Turkey is very lucky in terms of ancient settlements. It is home to many unexplored artifacts, along with well-preserved ancient cities from the Roman and Hellenistic periods.
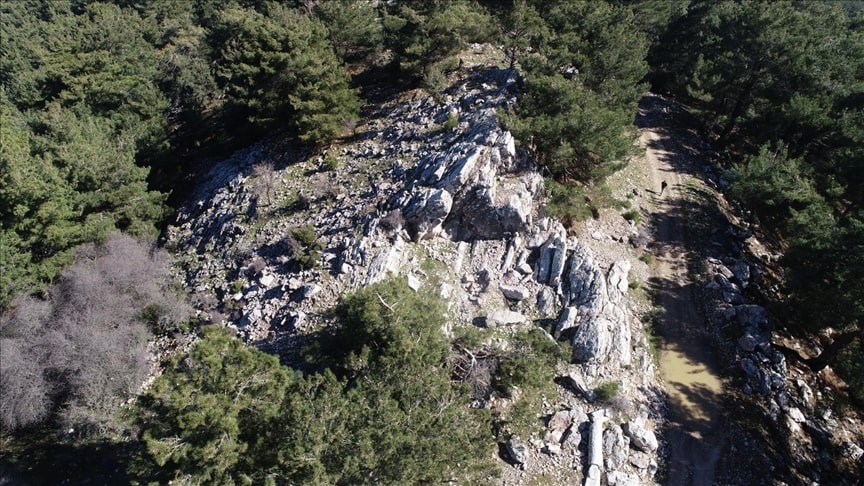
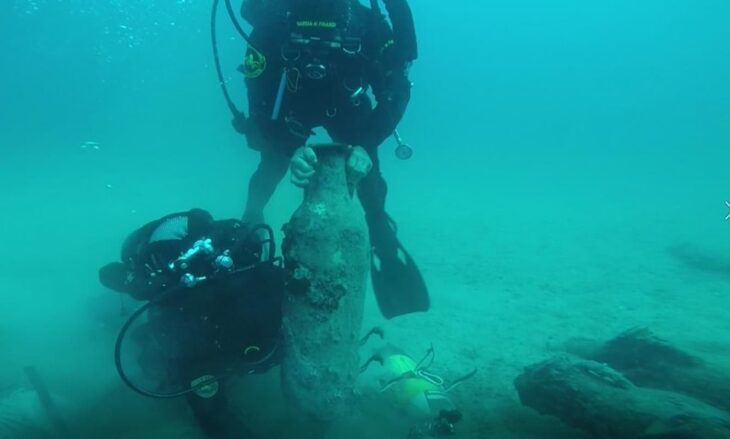
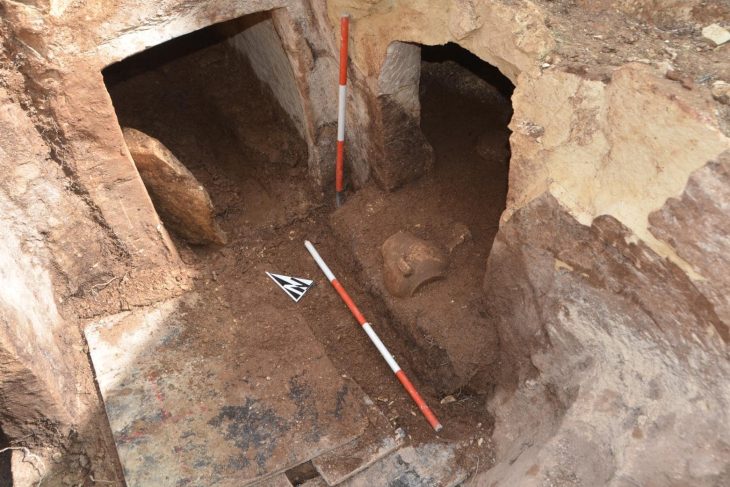
This time, the researchers discovered an ancient mine in the Karabağlar region of the city of Izmir. A stone quarry believed to have been used extensively in the Hellenistic and Roman periods has been discovered in western Turkey, authorities said on Saturday.
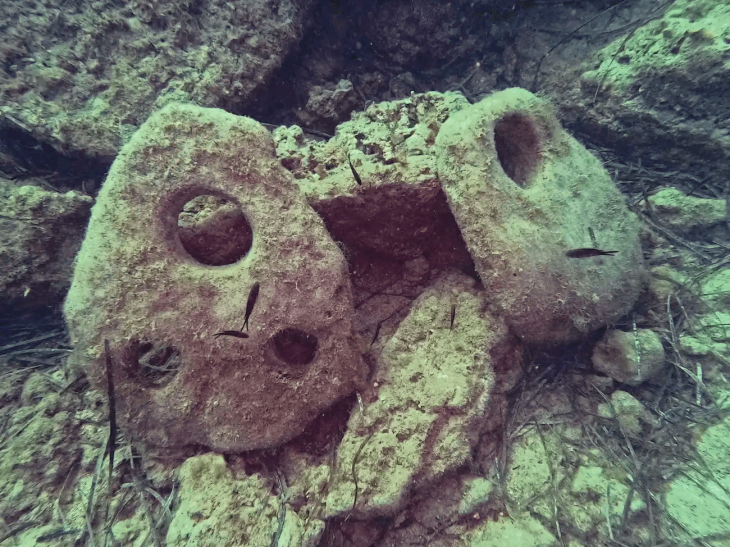
An ancient stone quarry was found in Tırazlı Village in the district of Karabağlar in İzmir. Tırazlı-Kesikkaya Antique Stone Quarry is thought to have been used extensively in the Hellenistic and Roman periods.
“The Tirazli-Kesikkaya Quarry is understood to have been in use in the beginning of the Hellenistic period, on the Kadifekale-Kemeralti axis of Smyrna City since its foundation,” Akin Ersoy, head of the Smyrna Ancient City Excavation project, said in the statement.
Ersoy, a lecturer at Izmir Katip Celebi University, said there were many other such facilities around the city center in ancient times.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
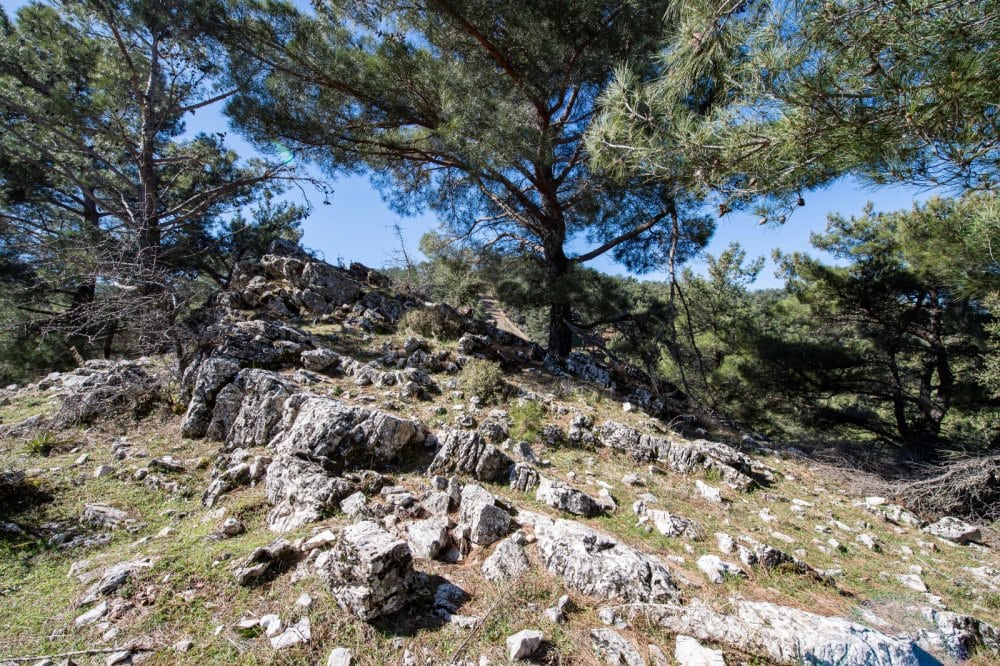

“It is understood that this quarry was used more actively to meet the needs of the magnificent buildings of Smyrna, which was growing and enriching especially in the Roman period,” he added.
Stating that stone quarries are important in the monumental buildings of the Ancient Age, Ersoy It is understood that “Tırazlı-Kesikkaya Stone Quarry was also used at the beginning of the Hellenistic Period, on the Kadifekale-Kemeraltı axis of Smyrna City since its foundation. “It is understood that this stone quarry was used more actively to meet the needs of the magnificent monumental buildings of Smyrna, which was growing and enriched especially during the Roman Period, and the number of monumental buildings increased in parallel with this situation,” he said.
He said it was unlikely that a single quarry would have met the demand for stone in such a large city, which is why researchers believe that there may be other quarries in the area.
The historical geography of Smyrna should be protected
Stating that there was various equipment around the city center in ancient times as well as today, Ersoy continued his words as follows: “In this sense, there are mills, farms, villages, quarries, water resources and castles in the countryside of Smyrna. Rural areas of cities with these facilities are defined as the historical geography of that city. Such areas or reinforcements constitute the historical heritage and accumulation of the ancient city. Unfortunately, today they are under threat, and these areas, which are part of the historical memory of cities, need to be protected. Initially, these points should be registered as protected areas. Later, residents and relevant enforcement authorities should protect such areas, “he said.