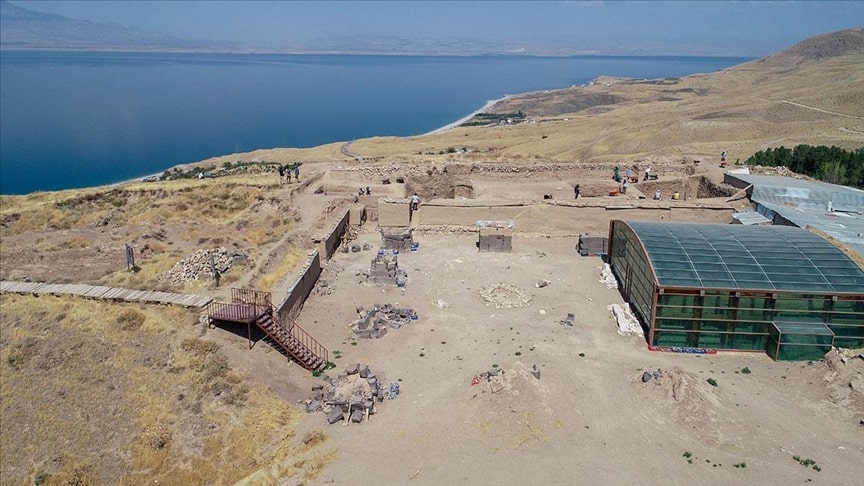
During the excavations carried out in the Ayanis Castle, which was built by the Urartian King Rusa II on the hill overlooking Lake Van, a new area used as a “garbage dump” by the royal family in the Urartians was unearthed.
Excavation and restoration work has been carried out for 34 years in the castle, which is located in the Tusba district of Van and is one of the most magnificent structures of the Urartian Kingdom.
The excavations carried out under the chairmanship of Atatürk University Archeology Department Lecturer Professor Mehmet Işıklı were concentrated on the northern slope of the castle this year.
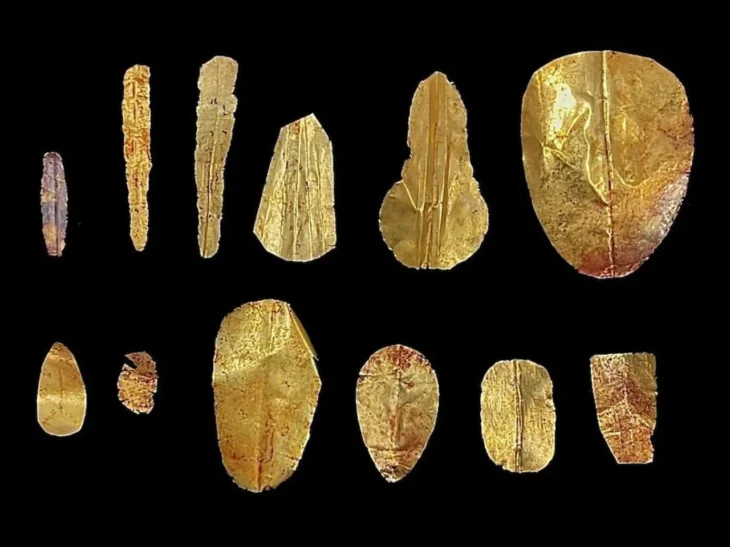
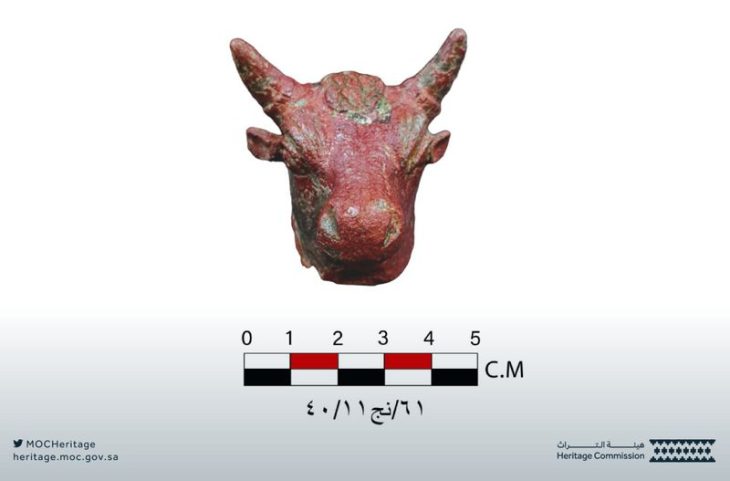
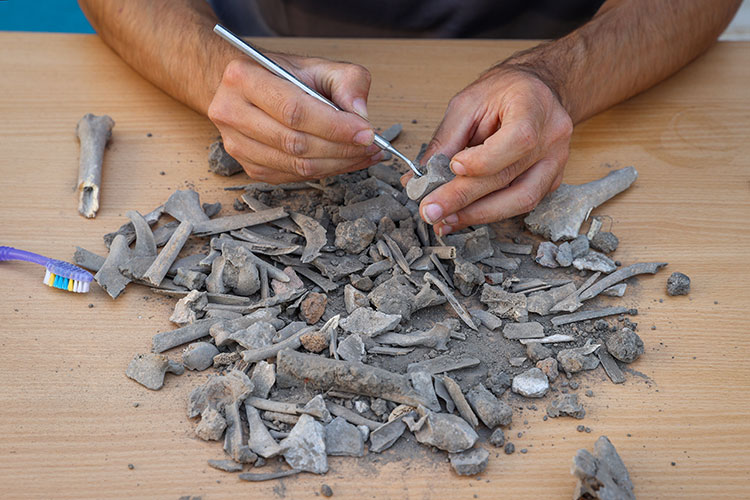
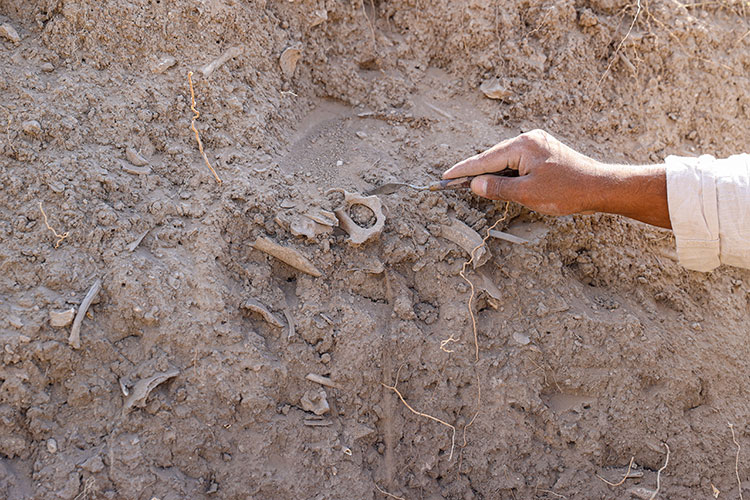
In the studies, a new area used as a garbage dump by the royal family in the Urartians was identified. In the excavations carried out here, seals, bulla (seal stamps), hooks, ceramic pieces, and numerous ovine and bovine animal bones used by the nobles of the Urartians were found.

The findings, which will be analyzed in the laboratory environment, are expected to give important clues about the economic and social life of the royal family in the Urartians, especially the nutritional conditions.
We were very excited by the finds
Professor Mehmet Işıklı told the Anadolu Agency (AA) that excavations have been carried out in the castle for 34 years with the support of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.

Explaining that this year the works were carried out in an important area, Işıklı said:
“We came across a surprise find around the castle. We saw very rich cultural deposits flowing down the walls. For archaeologists, this is a treasure. We found thousands of animal bones, objects that lost their function, written documents, and seals in this cultural deposit. We were very excited by the finds. In the researchs, we saw that this place is a dump. We tried to speed up the excavations. We collect the animal bones found here one by one and periodically separate them.
We are trying to reveal how the royal family was fed and what they consumed in which periods. In other words, we are trying to understand the human dimension of the Urartians. We know that the royal family, the nobility, and the elite lived in the castle. We are digging the garbage left by those elites. We try to learn about their lives down to the smallest detail and to catch clues,”

“For the first time, we excavate an area of a garbage dump in the Urartians”
Vedat Sezer, a doctoral student working on zooarchaeology, said: “Most of the bones belong to big and small animals. Some bones belong to migratory and aquatic birds. There are many traces of butchery and consumption on the bones. Seal impressions, bulla, and hooks, which have lost their function, were also thrown out of the wall. The most surprising ones were the seal impressions. The Urartians were spread over a wide geography. Many animal bones were found before. These were usually found in warehouses. We are excavating a garbage dump in the Urartians for the first time,” he said.