A rare Arabic inscription, possibly dating back to medieval times, was discovered at the site of a social housing project in Fgura, a town in Malta’s South Eastern Region.
The discovery is ‘very significant and rare’ according to the Superintendence for Cultural Heritage, being the second Arabic inscription found outside Rabat.
The Arabic inscription was discovered in a naturally carved well in fields adjacent to Triq id-Dejma, Triq il-Karmnu, and Triq tax-Xemx u l-Qamar, all of which have recently received Planning Authority approval for a social housing project.
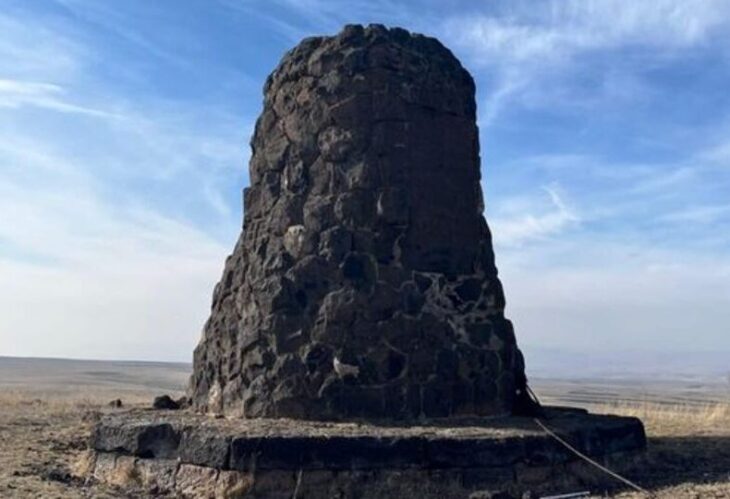
SCH said that the script was discovered carved on a limestone prismatic stele and is probably Kufic, a calligraphic that is closely linked to early Quran transcription and architectural decorations. The slabs also include other markings that may represent symbols rather than writing.
An official of the Superintendence for Cultural Heritage described the historical artifact as “a limestone prismatic stele, truncated at each end, bearing Arabic script.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The artifact is typologically similar to a number of stelae found by Sir Temi Zammit in the 20th century, who found an Arab cemetery that had been constructed on top of the Domus Romana in Mdina.

“Apart from another example found at Savina Square in Victoria in 1901, this is the only other example known to have been found outside of Rabat, making this discovery very significant and rare, both archaeologically as well as historically,” the spokesperson said.
The discovery was made inside a natural fissure on the site that was at some point repurposed as a well with an overall depth of roughly 8.5 meters.
The SCH thinks that the artifact was probably dumped there at some point in history and is therefore unlikely to be the main context for the inscription. However, no modern material was found within the fissure, so it is still able to provide a “secure archaeological context”, they said.
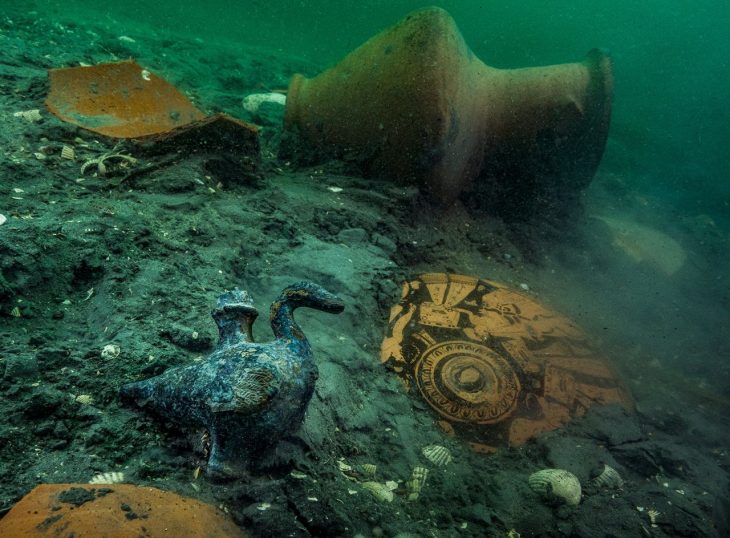
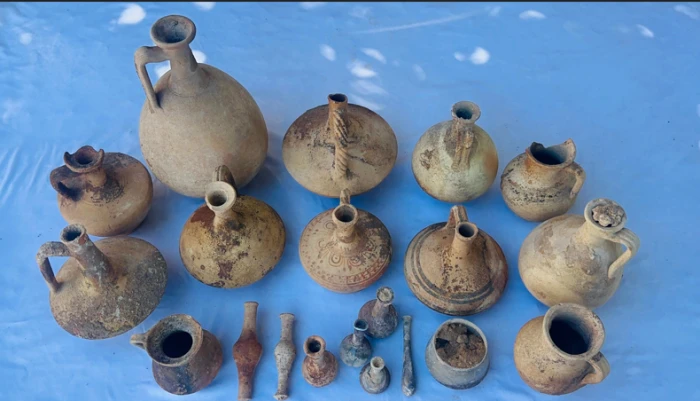
The stone slab was discovered alongside pottery that predates the 13th century. Numerous silo pits and agricultural trenches were also found at the site as a result of the archaeological assessment.
An Arabic language specialist from the University of Malta is working with the Superintendence to help decipher the inscription, which is thought to be crucial for establishing the object’s original use and providing precise dating.
The discovery is being hailed as a major find that sheds light on a previously unknown period in Maltese history when a sizable portion of the population was Muslim.