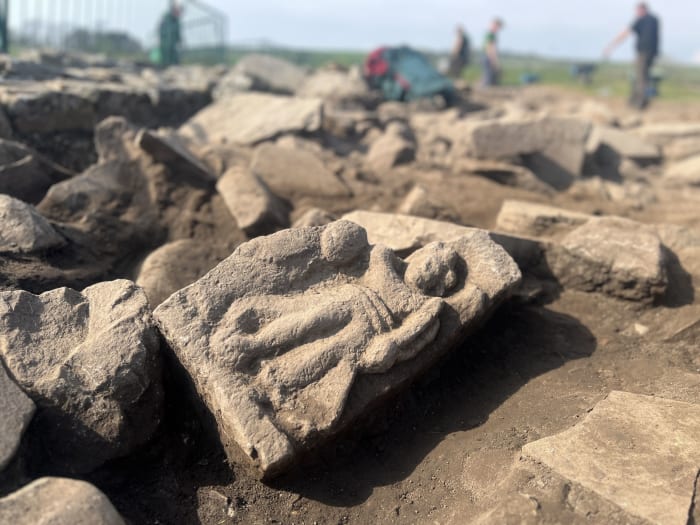
A rare and symbolically powerful Roman sandstone relief depicting Victoria, the goddess of Victory, has been unearthed at the Vindolanda Roman fort near Hadrian’s Wall, marking a significant archaeological discovery that echoes the end of the Severan wars in Roman Britain.
The finely carved sandstone relief measures 47 cm in height, 28 cm in width, and 17 cm in depth, further suggesting it was once part of a substantial architectural feature, possibly framing a central inscription.
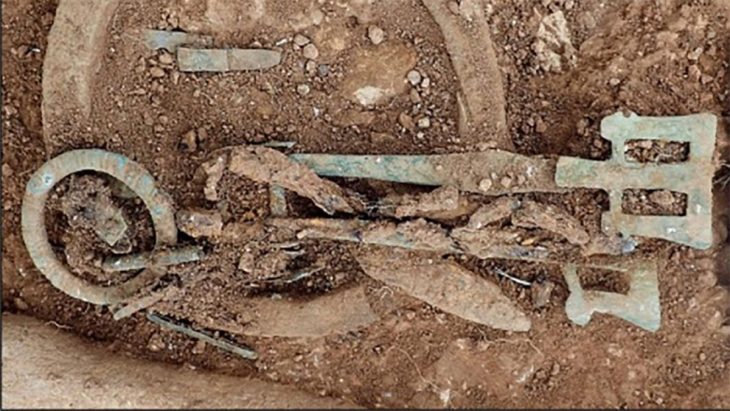
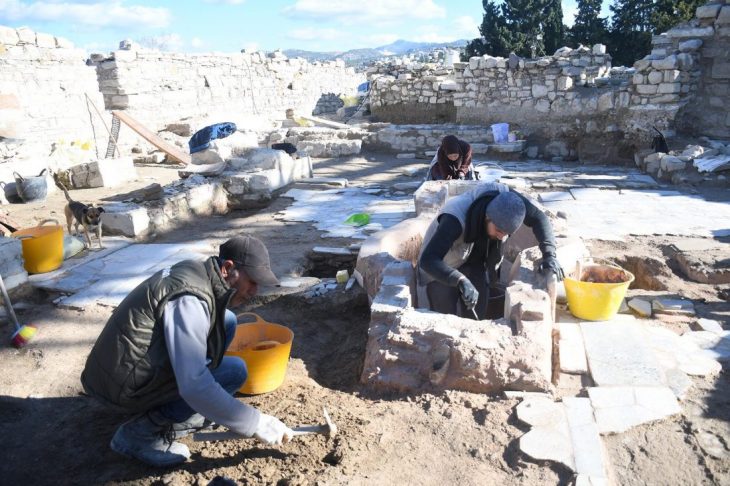
The intricately carved relief, believed to date to around AD 213, was discovered in a rubble layer above a former infantry barracks by long-serving excavation volunteers Jim and Dilys Quinlan from Merseyside. The couple, now in their 21st year of digging with the Vindolanda Trust, uncovered what is thought to be part of a larger commemorative monument once adorning a grand archway at the site.
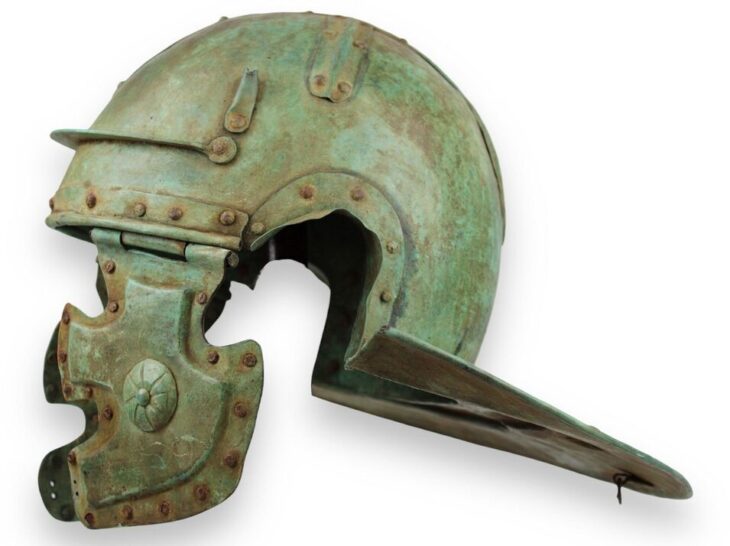
Victoria, the Roman equivalent of the Greek goddess Nike, personified military success and was frequently venerated in the Roman Empire during and after periods of conflict. Her presence in this context is particularly poignant: the barracks beneath the find were constructed shortly after the conclusion of the Severan military campaigns, which had significantly reshaped Britain’s Roman frontier.
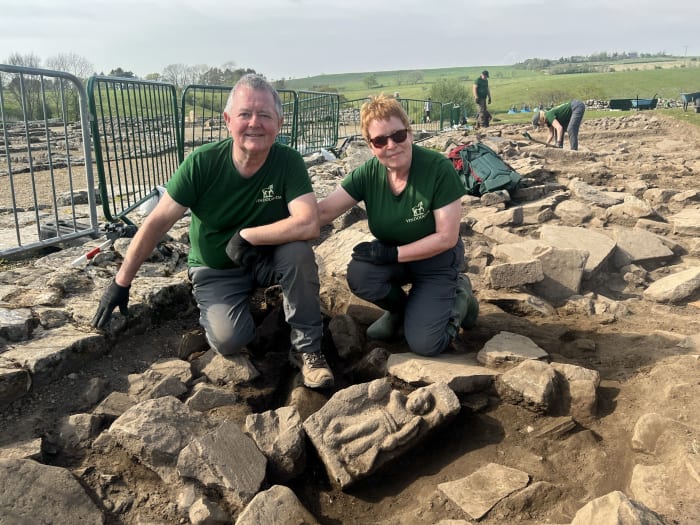

“Finds like this are increasingly rare these days from Roman Britain,” said Dr. Andrew Birley, Director of Excavations at the Vindolanda Trust. “The beautifully carved figure reminds us that Roman forts were not just functional military structures—they carried cultural and symbolic significance for the soldiers who lived there.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The relief is believed to have framed an inscribed panel that once stood as part of a monumental gate structure, possibly celebrating peace and stability after years of warfare.
Adding to the excitement, Barbara Birley, curator at the Vindolanda Trust, noted that the relief may have originally been painted in vivid colours, a practice common with Roman stone carvings. “We’re storing the piece unwashed for now,” she said, “as we begin detailed analysis to detect any traces of ancient pigment.”
Thanks to the expertise of Professor Rob Collins, Head of Archaeology at Newcastle University, the stone’s depiction of Victory has been formally identified and authenticated.
The relief is slated to go on public display in early 2026 as part of Vindolanda’s “Recent Finds” exhibition, promising to be a major highlight for visitors to this internationally renowned Roman site.
Cover Image Credit: The Vindolanda Trust