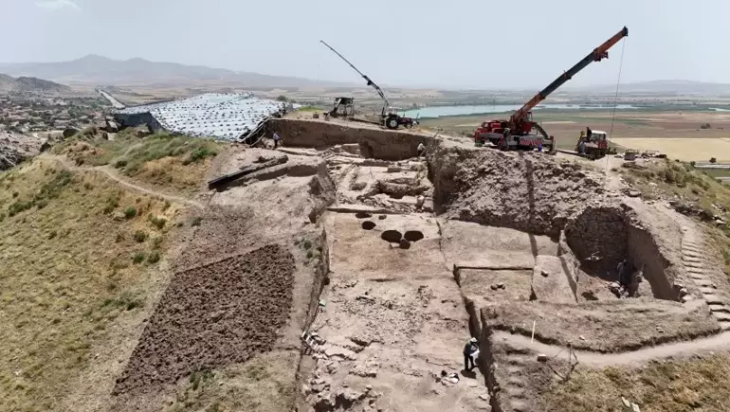
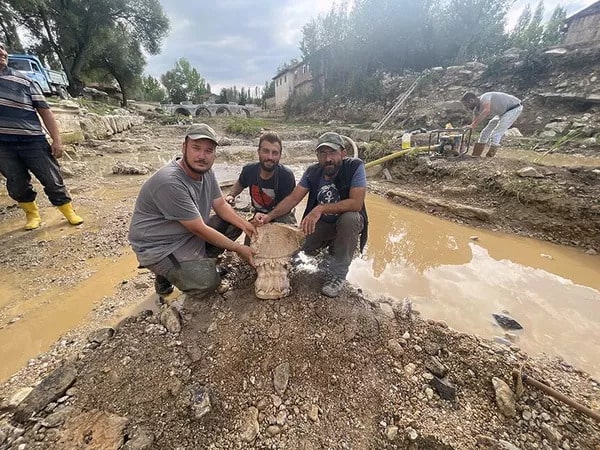
Archaeologists have unearthed a Roman-era marble sundial in the ancient city of Aizanoi in the Çavdarhisar district of Kütahya province in Turkey’s Aegean region.
Aizanoi ancient city is in the Çavdarhisar township, 57 kilometers from Kütahya’s city center. Dubbed as the “Second Ephesus” – another iconic ancient city in Turkey – the site joined the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List in 2012.
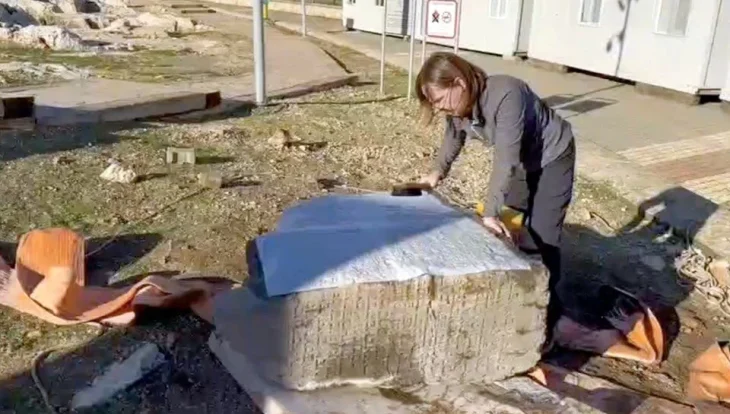
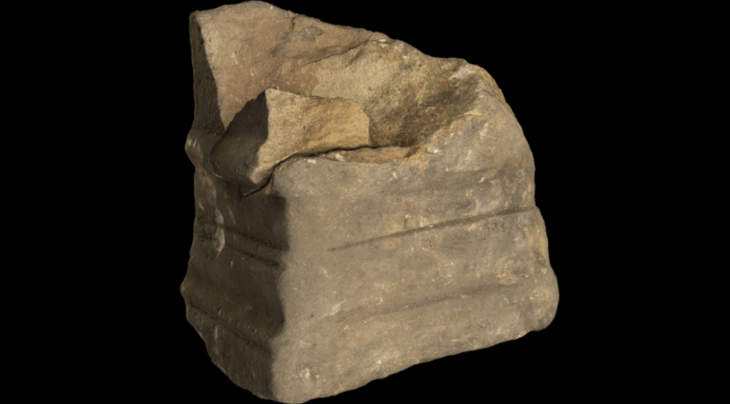
The sundial dates to the early imperial period, about 2,000 years ago, and is the first sundial found at Aizanoi. Made of white marble, the sundial is almost intact with only a few missing fragments. It measures 18 inches high by 17 inches wide and is in excellent condition, with all of its original lines and inscriptions. The dial curves over an acanthus leaf base on top of an animal paw pedestal.
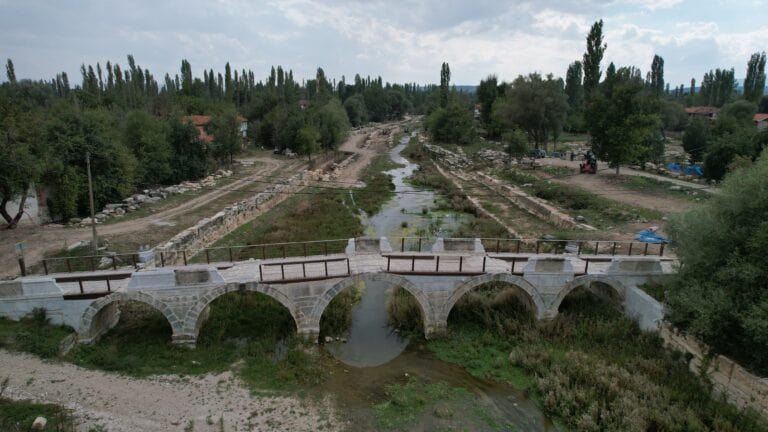
The sundial was discovered during an excavation of Roman bridges and bank walls on the river (the Penkalas in antiquity; now known as the Kocaçay) that ran through the ancient city of Aizanoi.

In antiquity, sundials were installed in public spaces like the city agora or temple precinct so people could tell time, serving as town timekeepers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A day was divided into periods in Roman timekeeping based on the available technology. Initially, the day was divided into two parts: ante meridiem (before noon) and post meridiem (after noon). With the advent of the sundial circa 263 BC, the period of the natural day from sunrise to sunset was divided into twelve hours.
The sundial was imported from Sicily in 263 BC. Sundials were used to calibrate water clocks. Sundials, also known as shadow clocks, had the drawback of only operating in bright sunlight and requiring seasonal and latitude-dependent calibration.
Excavations carried out by Kütahya Dumlupınar University (DPU) continue under the direction of Professor Gökhan Çoşkun.

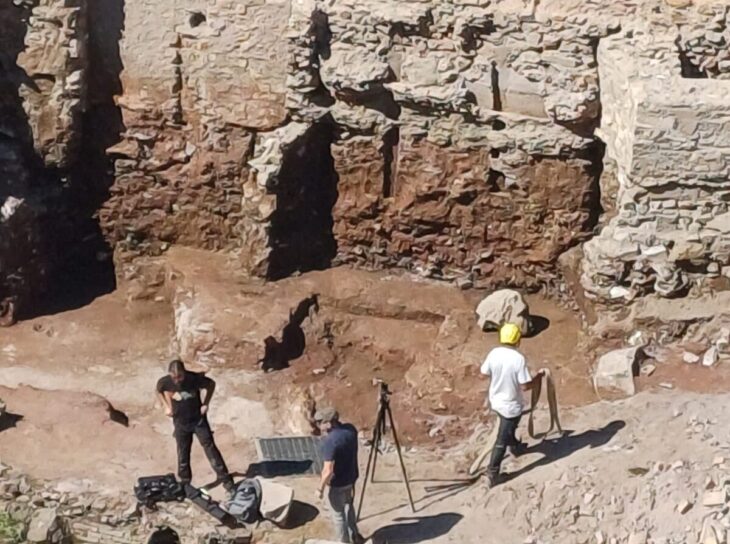
Excavation coordinator Professor Gökhan Coşkun of Dumlupınar University told that the work in Aizanoi, a site that dates back 5,000 years, was carried on without interruption with 100 workers and 27 technical personnel.
Coşkun said the excavations were carried out mainly in the bed of Koca Çay as part of the Penkalas project.
The ultimate goal of the project is to raise the water level of the river enough to run boats between the two bridges. Since 2019, archaeologists have been removing stones, sculptures, and other architectural features that had accumulated on the riverbed and bank over the centuries. So far, over a thousand shaped and carved stones have been recovered, including headless statues, bodiless heads (none of which match), and blocks from bridge balustrades and parapets.