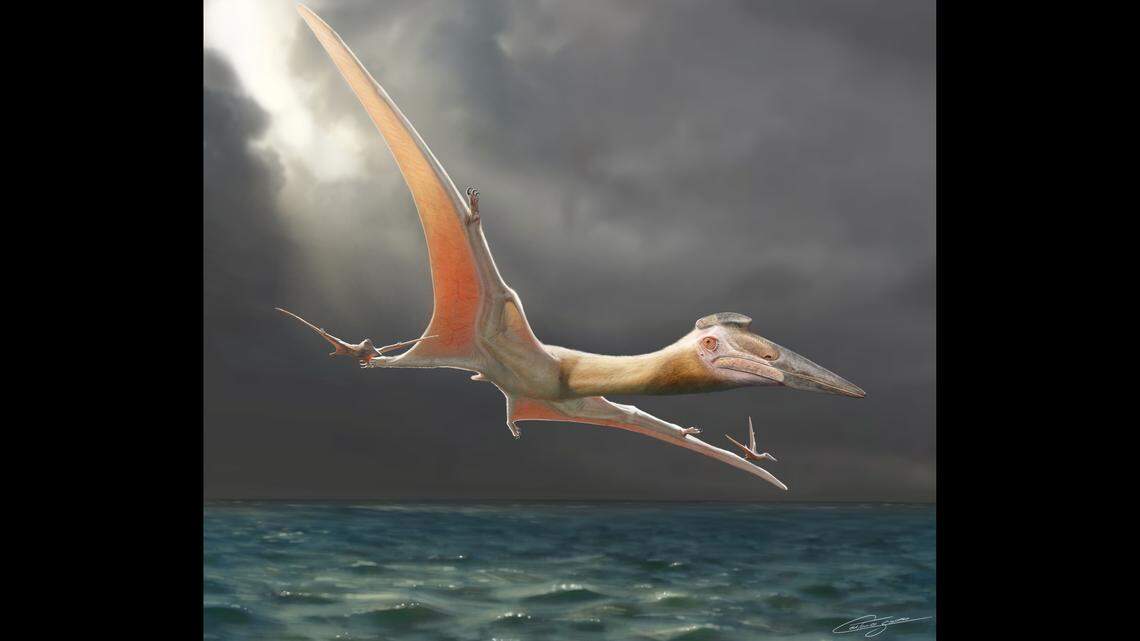
A colossal flying reptile that once soared over the Cretaceous skies has been discovered in Syria — marking the first-ever pterosaur fossil found in the country. The rare bone, rediscovered nearly two decades after it was first unearthed, belonged to an animal so large that its wings may have stretched more than 10 meters (33 feet) across, placing it among the largest known creatures ever to take flight.
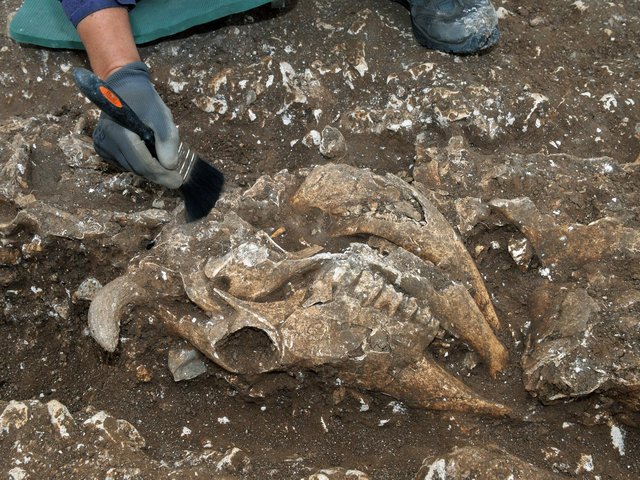
When a local geologist uncovered a massive bone fragment in a phosphate mine near Palmyra in the early 2000s, few could have imagined its scientific importance. The fossil was briefly examined, then forgotten for years amid regional instability and lack of funding. It wasn’t until Syrian paleontologist Wafa Adel Alhalabi revisited the specimen that its true nature came to light — a breakthrough now published in The Science of Nature journal.
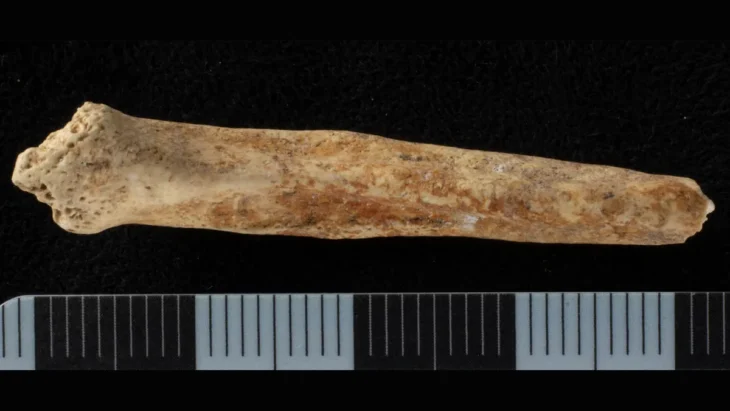
Alhalabi, working independently and often without institutional support, transported the fossil to her home in Latakia to conduct a detailed study. “I had to use my own money to travel and prepare the specimen using basic tools,” she explained. “It created so much dust and noise that it drove my family crazy.” But the effort paid off: the fossil turned out to be the left humerus — the upper arm bone — of a giant pterosaur.
A Syrian First
The fossil represents not only the first pterosaur ever discovered in Syria, but also one of the largest examples of its kind in the Middle East. Measuring 29 centimeters (11.4 inches) in its preserved portion, researchers estimate the complete bone would have been roughly 10% smaller than that of Quetzalcoatlus northropi — the record-holding giant from North America with a wingspan of around 11 meters (36 feet).
“This animal likely reached up to 10 meters in wingspan, rivaling the largest known pterosaurs,” said study co-author Felipe Pinheiro of the Universidade Federal do Pampa in Brazil. “It demonstrates that these colossal fliers were not confined to a few regions but were widespread even in what is now the Middle East.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A Giant Among Azhdarchids
The fossil belongs to the Azhdarchidae, a family of toothless, long-necked pterosaurs that dominated the skies near the end of the Cretaceous Period. Their members, including Quetzalcoatlus and Hatzegopteryx, were apex aerial predators — and, at times, terrestrial stalkers that hunted small animals on land using their elongated beaks.
Most azhdarchid remains are found in inland or riverbed sediments, but the Syrian specimen was recovered from marine deposits in the Palmyrides mountain chain, near the Mediterranean coast. This unusual context suggests that these giants may have lived — or at least foraged — along coastal environments, broadening our understanding of their ecological range.
“Finding such a large azhdarchid in marine rocks is rare,” the authors wrote. “It reveals that these creatures were capable of thriving in diverse habitats, from continental plains to coastal shores.”
Echoes of a Lost Sky
During the Late Cretaceous, about 70 million years ago, much of modern Syria was part of a shallow sea extending across the Arabian Plate. The discovery of a giant pterosaur in these sediments points to the region’s rich, yet still poorly explored, fossil record. Researchers hope this finding will encourage further paleontological work in the Middle East, where political turmoil and underfunding have long hindered scientific fieldwork.
The study’s international team — including scientists from the University of São Paulo, Université de Rennes, and Universidad del País Vasco — emphasized that even with a single bone, the discovery reshapes the map of known pterosaur distribution just before their extinction at the end of the Cretaceous.
The Azhdarchids were among the last survivors of the pterosaur lineage, vanishing around 66 million years ago in the same mass extinction that ended the reign of the dinosaurs. Their disappearance closed a remarkable chapter in the evolution of flight — one that began more than 200 million years earlier.
“Even one fragment like this carries a story of deep time,” Alhalabi said. “It reminds us that Syria’s geological past holds many secrets still waiting to be uncovered.”
Alhalabi, W.A., Pinheiro, F.L., Jaoude, I.B. et al. Recovering lost time in Syria: a gigantic latest Cretaceous azhdarchid pterosaur from the Palmyrides mountain chain. Sci Nat 112, 78 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-025-02032-9
Cover Image Credit: The massive animal had a 33-foot wingspan. Felipe Pinheiro
















