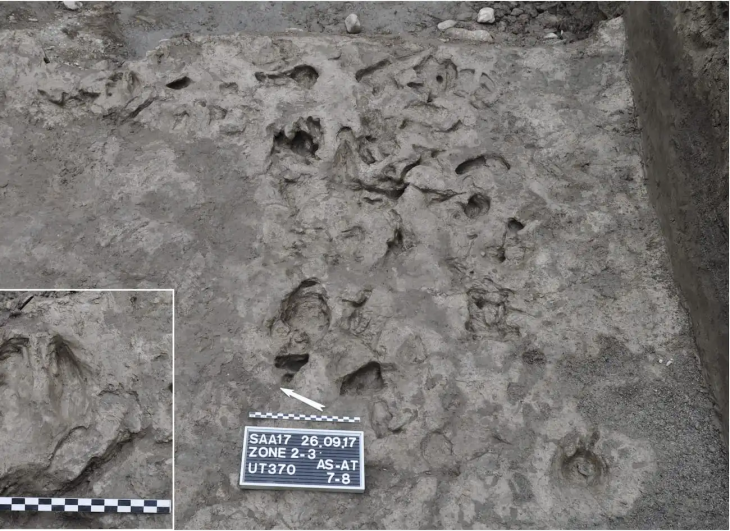
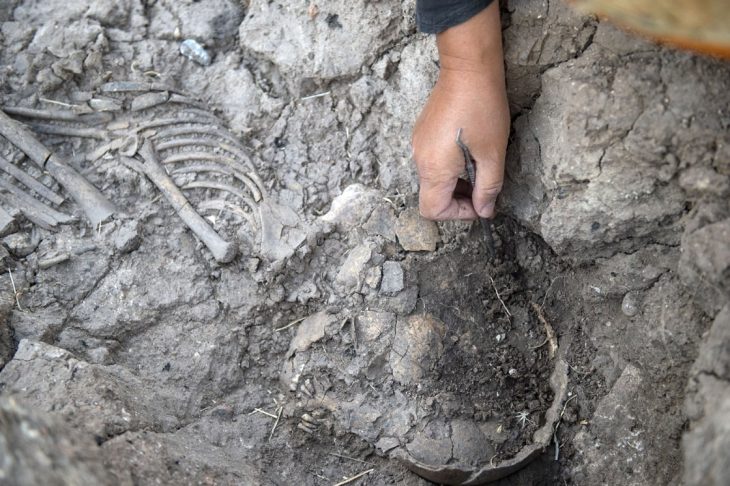
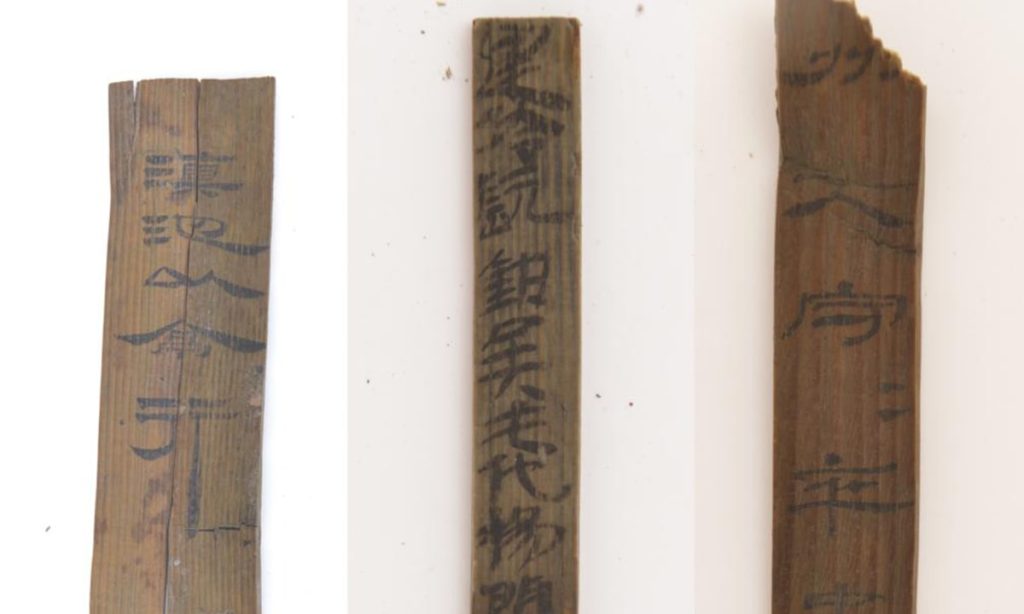
Thousands of bamboo slips (rectangles tied together to form books) have been discovered at the Hebosuo archaeological site in southwestern China’s Yunnan province.
The Yunnan Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology announced that more than 10,000 ancient bamboo and wooden slips, known as jiandu, have been found at the more than 2,000-year-old Hebosuo Site in Kunming, Southwest China’s Yunnan Province.
Bamboo or wooden slips were bound together to create “books” that could be written on and rolled up like scrolls before paper was invented and used extensively.
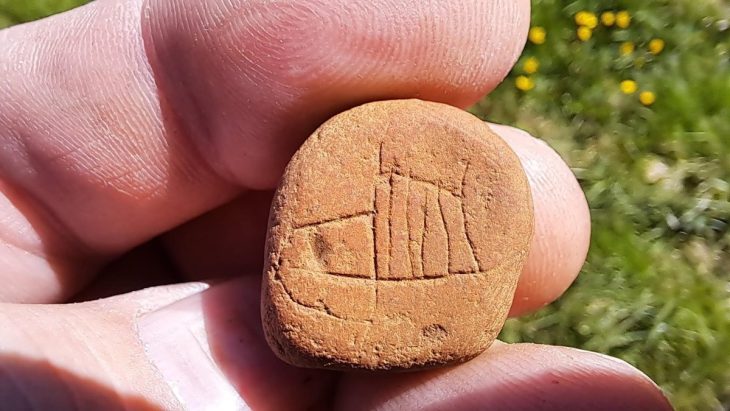
About 2,000 of them, or 1,300, are from the Han Dynasty (202 B.C.–220 A.D.), and 837 are seal impressions. In Western Han tombs, bamboo slips are frequently literary works and books about agriculture and medicine, but in this discovery, the majority of the writings is administrative.
The seal impressions are particularly noteworthy because they include official seals from 20 of the 24 counties ruled by the ancient Dian kingdom, a non-Han culture of agriculture-based settlements and exceptionally sophisticated metal workers centered in modern-day Yunnan. Emperor Wu of Han annexed the kingdom in 109 B.C.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Some of the slips list the names of 12 counties, including “Dian Chi county” and “Jian Ling county,” that once belonged to the Yizhou Prefecture, which was established by Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty (206BC-AD220). Wu did this after defeating the Dian Kingdom, which was established by an ancient ethnic group that lived along what is now the southwest border of Yunnan Province.
Other characters such as “county magistrate,” and “Dian Cheng” (prime minister of Dian management) were also discovered on the slips, Tao Zhongjun, a Chinese historian, told the Global Times on Tuesday, noting that such information shows a “well designed” social administrative system was used to govern the southwest border area.
Titles such as “Dian Cheng” reveal special political roles were set up by the Han government in the southwest area, said Jiang Zhilong, lead archaeologist on the Hebosuo project.

“Such discoveries are evidence that shows China was a unified country made up of multi-ethnic cultures,” Jiang noted.
Parts of the Analects of Confucius, the fundamental philosophical guide to Confucianism, were also found on the slips.
They also the content of the slips covers a wide variety of topics, including judicial documents and texts related to the administrative system, transportation, and ethnic relations.
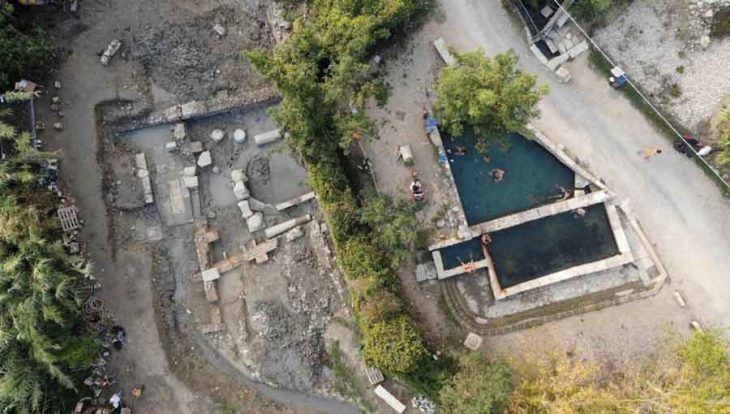
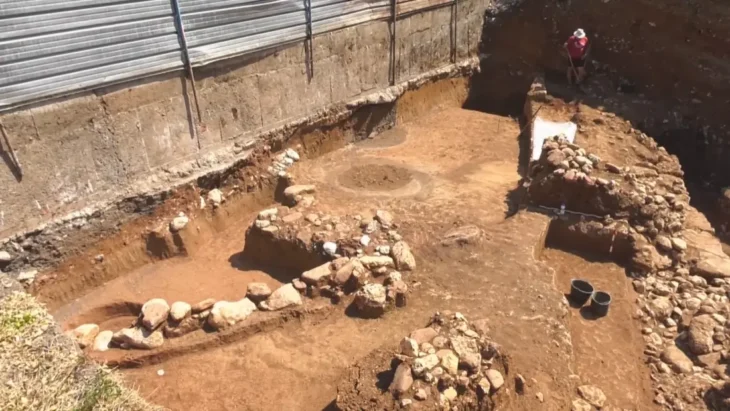
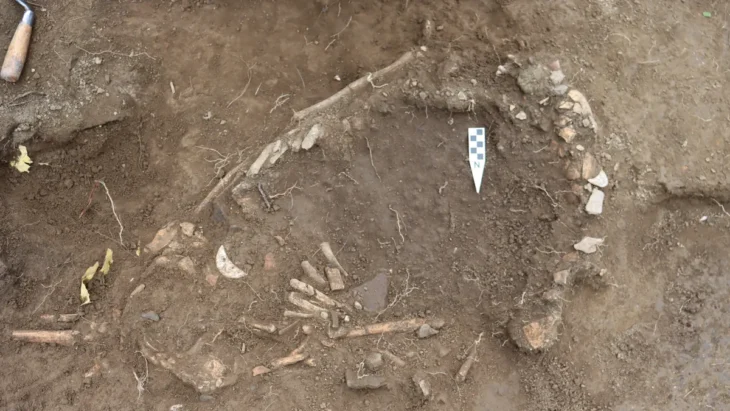
The archeologists also found house ruins and road ruins suggesting roads as wide as 12 meters at the Hebosuo site, Jinning District of Kunming, capital of Yunnan, a core residential area of the ancient Yunnan region.
The cover photo used is for representation purposes