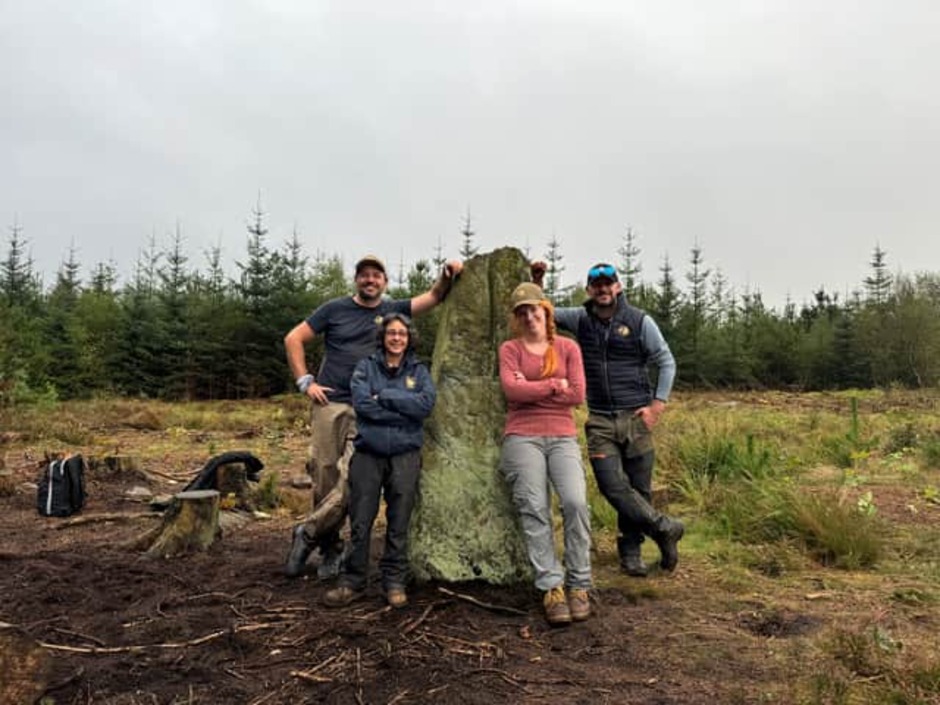
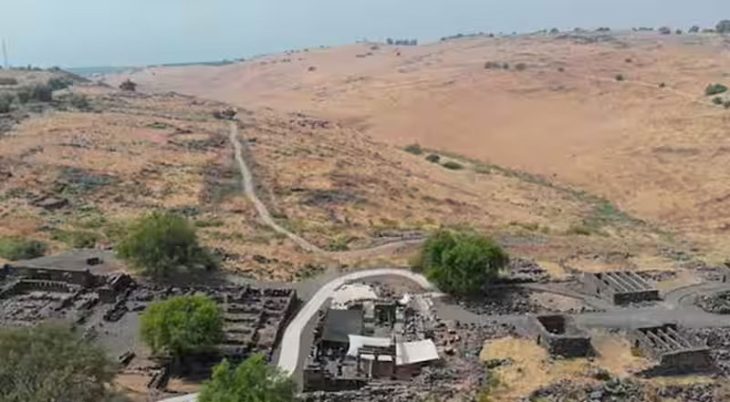
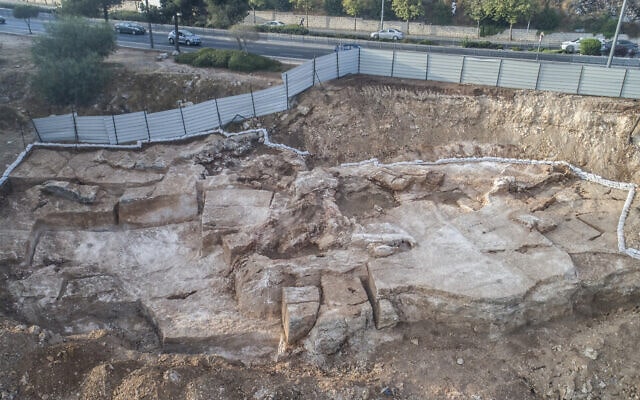
In a remarkable revelation, archaeologists have uncovered that the Farley Moor stone, previously thought to be a solitary monument, is actually part of a significant Bronze Age ceremonial site in Farley Wood, Derbyshire. This discovery, made by Forestry England in collaboration with the archaeology series Time Team, dates back approximately 3,700 years.
Standing at an impressive 2 meters tall and half a meter wide, the Farley Moor stone is the third largest of its kind in the Gritstone Moors, which span the Peak District and Yorkshire Dales. Initially regarded as an isolated structure, recent excavations have transformed our understanding of this ancient site. The archaeological team has revealed that the standing stone is part of a larger stone circle, which includes five additional stones and a ceremonial platform.
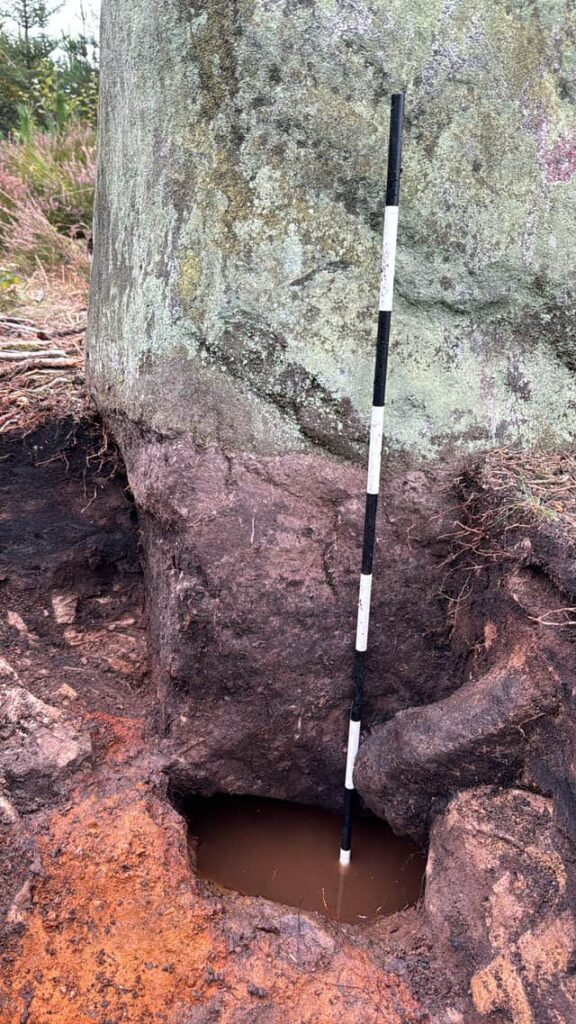
The excavations have provided compelling evidence of a ceremonial platform located adjacent to the standing stone, strategically positioned above a natural spring. This placement suggests that the site held significant ritualistic importance for the communities that inhabited the area during the early Bronze Age.
Further analysis indicates that the stone circle, measuring approximately 25 meters by 23 meters, would have originally featured six standing stones. Carbon dating has confirmed that this prehistoric feature dates back to around 1,700 BCE, placing it within a broader context of ceremonial monuments that were prevalent during the second and third millennia BCE.

Dr. Derek Pitman, an Associate Professor of Archaeology and Anthropology at Bournemouth University, expressed his enthusiasm for the discovery, stating that working on such a significant prehistoric monument is a “dream come true.” He emphasized that the scale of activity likely present in the landscape underscores the extensive impact of Bronze Age ritual life, extending far beyond well-known sites like Stonehenge. Dr. Pitman also highlighted the importance of investigating sites that have remained concealed in the nation’s forests for decades, suggesting that there is a wealth of archaeological potential still waiting to be uncovered.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery of the Farley Moor stone circle adds to the rich tapestry of prehistoric sites in the Peak District, which is already home to 25 known stone circles. Among these, the Arbor Low stone circle stands out as one of the most significant, featuring a large circular earthwork and a series of standing stones that hint at its ceremonial use. Similarly, the nearby Nine Ladies stone circle, located on Stanton Moor, is renowned for its picturesque setting and historical significance, drawing visitors and researchers alike.
Moreover, the Peak District is dotted with other ancient monuments, including burial mounds, henges, and rock art, which collectively paint a picture of a vibrant prehistoric landscape. The presence of these structures suggests that the area was a focal point for ritual activities and community gatherings, reflecting the social and spiritual lives of its ancient inhabitants.
A comprehensive landscape survey conducted by the archaeological team suggests that there may be many more undiscovered prehistoric monuments in the vicinity, hinting at a vibrant and complex ancient landscape waiting to be explored. This groundbreaking find not only reshapes our understanding of the Farley Moor site but also highlights the potential for further archaeological discoveries in Derbyshire, offering a glimpse into the ceremonial practices of our ancient ancestors and their connection to the land.
Cover Image Credit: The Time Team Expedition crew. Forestry England