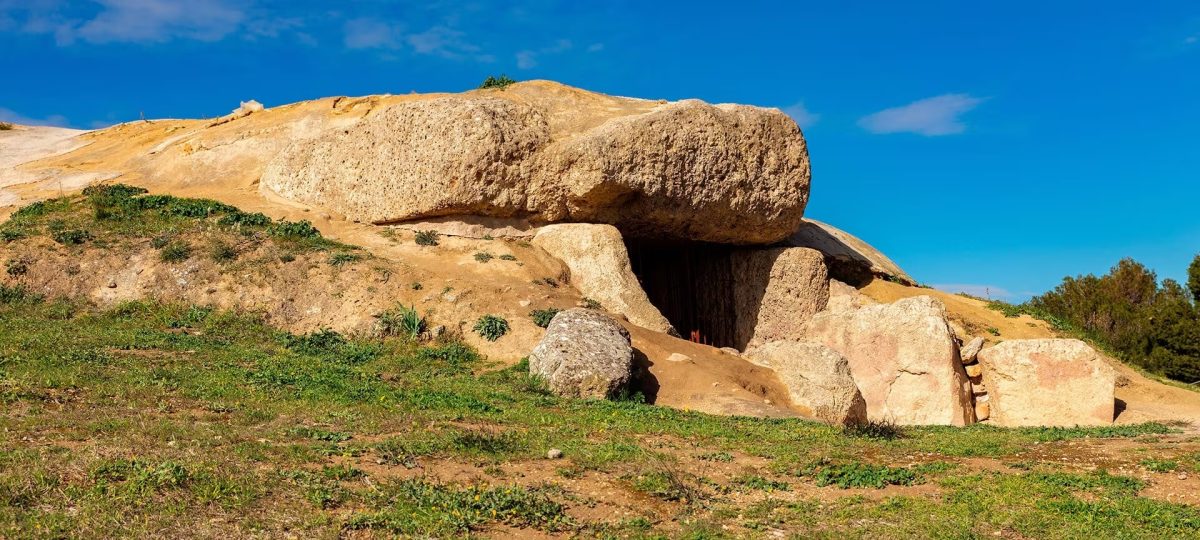
A new investigation tracing the source of the gigantic stones that make up the Menga dolmen in southern Spain reveals that it is one of the greatest achievements of Late Neolithic engineering.
In their study, published in Scientific Reports, the group used new technology to learn more about the stone that was used to create the ancient burial site and to explore how wood and rope would have been used in its construction.
Located near Antequera in Malaga (Andalucia, Spain), Menga is part of a UNESCO World Heritage site consisting of three dolmens constructed between 3800 – 3600 BC. It is one of the largest megalithic structures in Europe and was built on the top of a hill with giant rocks. It is renowned for its enormous orthostats or vertical stones, one of which weighs nearly 150 tons.
For many years, researchers have been haunted by the question of how the ancients, who possessed primitive tools, were able to process and move such large building blocks. A new study was designed to find the answer.
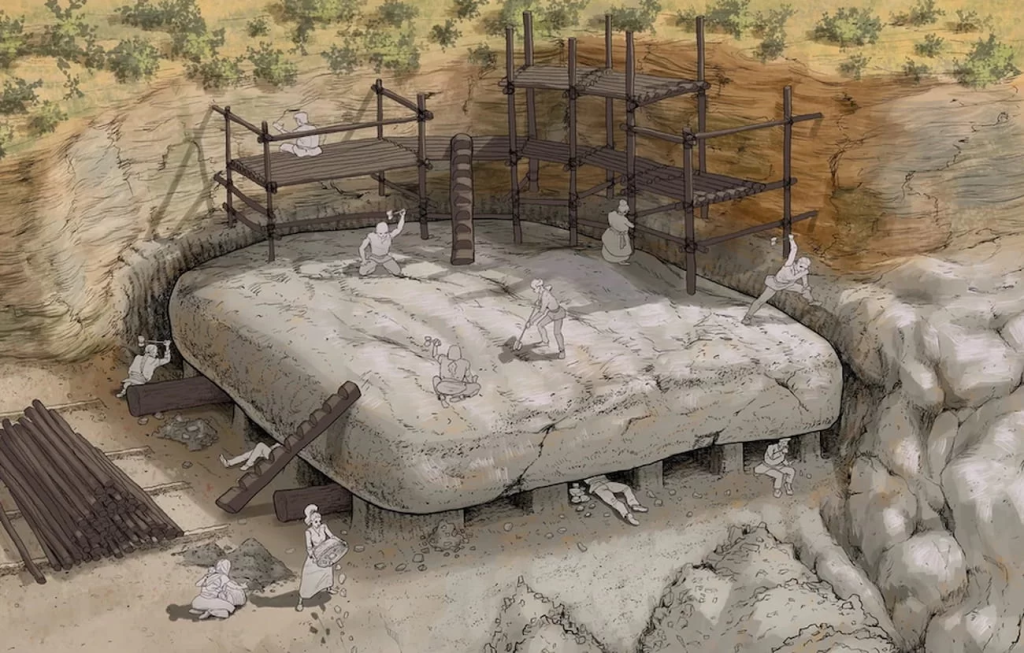

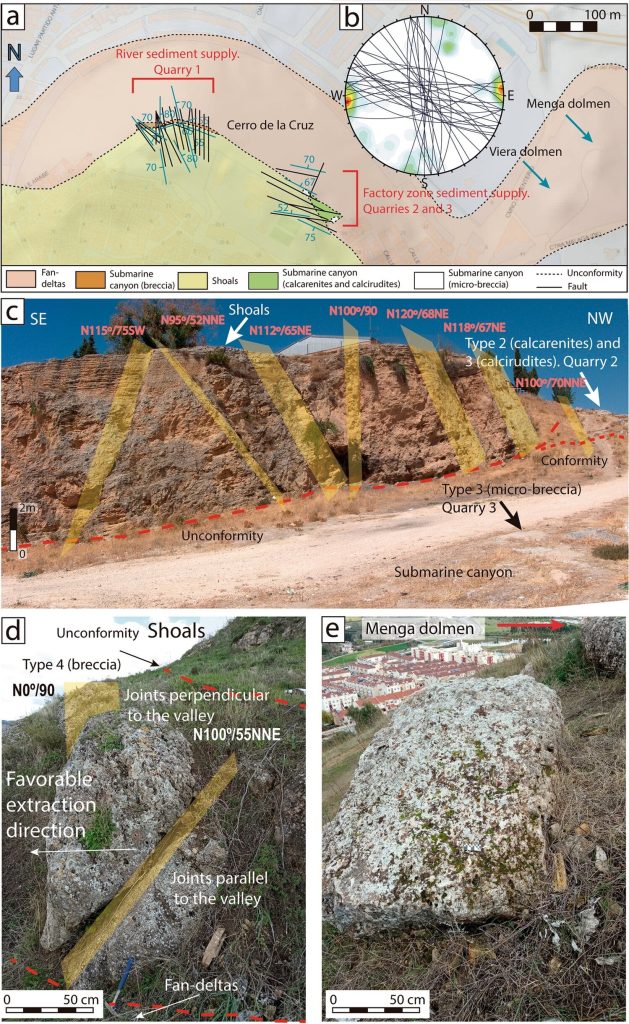
Scientists have carefully studied the composition of the stones used by ancient builders. This made it possible to identify the location of the quarries from where they were probably transported to the construction site.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Using petrographic and stratigraphic analysis techniques, the researchers discovered most of the stones were calcarenites, “a poorly cemented detrital sedimentary rock comparable to those known as ‘soft stones’ in modern civil engineering. Petrologic examination identified five distinct stone types—calcirudites, calcarenites and calcareous breccias—matching sedimentary facies at Cerro de la Cruz. They were quarried from a rocky outcrop located at a distance of approximately 1 km.
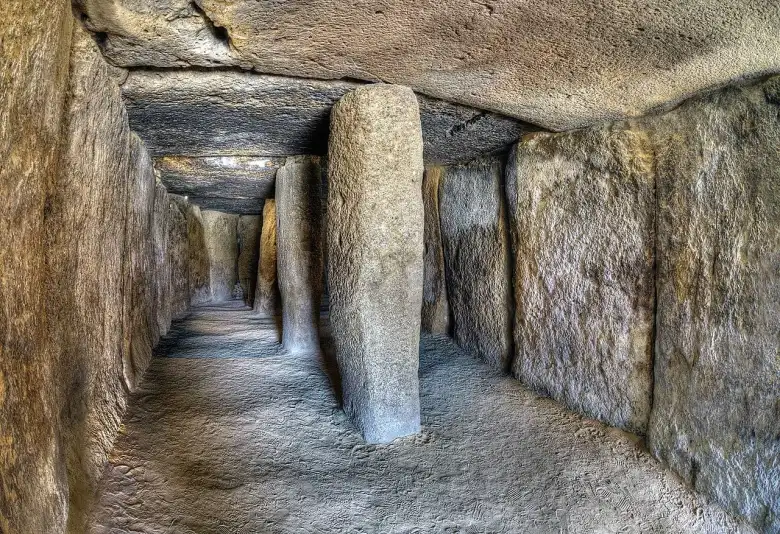

The researchers write in their paper that moving and building a dolmen from such large, massive but fragile stones would require careful planning and very complex engineering work. This is especially true of the keystone, that is, that large rock that was somehow placed on top of the chamber and still serves as the roof of the dolmen.
Calculations made it clear that it weighs about 150 tons. Scientists say lifting it and placing it on top of the camera would require scaffolding and strong cables. To transport such blocks without damaging them, very smooth roads would be required, which would have been difficult to imagine 5,700 years ago.
The research team also claims that the dolmen was deliberately oriented in a certain way to point in the desired direction. In particular, its position is oriented towards the nearby mountains, resulting in complex light patterns within the camera.
Furthermore, modern scientists have concluded that ancient engineers developed a method that allowed smaller stones to be installed along the edges of the chamber. It is assumed that they reliably protected the dolmen from sewage and prevented erosion.
In addition to pinpointing the origin of the Cerro de la Cruz quarries and tracking the logistics of transportation, the study sheds light on the extensive planning, labor coordination, technical expertise, and calculations that went into building Menga.
doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-47423-y
Cover Photo: Spain.info