The Giza Pyramids are one of the world’s most iconic cultural landscapes, and they have fascinated humans for thousands of years. It has been argued for years as to how these historic structures were constructed.
The Nile River is depicted as a geometric mountain chain. The Great Pyramid, which was built to commemorate the reign of Pharaoh Khufu, the second king of Egypt’s fourth dynasty, covered 13 acres and stood more than 480 feet when it was finished around 2560 B.C. 2.3 million limestone and granite blocks, each weighing more than 2 tons, were miraculously transported across miles of desert from the Nile’s banks to the pyramid site on the Giza Plateau.
It would have been exhausting to transport these stones over land. For a very long time, scientists assumed that the process required the use of a river or channel, but today the Nile is miles away from the pyramids. However, on Monday, however, a team of researchers reported evidence that a lost arm of the Nile once cut through this stretch of desert and would have greatly simplified transporting the giant slabs to the pyramid complex.
The new study, which was released on Monday in the journal PNAS, evaluated the environmental factors that allowed the construction of the Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure pyramids at Giza, which tower over the west bank of the Nile.
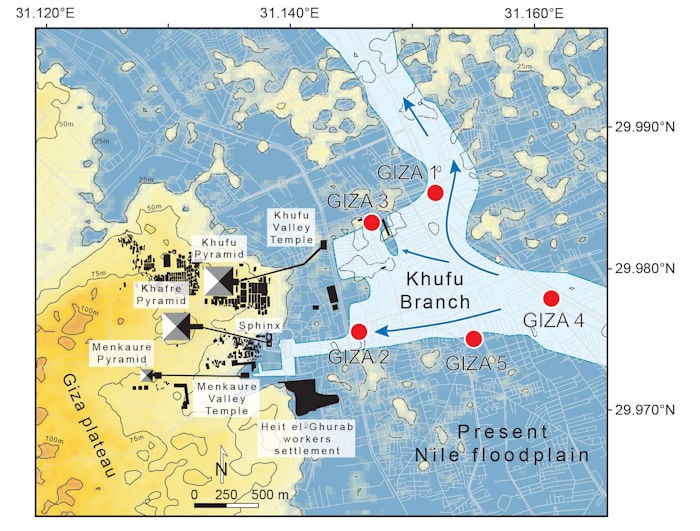
The scientists reconstructed the rise and fall of the Khufu Branch, a now-extinct Nile tributary, over the previous 8,000 years using clues preserved in the desert soil. Their findings, propose that the Khufu Branch, which dried up completely around 600 B.C., played an important role in the construction of the ancient wonders.
“It was impossible to build the pyramids here without this branch of the Nile,” said Hader Sheisha, an environmental geographer at the European Center for Research and Teaching in Environmental Geoscience and an author of the new study.
The recent Wadi al-Jarf papyri discoveries, which document contemporary Nile boat transport of stone blocks for pyramid construction from the cliffs opposite Giza and from the Red Sea, have helped to solve some of the mysteries surrounding those pyramid constructions.
The discovery of a trove of papyrus fragments at the site of an ancient harbor near the Red Sea in 2013 sparked the project. Some of the scrolls date from Khufu’s reign and tell of an official named Merer and his men’s efforts to transport limestone up the Nile to Giza, where it was fashioned into the Great Pyramid’s outer layer.
Today, the Nile flows more than 7 kilometers east of the Giza pyramids. However, Nile flow through a channel that linked the Giza plateau to the Nile, dubbed the “Khufu channel” after the famed Khufu pyramid at Giza (2,583,283 m3, 146 m high), has been hypothesized from modern wastewater project corings and its 1.8-kilometer-long trench that cut through an ancient channel—perhaps even through Khufu’s palace.”
The Wadi al-Jarf papyri describe the transport of stone to Giza via a branch of the Nile. Examinations of sediment collected near the pyramid site, as well as bones and teeth from mummies from the time period, revealed that the area had become much drier later on. Studying pollen grains provided evidence of ancient plant life that could not have survived without water.
“This fluvial channel, the Khufu branch, enabled navigation to the Pyramid Harbor complex, but its precise environmental history is unclear. To fill this knowledge gap, we used pollen-derived vegetation patterns to reconstruct 8,000 y of fluvial variations on the Giza floodplain… Our results show that Giza’s waterscapes responded to gradual insolation-driven aridification of East Africa, with the lowest Nile levels recorded at the end of the Dynastic Period.
Cover Photo: Artist’s reconstruction of the now defunct Khufu branch of the Nile River. Credit: Alex Boersma/Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2022). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2202530119