A 4,000-year-old settlement and ancient artifacts have been discovered in the Balasore district, India.
The Odisha Institute for Maritime and South East Asian Studies (OIMSEAS), an archaeological wing of the State government, continues to work in the region.
The OIMSEAS requested permission from the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to record the site at Durgadevi hamlet in Remuna tehsil after discovering indications of fortified early medieval structures near Balasore town. Durgadevi has located 20 km from Balasore town.
Archaeologists discovered distinct traces of three cultural periods at the excavation site: Chalcolithic (2000 BCE to 1000 BCE), Iron Age (1000 BCE to 400 BCE), and Early Historic Period (1000 BCE to 400 BCE) (400 BCE to 200 BCE).
The purpose of the start of the excavation is to link the simultaneous growth and development of marine activities with the urbanization of the east coast of India, link the Ganges valley in the north with the Mahanadi valley in the central state of Odisha, paying particular attention to the early culture of the north The development of Odisha, the institute informed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
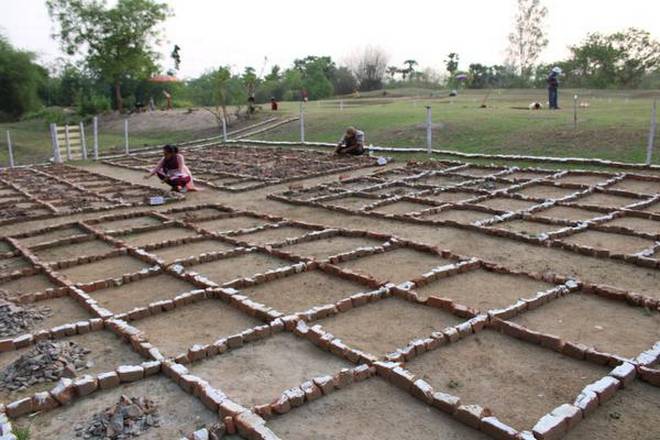

“Two small nullas, Gangahara and Prassana, join the site on its north and south, forming a natural moat for the site, which was an ancient water management system developed at least 4,000 years back from the present,” the institute told The Hindu.
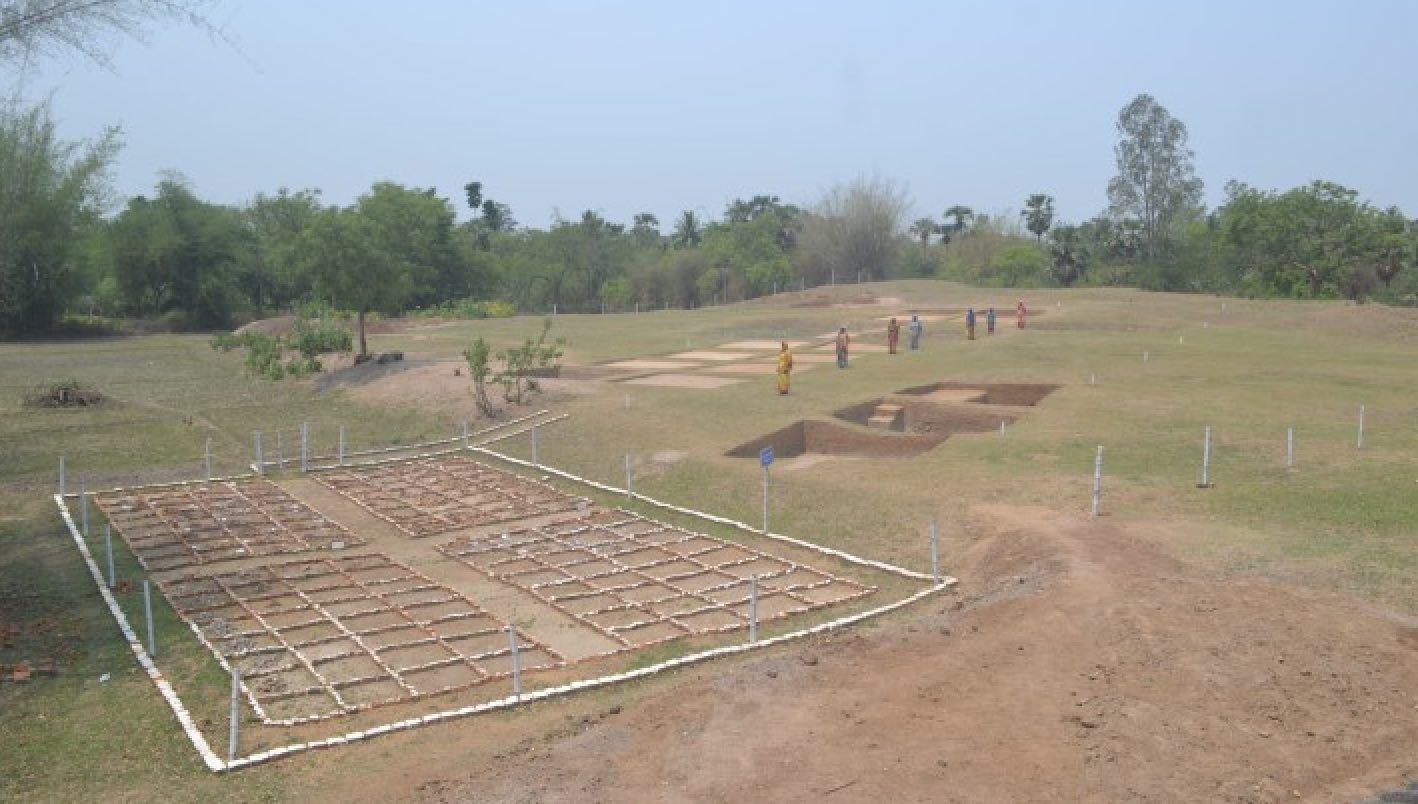
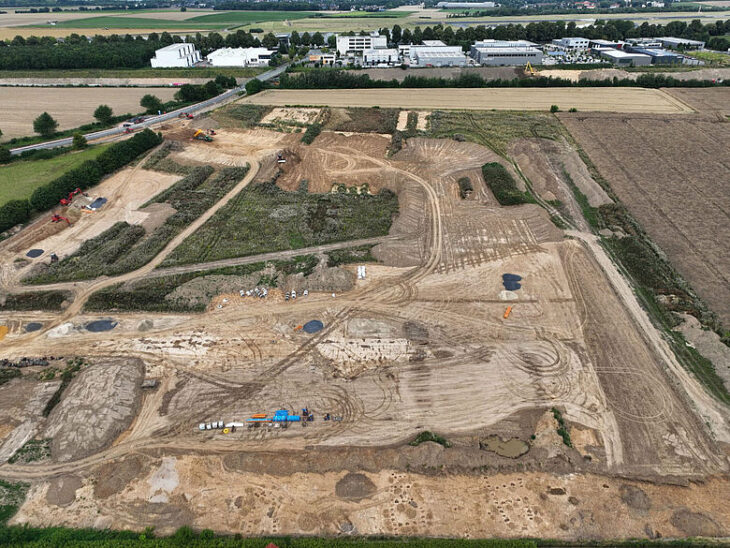
According to the OIMSEAS, horizontal excavation was centered on a two-acre area of high ground, where a cultural deposit of 4 to 5 meters was discovered. Archaeologists discovered a human settlement as well as Chalcolithic era artifacts.
“The major discovery of the Chalcolithic period of Durgadevi is the base of a circular hut, black on red painted pottery, black slipped ware, red slipped ware and copper objects. The floor of the circular hut is rammed with red soil,” Sunil Kumar Pattnaik, archaeologist and Secretary, OIMSEAS.
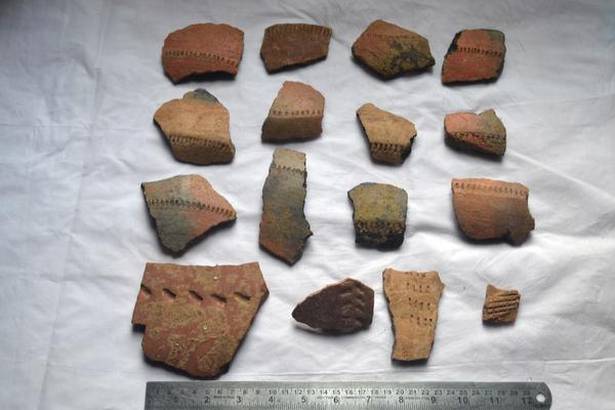

“From the base of the circular hut and the utilitarian objects found, the lifestyle of the people has been derived. People were mostly leading a settled life and had started agriculture, and domestication of animals and fishing,” he said.
Similarly, cultural material evidence and remnants discovered during this era include pottery, black burnished ware, black and redware, iron items such as nails, arrowheads, and crucible and slag of various types from the Iron Age.
“The use of iron is a landmark phase in the growth of civilization in Odisha, particularly in north Odisha. There are several iron age sites discovered by various archaeologists in the upper and middle Mahanadi valley, but in north Odisha, this is the first site,” said Mr. Patnaik.
“The lifestyle of the people, which is derived from the cultural materials, was very improved at that time, from an agricultural base to trade and construction of fortification around the site with a moat, which signify the emergence of urbanization at Durgadevi around 400 BCE to 200 BCE,” said the OIMSEAS Secretary.
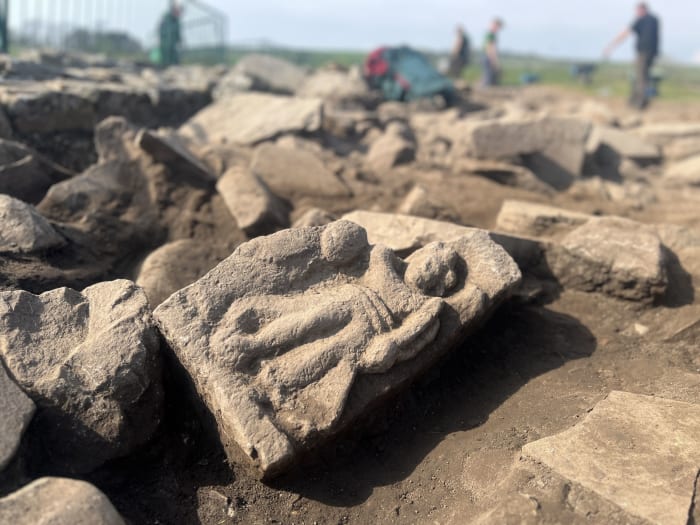
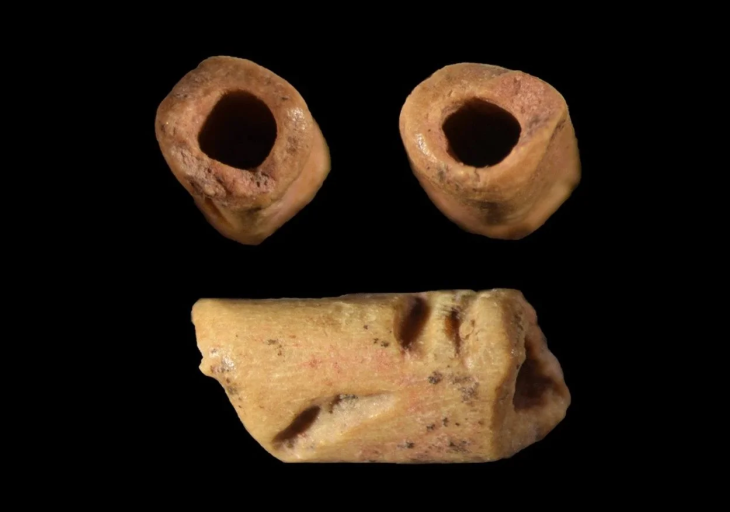
The site also found cultural materials from early historical periods, such as red pottery specimens, terracotta ear studs, bracelets, beads, and some cone-shaped objects.