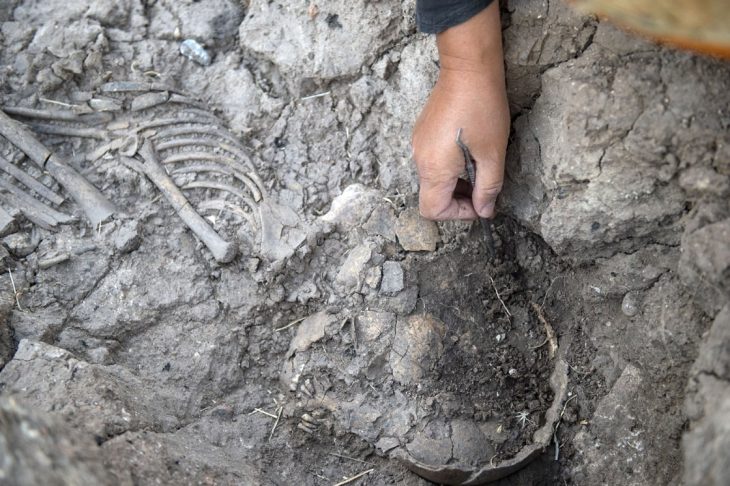
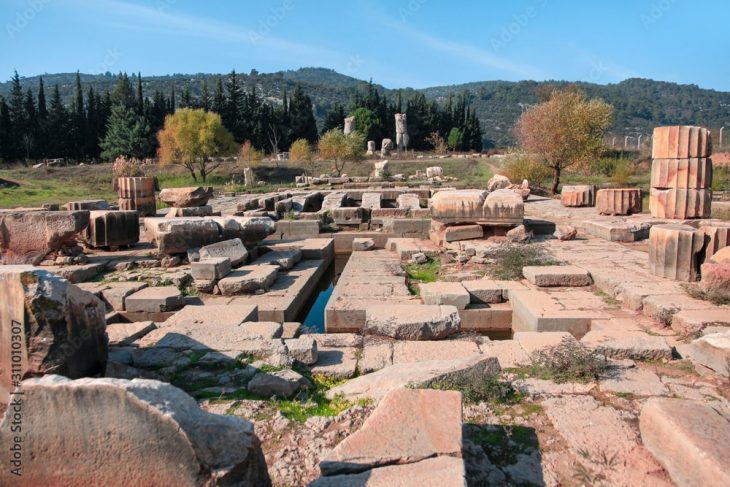
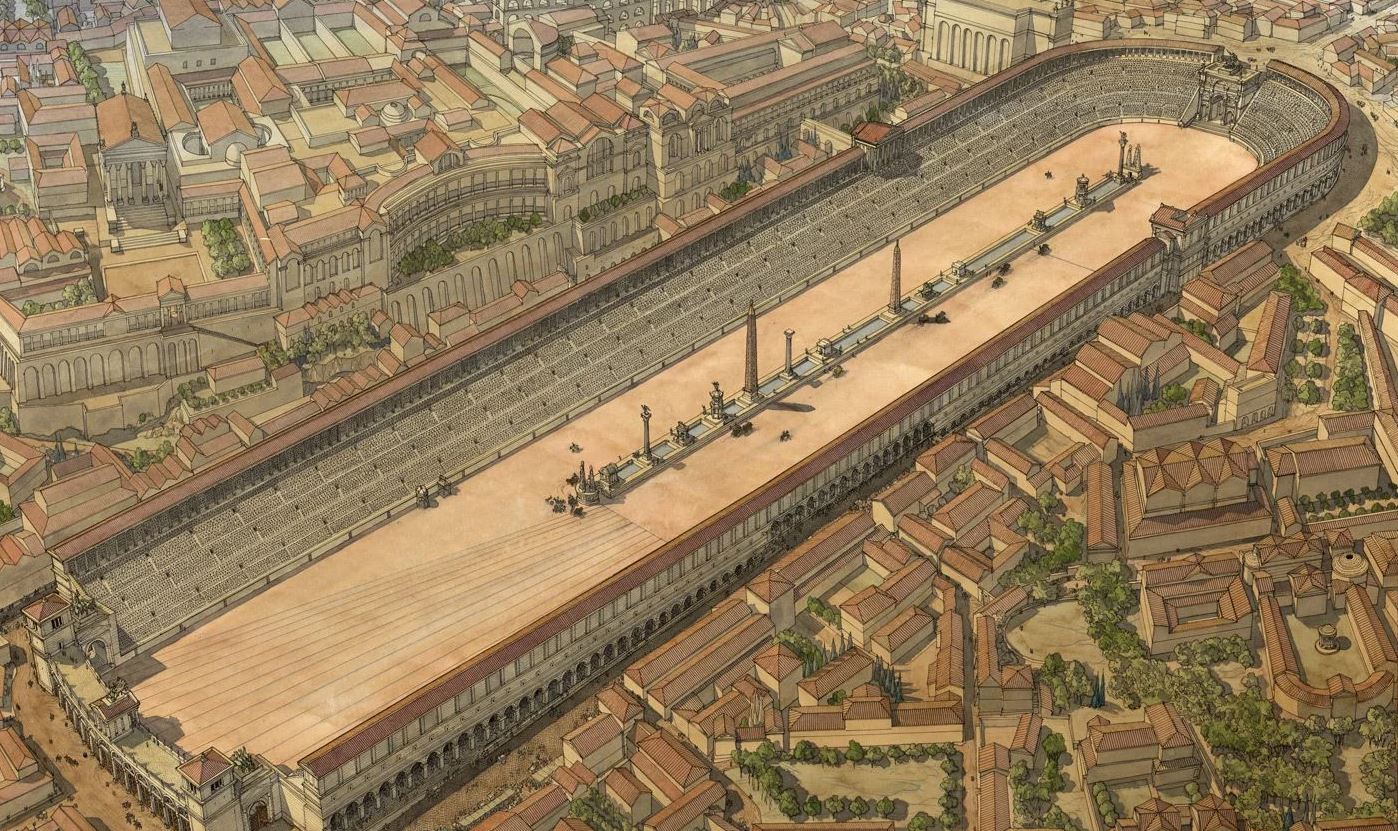
In a remarkable archaeological breakthrough, researchers in central Türkiye have confirmed the discovery of a 2,000-year-old Roman hippodrome (Roman Circus) buried beneath what was once a municipal landfill in Kayseri.
The site—today home to a popular open-air marketplace known locally as Bitpazarı—was for decades used as a dumping ground for rubble and city waste. Beneath those layers of debris, however, lies one of Anatolia’s grandest relics of the Roman world: a vast arena where horses once raced before cheering crowds in the ancient city of Caesarea.
Uncovering a Lost Monument
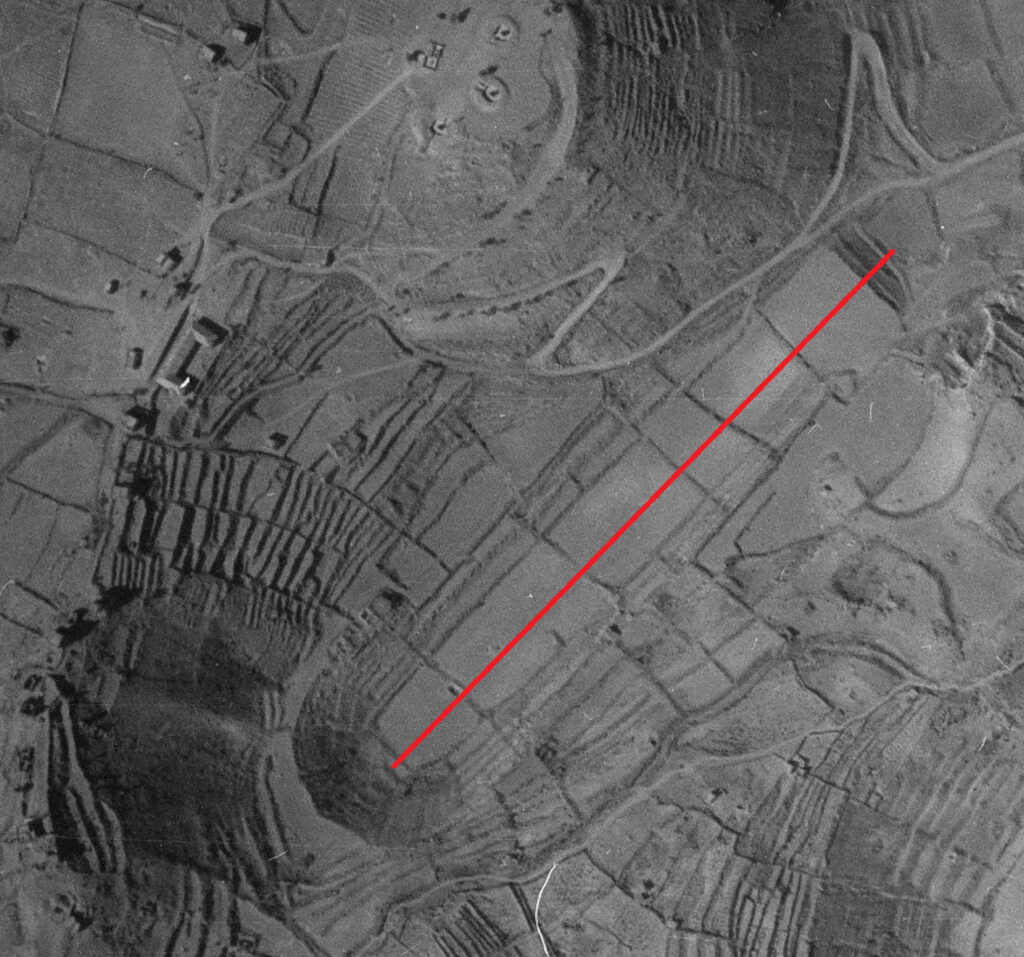
The finding makes this the third known Roman hippodrome in Anatolia, following those discovered in Ephesus and Pergamon. The project, initiated by the Kayseri Metropolitan Municipality, began with the study of 19th-century travelers’ notes and maps.
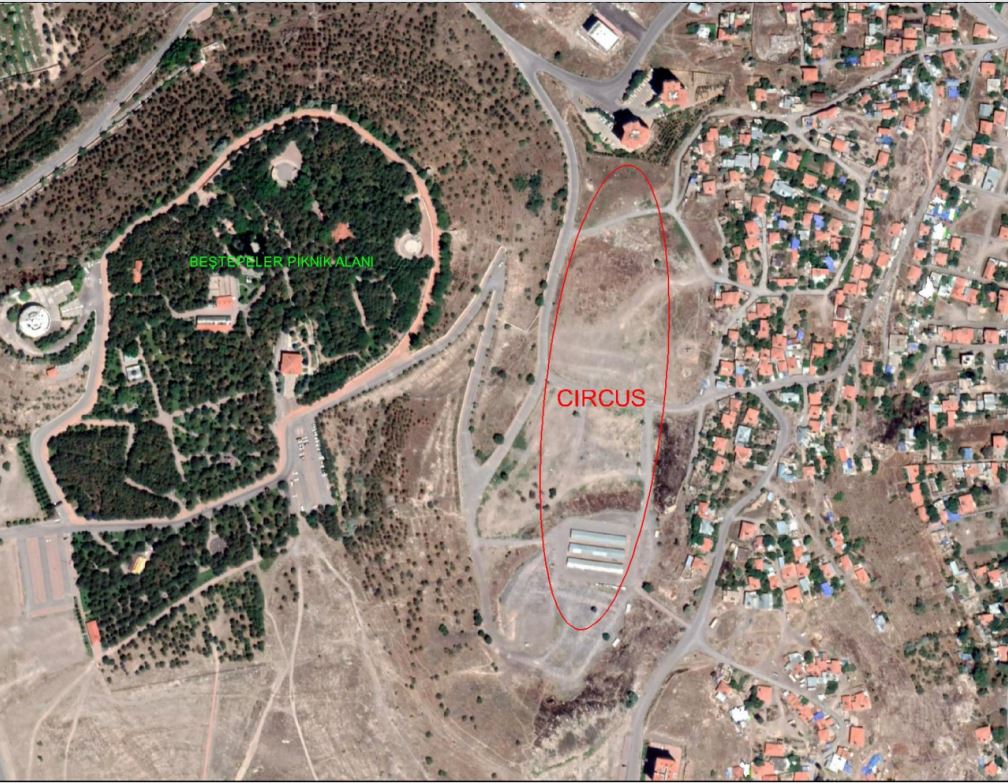
One such document, drawn by Greek scholar Gregorios Bernardakis, marked a mysterious structure labeled “Circus.” When municipal experts overlaid that historic map with modern aerial imagery, they noticed a subtle oval shape hidden beneath the urban landscape.
Subsequent archaeo-geophysical surveys confirmed the presence of massive subsurface foundations matching the typical plan of a Roman hippodrome—an elongated arena used for chariot and horse races. Preliminary measurements suggest the structure stretched about 450 meters, making it one of the largest known examples in the region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Buried Beneath a Former Landfill
The same ground, however, was drastically altered in the 20th century. Archival photos and maps show that between 1950 and 1980, the area served as Kayseri’s main landfill. Over that period, nearly 20 meters of rubble and waste accumulated across the site.
Local historian Mustafa Cingil explained the paradox with a mix of fascination and regret:
“During earlier municipal administrations, the land was used as a dumping site and landfill. As a result, the ancient hippodrome now lies buried beneath tens of thousands of tons of debris.”
Ironically, this unintentional burial may have helped preserve the structure from modern development. Beneath the surface, the hippodrome’s outlines remain intact—its curved ends still mirrored in the gentle slopes around Beştepeler Park.

A City with Deep Roots
The discovery also reawakens interest in Kayseri’s layered history. Known as Mazaka in the Hellenistic era, the city became Eusebia under the Cappadocian kings before taking the Roman name Caesarea during the reign of Emperor Tiberius (AD 14–37).
As the capital of the Cappadocia Province, Caesarea flourished as an administrative and cultural center. Scholars believe the hippodrome was likely commissioned in the late 1st century BC or early 1st century AD, possibly during the rule of King Archelaus, who oversaw Cappadocia’s transition into a Roman client state.
Here, Roman citizens and local elites would have gathered to watch chariot races, athletic contests, and imperial ceremonies—spectacles that reinforced both civic pride and imperial identity.
Recognition and Preservation
Following months of study, the Kayseri Cultural Heritage Preservation Board officially designated the area as a third-degree archaeological site on September 25, 2025, ensuring its legal protection.
While full excavation remains a challenge—given the depth of landfill deposits and the active market above—the discovery has already reshaped how historians view Kayseri’s Roman past.
City officials have stated that the site will undergo continued geophysical monitoring and non-invasive documentation, with hopes of revealing more of the structure without disturbing daily life in the area.
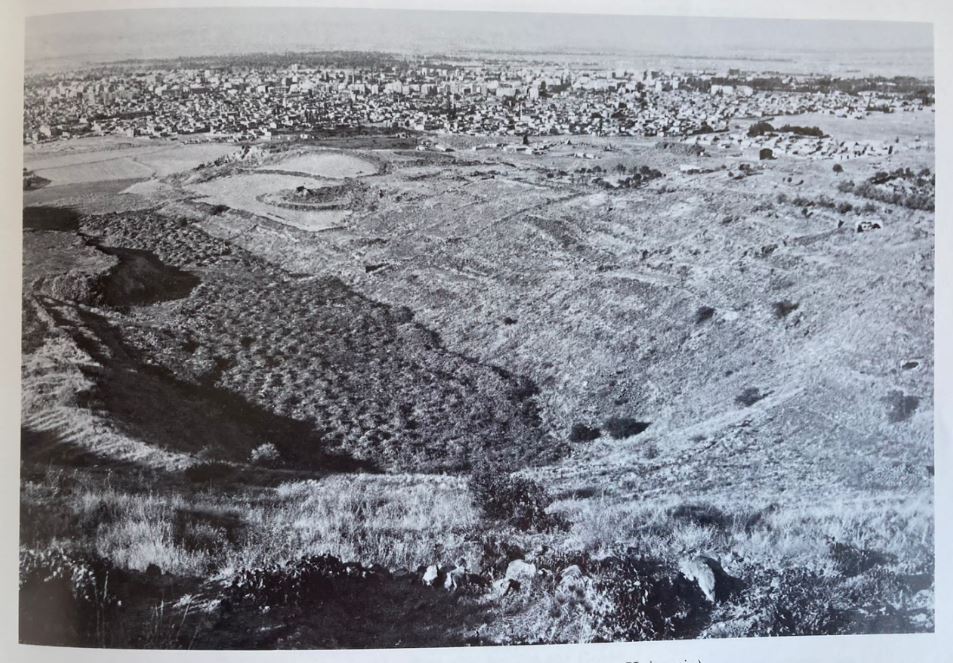

A Forgotten Arena Beneath Modern Life
Today, vendors at Bitpazarı sell vintage tools, books, and ceramics, unaware that beneath their stalls lies the grand arena of a Roman city. The irony is poetic: a place once filled with discarded objects now rests atop a forgotten monument of empire.
The Kayseri Hippodrome, buried beneath decades of waste, stands as a reminder that history often hides beneath the ordinary—that under even a city’s former landfill, the echoes of ancient glory still endure.