Volunteer archaeologists have discovered a 1900-year-old military decoration (Phalera) that was awarded to distinguished soldiers and troops in the Roman army in Vindolanda, in northern England.
Vindolanda was a Roman auxiliary fort (castrum) one mile south of Hadrian’s Wall in northern England. Roman Vindolanda Fort is one of Europe’s most important Roman archaeological sites and situated on the Stanegate Road.
The site itself is made up of nine forts that are built on top of each other. Soldiers from all over the Roman Empire were stationed here, including Belgium, Germany, and France. The visible stone fort dates from the third century and includes the fort walls, the headquarters building, the Commanding Officer’s house, granaries, and barracks. The extramural settlement’s ruins can be found just outside the fort’s walls. A main street is lined with houses, shops, a tavern, and a bathhouse.
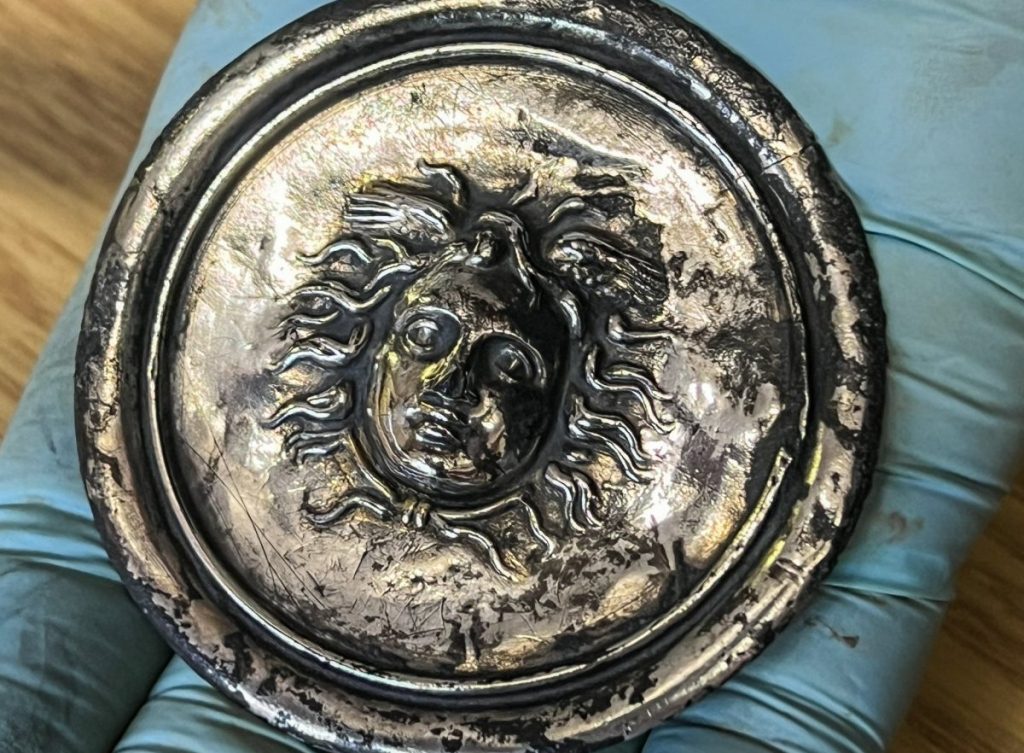

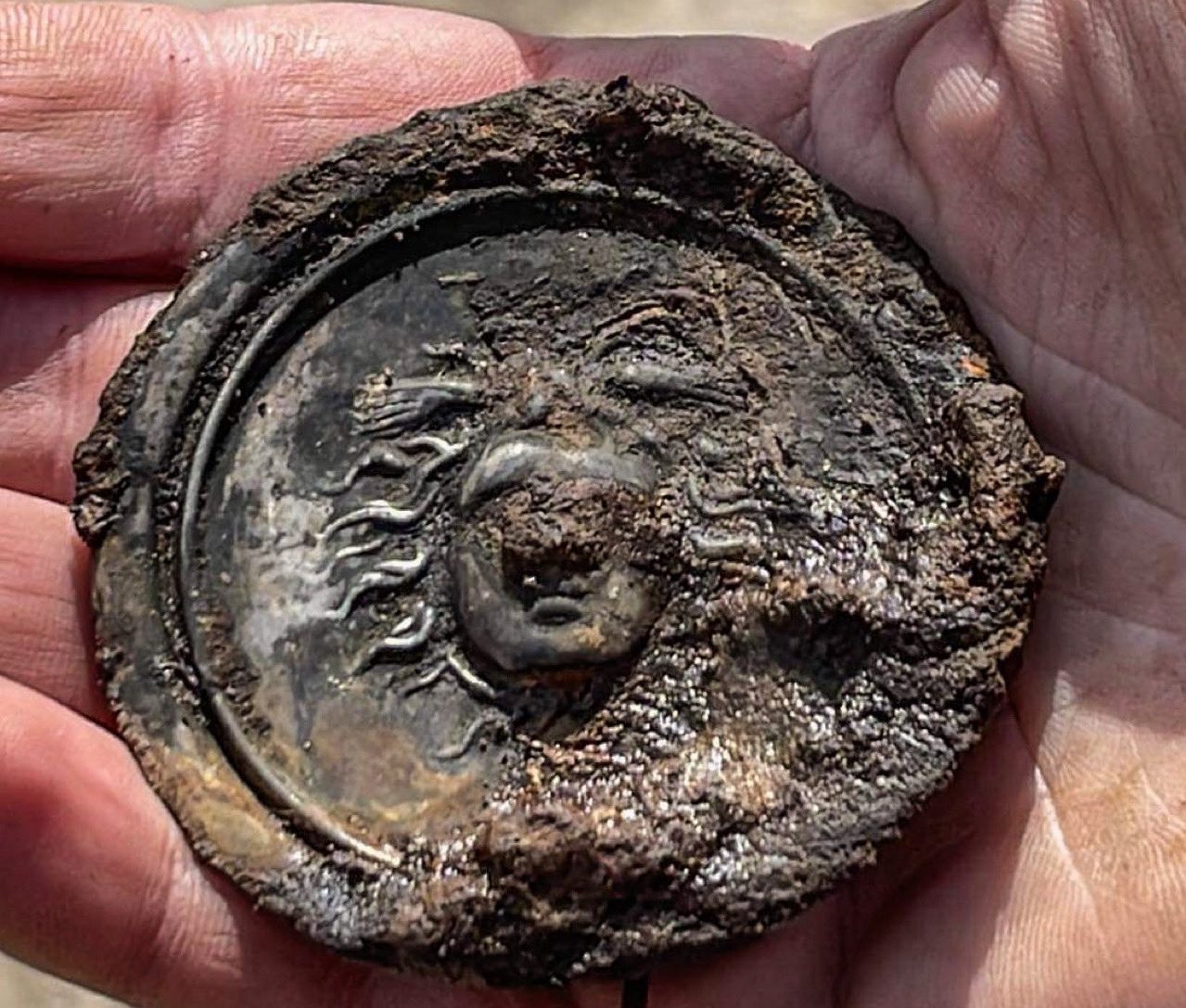
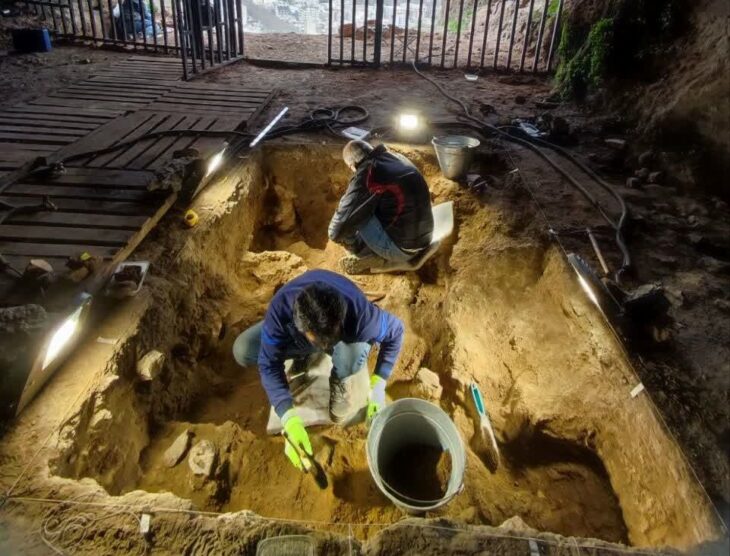
Excavations take place on the site every year and attract hundreds of volunteers from all over the world. Recent excavations on the floor of a barracks building uncovered a silver phalera disk, which Roman soldiers wore on their breastplates during parades.
The silver military decoration bearing the head of Medusa, a monster in the form of a woman with snakes for hair, the very sight of which would turn a person to stone. Medusa, also known as Gorgo in Greek mythology, was one of the three monstrous Gorgons, who were generally described as winged human females with living venomous snakes in place of hair.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The head of Medusa was carved in relief on the silver phalera unearthed in the Vindolanda. The head of Medusa also functions as a kind of apotropaic symbol, that is, as a protector.
Volunteer archaeologists have also found during this season’s excavations, a spearhead, a copper alloy spoon, a stamped mortarium rim, Samian pottery, a melon bead, an enameled bow brooch, a copper alloy scabbard chape (the protective fitting at the bottom of a scabbard or sheath for a dagger), and a well preserved wooden bath clog.
The discovery was shared on the Vindolanda Trust Twitter account.