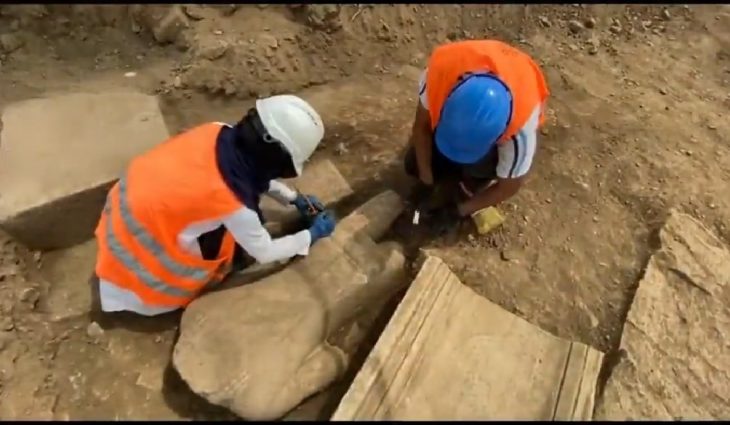
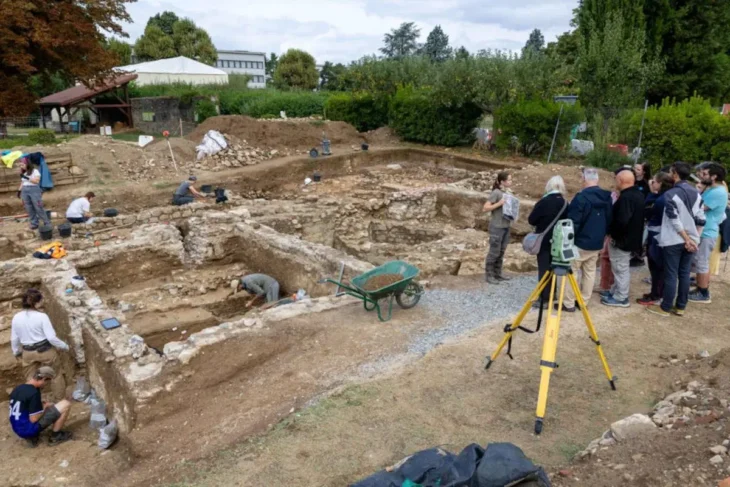
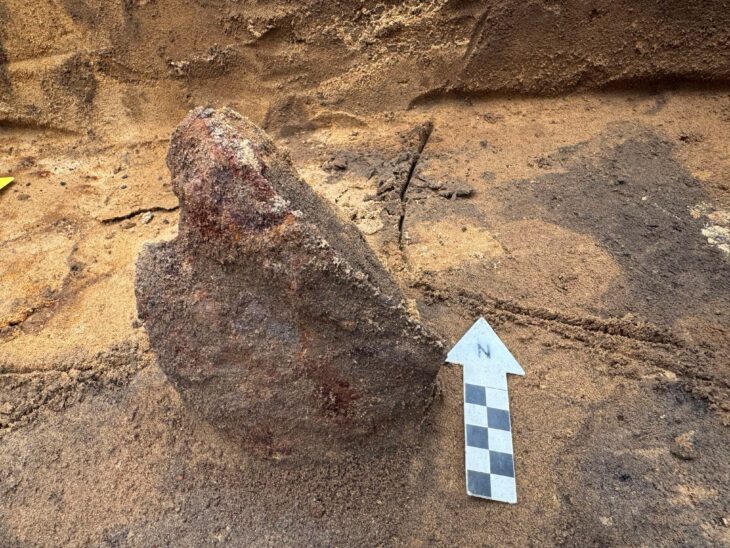
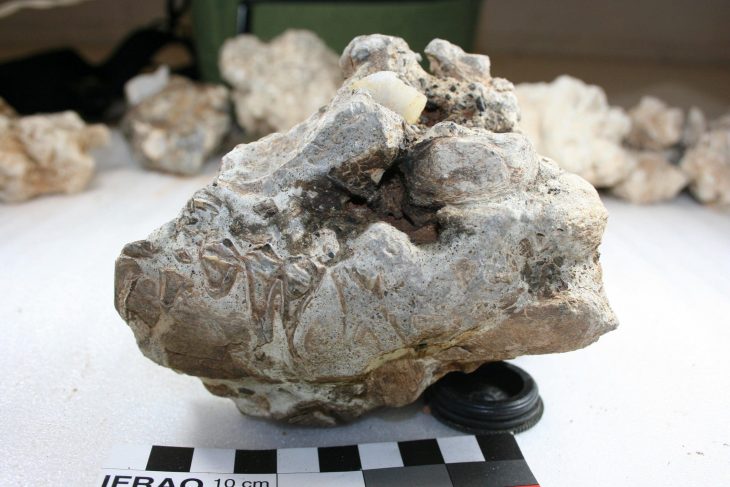
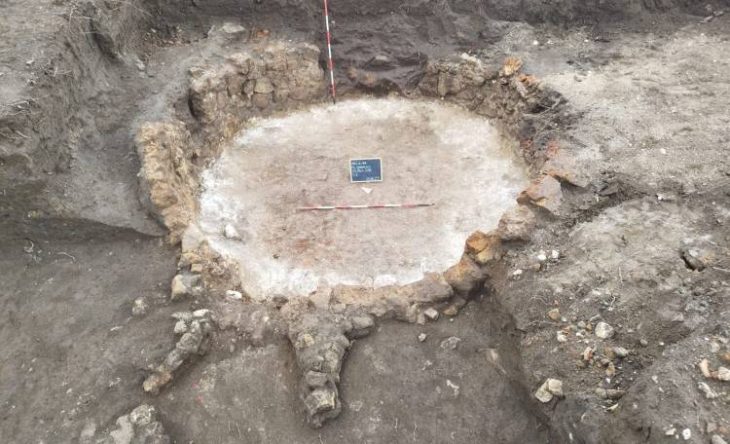
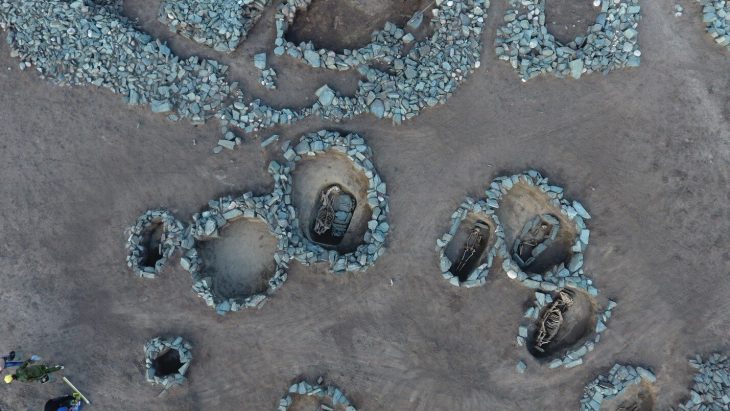
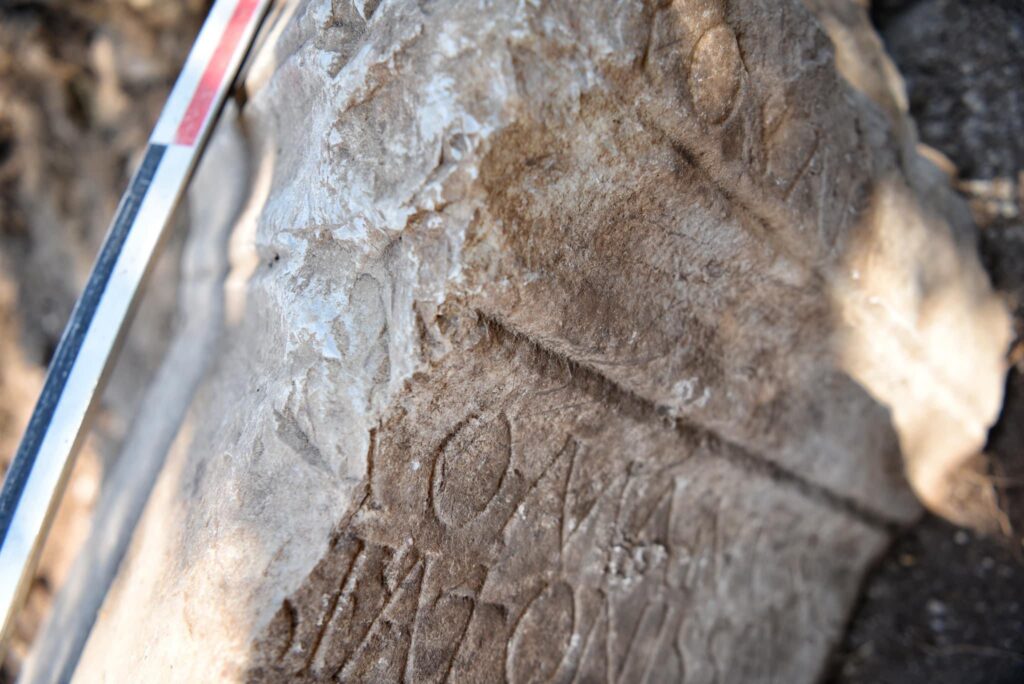
Excavations at Vuçak Castle in the Kosovo countryside have led to a remarkable discovery: a Roman altar dating back to the 3rd century C.E. This significant find, announced by Kosovo’s Prime Minister Albin Kurti, was uncovered within the outer walls of the castle, which is located just southwest of the town of Drenas in the village of Vuçak.
The altar, described as a spolia—architectural fragments repurposed from their original context—was used in the construction of the castle during the Justinian period (527–565 C.E.). Kurti emphasized the importance of this altar, stating that it serves as evidence of continuous life and culture from prehistory through antiquity and into the Middle Ages. “The altar is of particular importance as evidence of continuous life and culture from prehistory and antiquity to the middle ages,” he wrote, highlighting the significance of the discovery in understanding the region’s historical narrative.
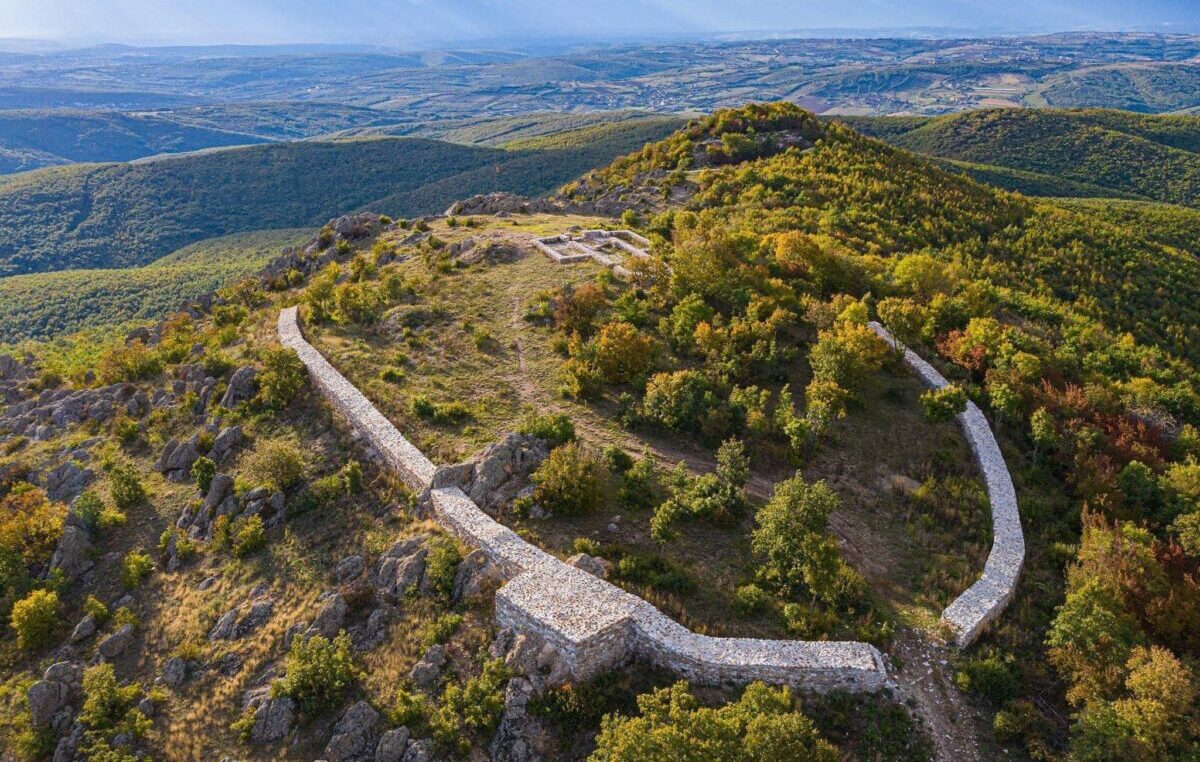
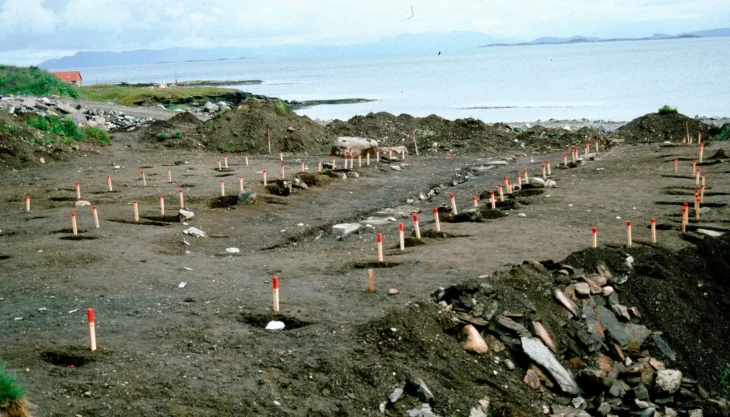
Vuçak Castle itself is situated in a prominent location, perched atop a hill that offers a commanding view of the surrounding valley. The castle features a circular outer wall that once served as a formidable defense for the community within. According to the Archaeological Guide of Kosovo, the site has a rich history, having been used from prehistoric times through the medieval era. The castle was a center of defense for the local population, reflecting the strategic importance of the area throughout various historical periods.
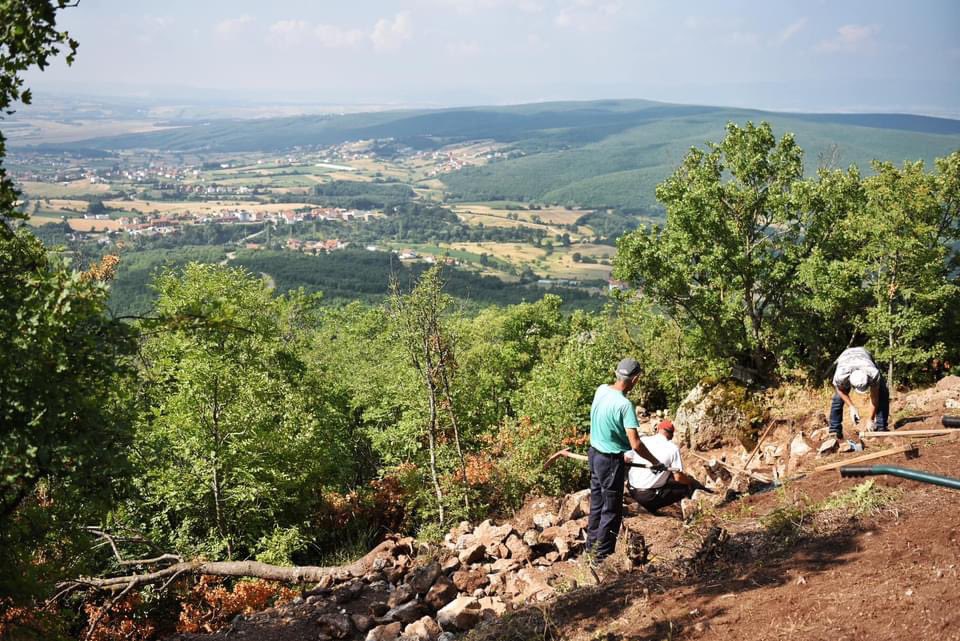

Archaeological findings confirm human activity in the region, with traces of ruins that follow the terrain’s configuration, including two forts known as Gjyteti i Madh (Big Fort) and Gjyteti i Vogël (Small Fort). These structures are indicative of the area’s long-standing significance as a defensive stronghold.
The land of modern-day Kosovo was once part of the ancient state of Dardania, which developed during the 4th century B.C. Edi Shukriu from the University of Pristina notes that the Dardanians fought alongside the Illyrians against Roman invasion after the conquest of Macedonia. However, Dardania eventually fell and became part of the Roman province of Moesia in 44 A.D. The Romans established a network of roads under Emperor Augustus that traversed what is now Kosovo, fostering an economy based on trade, mining, agriculture, and handicrafts.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

In the year 518, a devastating earthquake struck the region, leading to the destruction of many cities. Emperor Justinian later ordered the reconstruction of these towns, coinciding with the period when the Roman altar was repurposed for the castle walls. This historical context adds depth to the significance of the altar’s discovery, as it illustrates the continuity of life and culture in the region despite the challenges faced over the centuries.
As excavations at Vuçak Castle continue, the discovery of the Roman altar not only highlights the historical significance of the site but also sheds light on the rich cultural heritage of the region.

Kosovo, which declared independence from Serbia in 2008, has a complex history that is being further explored through these archaeological efforts. The ongoing work at Vuçak Castle promises to reveal more about the continuous thread of life and culture that has persisted through the ages in this historically rich area, offering insights into the lives of those who once inhabited this strategic stronghold.
Cover Image Credit: Albert Sinani Albin Kurti via X