Archaeologists have discovered an exceptional Christian ancient ivory reliquary box in Austria that is thought to be around 1,500 years old.
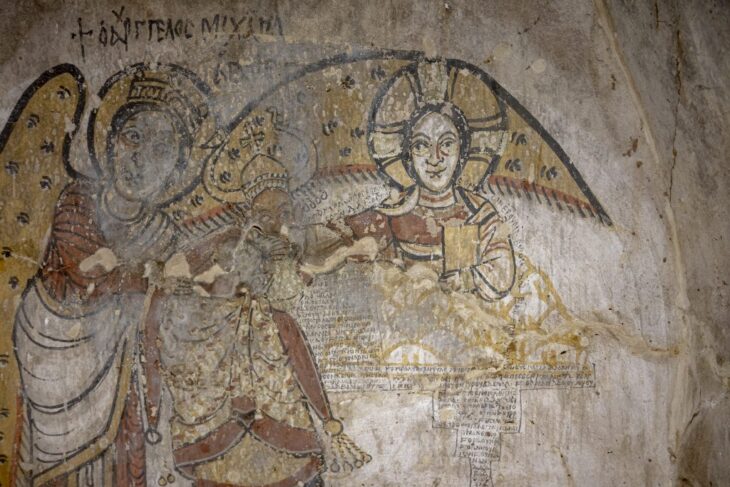
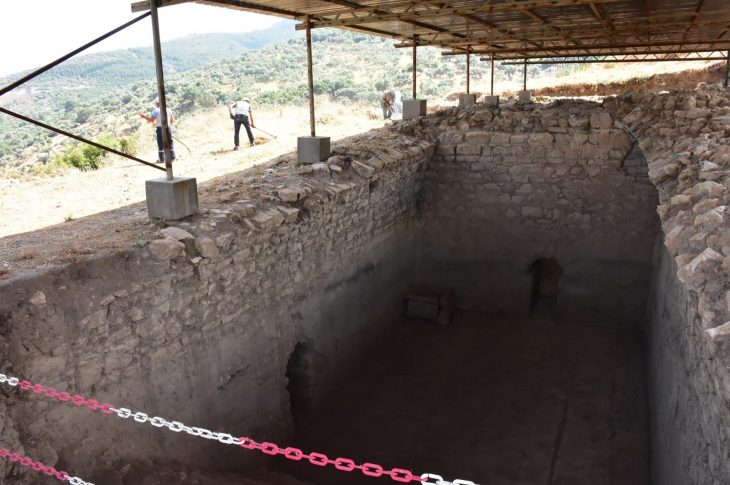
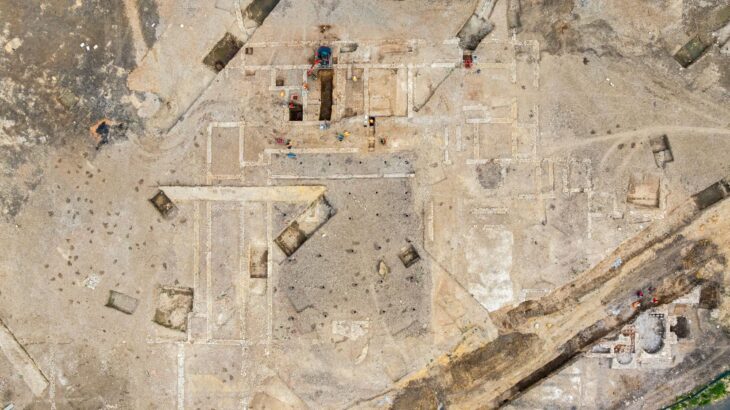
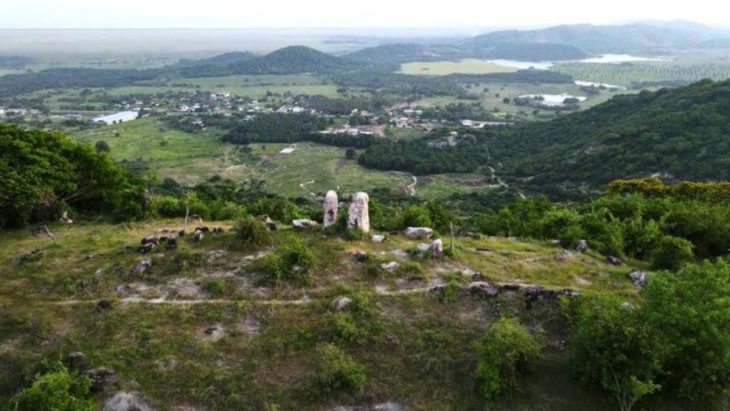
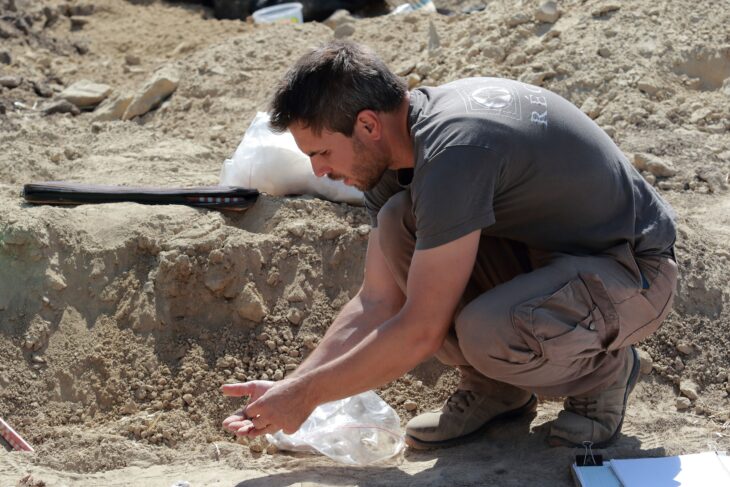
Innsbruck archaeologists have been excavating in an old hilltop settlement in southern Austria since the summer of 2016. They made the incredible discovery of a Christian reliquary concealed in a previously unknown church two years ago. This reliquary contained an ancient ivory box, richly decorated with Christian symbols.
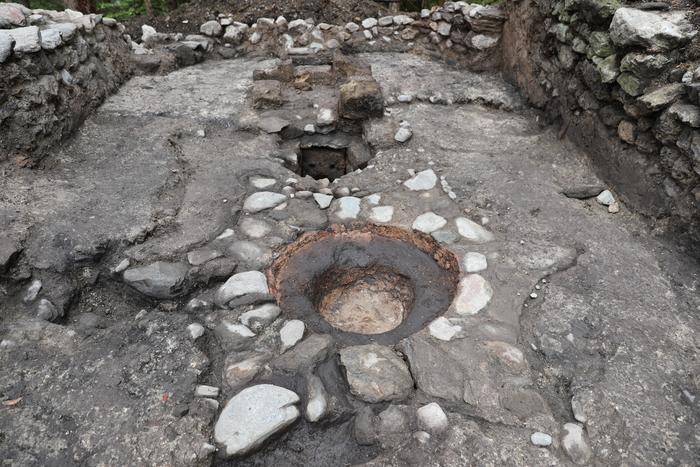
The incredible artifact was discovered on August 4, 2022, in an early Christian church on the Burgbichl hill in Irschen, southern Austria, by a team headed by archaeologist Gerald Grabherr. A marble shrine measuring around 20 by 30 centimeters was hidden under the altar in the side chapel area.
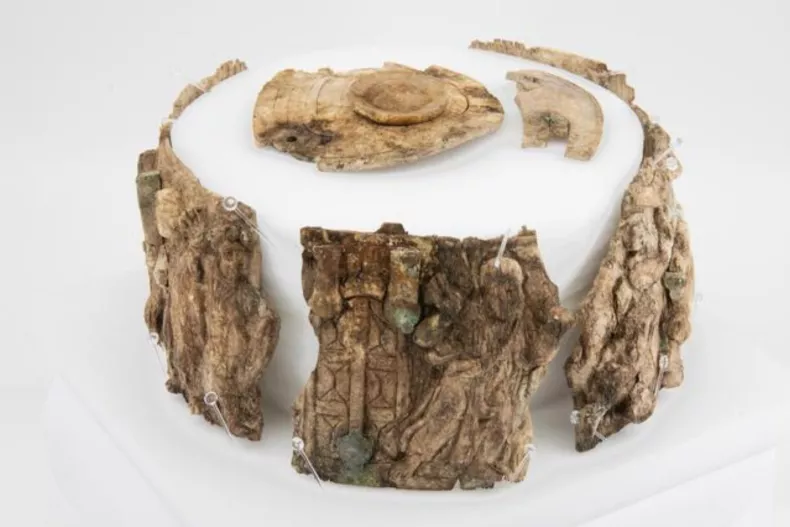
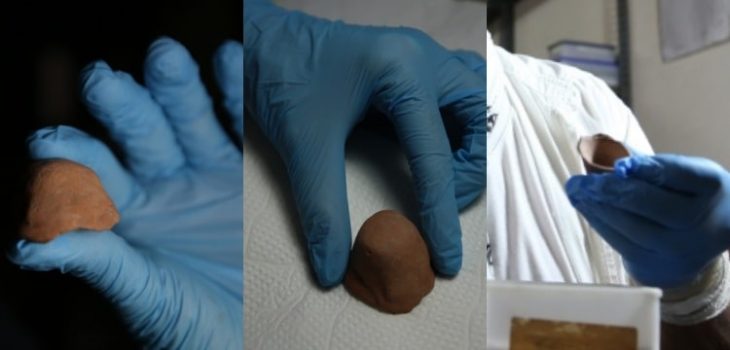
The artifact in question is heavily fragmented, but researchers said the pieces once formed a type of round container known as a “pyx” that in this case was made of ivory and richly decorated with Christian motifs.
The shrine contained a heavily fragmented ivory “box” (pyx) richly decorated with Christian motifs – a reliquary that is normally taken away as the “holiest” part when a church is abandoned. In this case, however, it was left behind. It is the first such pyx to be found in an archaeological context in Austria.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
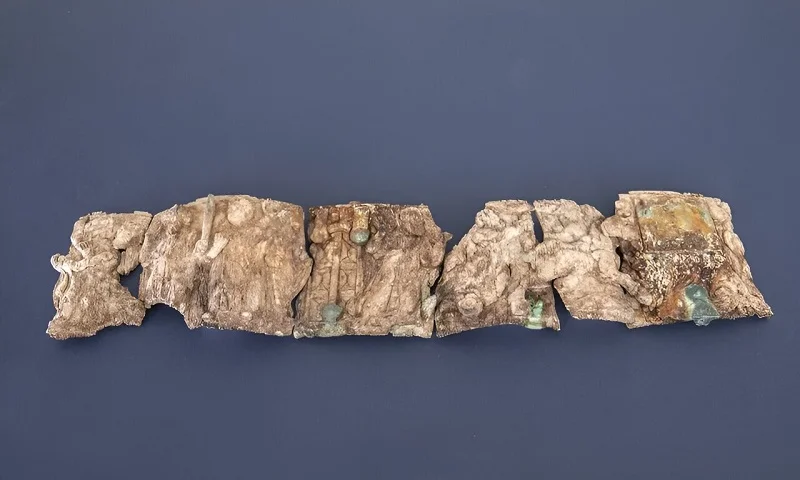

“We know of around 40 ivory boxes of this kind worldwide and, as far as I know, the last time one of these was found during excavations was around 100 years ago – the few pyxes that exist are either preserved in cathedral treasures or exhibited in museums,” explains the finder, Gerald Grabherr.
While the archaeologists initially assumed that the remains of a saint – i.e. a relic in the classic sense of the word – were also found in the marble box, the layering of the fragments found in the shrine indicates that the ivory pyx was already broken in late antiquity and was buried in the altar.
“The pyx was presumably also seen as sacred and was treated as such because it was in contact with a relic. The archaeological and art-historical significance of the pyx cannot be denied,” emphasizes Gerald Grabherr.
At one end, the pyx shows a figure at the foot of a mountain – the man depicted is turning his gaze away and a hand rising out of the sky above him, placing something between the person’s arms.

“This is the typical depiction of the handing over of the laws to Moses on Mount Sinai, the beginning of the covenant between God and man from the Old Testament,” says Gerald Grabherr. This is followed by depictions of biblical figures. At the end, you can see a man on a chariot with two horses harnessed to it – and here, too, a hand coming out of the clouds pulls this figure up into heaven. “We assume that this is a depiction of the ascension of Christ, the fulfilment of the covenant with God. The depiction of scenes from the Old Testament and their connection with scenes from the New Testament is typical of late antiquity and thus fits in with our pyx; however, the depiction of the Ascension of Christ with a so-called biga, a two-horse chariot, is very special and previously unknown.”
Since its discovery, the 1,500-year-old ivory pyx has been conserved at the University of Innsbruck.
Ivory stored underground absorbs moisture, making it very soft and easily damaged. Uncontrolled drying can lead to shrinkage and cracks.
Ulrike Töchterle, head of the restoration workshop in Innsbruck, said, “The high humidity in the marble shrine meant there was a high risk of condensation and mold, so we had to ensure a careful and prolonged drying process.”
Over the past two years, the individual pieces of the ivory pyx have been conserved for scientific analysis. The larger parts are deformed, so the pyx cannot be restored to its original state. However, researchers are working on a 3D reconstruction.