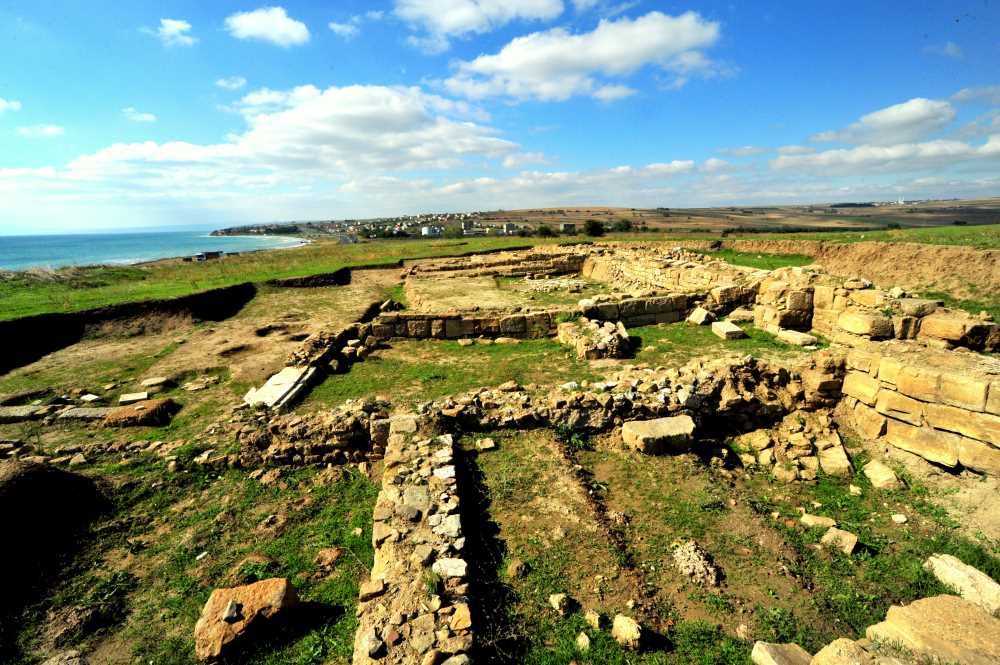
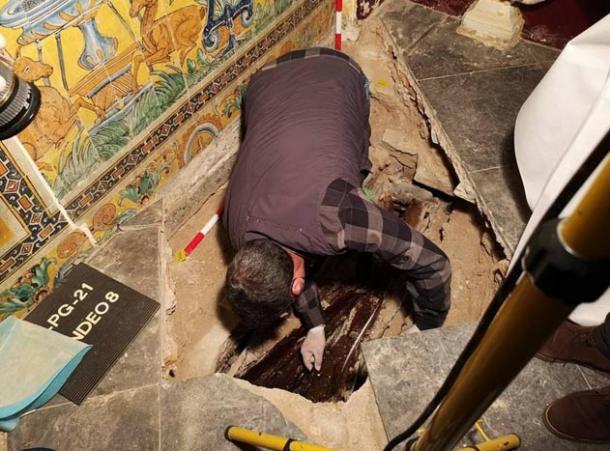
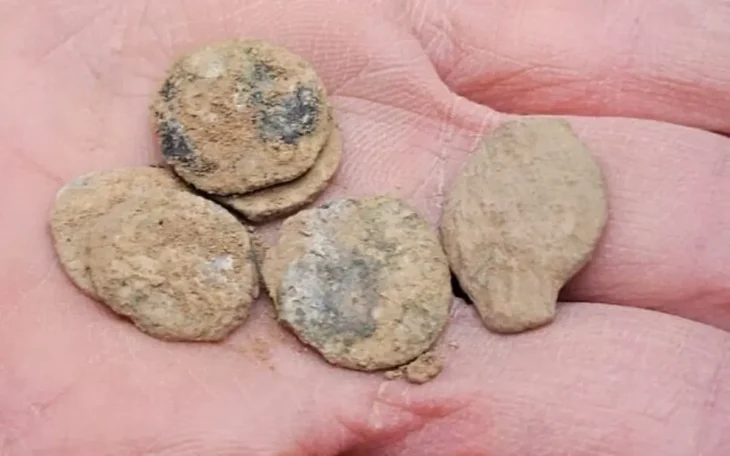
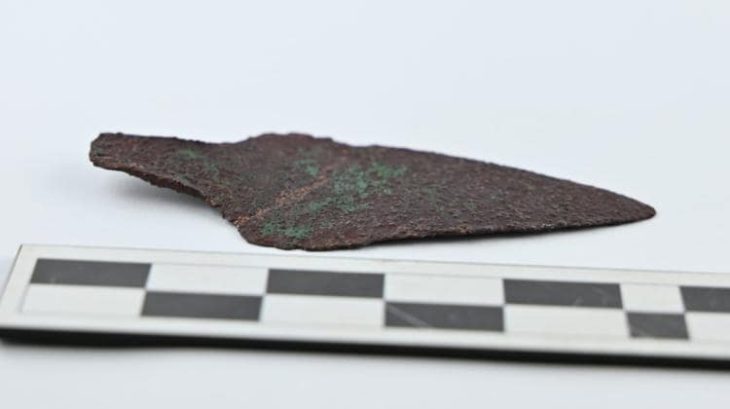
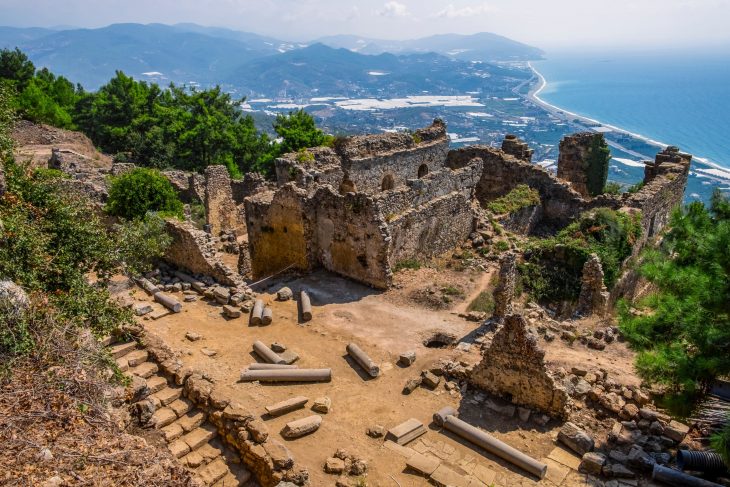
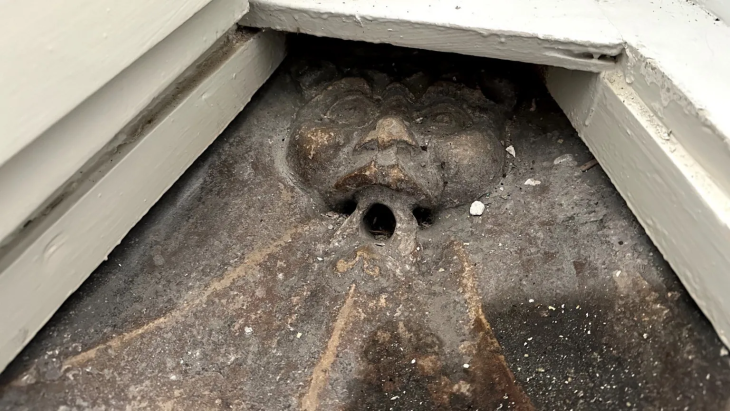
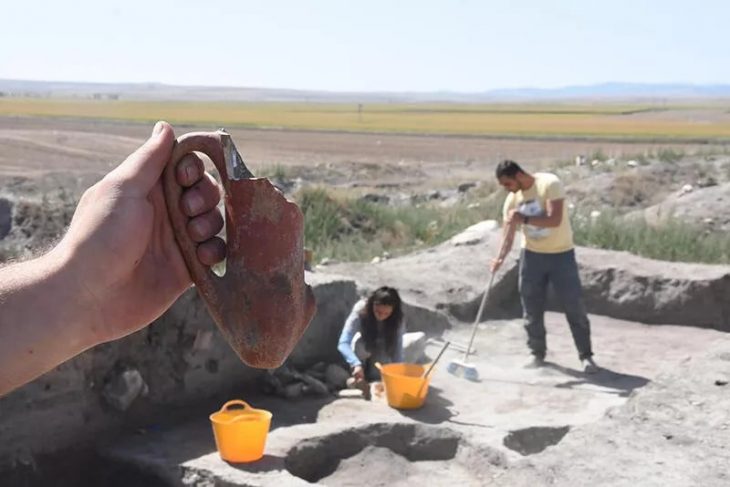
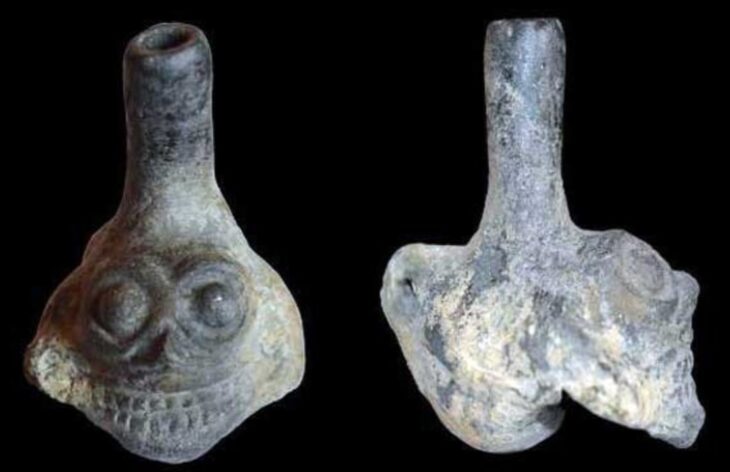
Archaeologists have unearthed a “pharmaceutical production area” supported by a water source during ongoing excavations in the Thracian Ancient City Heraion Teikhos, in the northwestern province of Tekirdağ.
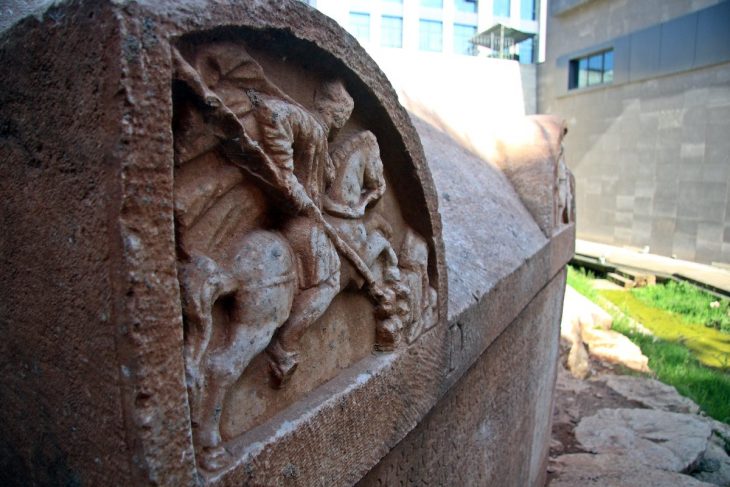
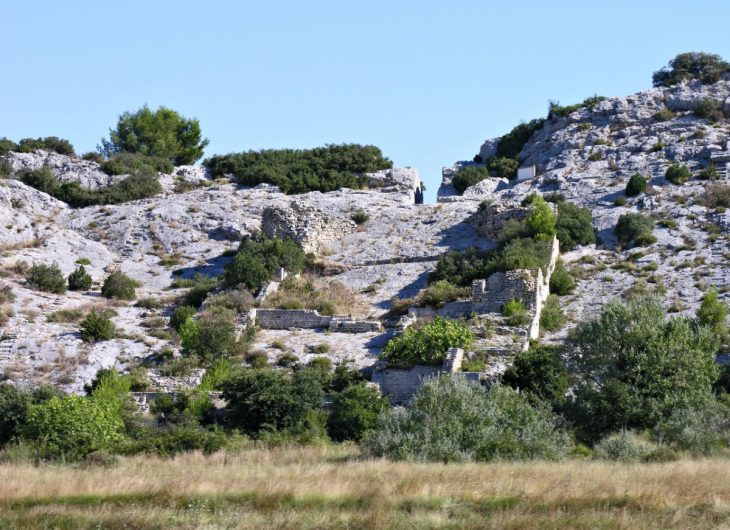
Heraion Teichos ancient city on the İstanbul-Tekirdağ highway, situated on the banks of the Marmara Sea in Tekirdağ Province, is extremely important since it is the only Thracian city excavated in Türkiye.
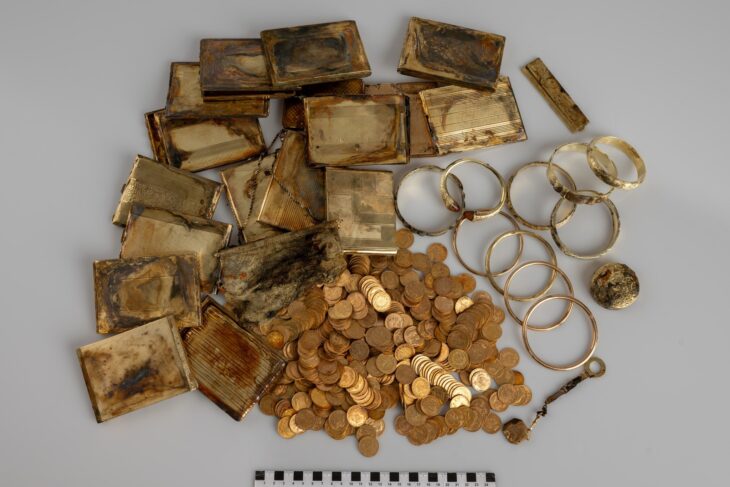
In recent years, scientific data revealed by archaeological excavations prove that the city has been inhabited from third millennium B.C.E. to XIII century. Century A.D. The city lived its most brilliant periods from 5Th century B.C.. to 1st century A.D.
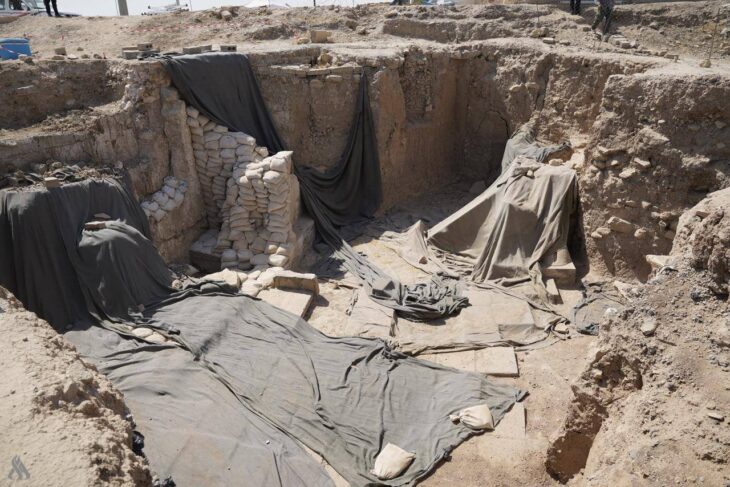
In 2021, a team of researchers from Istanbul Rumeli University unearthed a 2,800-year-old temple in Türkiye’s ancient Thracian city of Heraion Teikhos. Now, a water system has been identified leading to a space within the temple that researchers call an “ancient pharmaceutical production area.”
Professor Dr. Neşe Atik told Hurriyet Daily News, “Heraion Teikhos is a Thracian City, the first Thracian settlement in our country where excavations are still being carried out, and the only excavation site that yields Thracian finds.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Atik stated that the aim of the excavations is to identify pharmaceutical production areas, the size of which is not yet known, and how the water was transported.
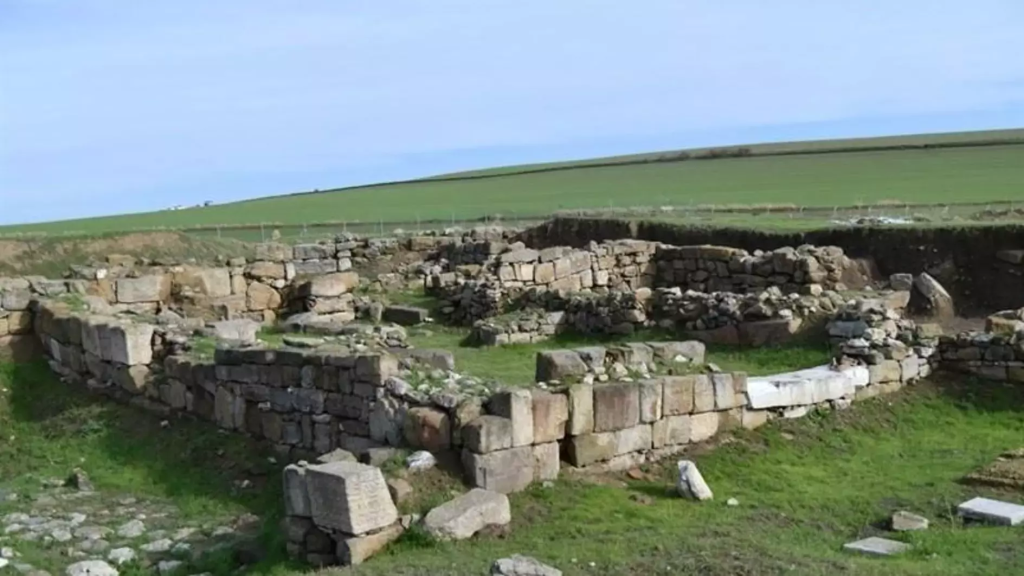

“Water systems in hilltop settlements were usually built with large water cisterns in ancient times. The 2023 excavations at the Heraion Teikhos settlement yielded findings indicating that water was transported not from cisterns but from an area a few kilometers to the east of the excavation site, which is still wooded today. In addition to this, a new pharmaceutical was unearthed in the west of the settlement. Terracotta pipes connecting the pools and stone channels also revealed that there was a pharmaceutical production area spread over the entire excavation area,” Atik said.
“The fact that the medicine ovens and the clean water system and pools required for medicine making were located close to each other in the same areas is scientifically important since it is the first time they have been identified archaeologically,” she concluded.
The Thracians were a group of tribes renowned for their rich culture and formidable warriors, that thrived in Southeast Europe from as early as 2000-1500 BC. They were a group of tribes who occupied the southeastern part of the Balkan Peninsula.
The Thracians are most famous for their magnificent metalwork, particularly in gold and silver, and for people like the fabled Spartacus, who was descended from them. Their culture, interwoven with Greek and later Roman influences, contributed significantly to the tapestry of classical antiquity, but it remains shrouded in mystery due to a lack of written records.