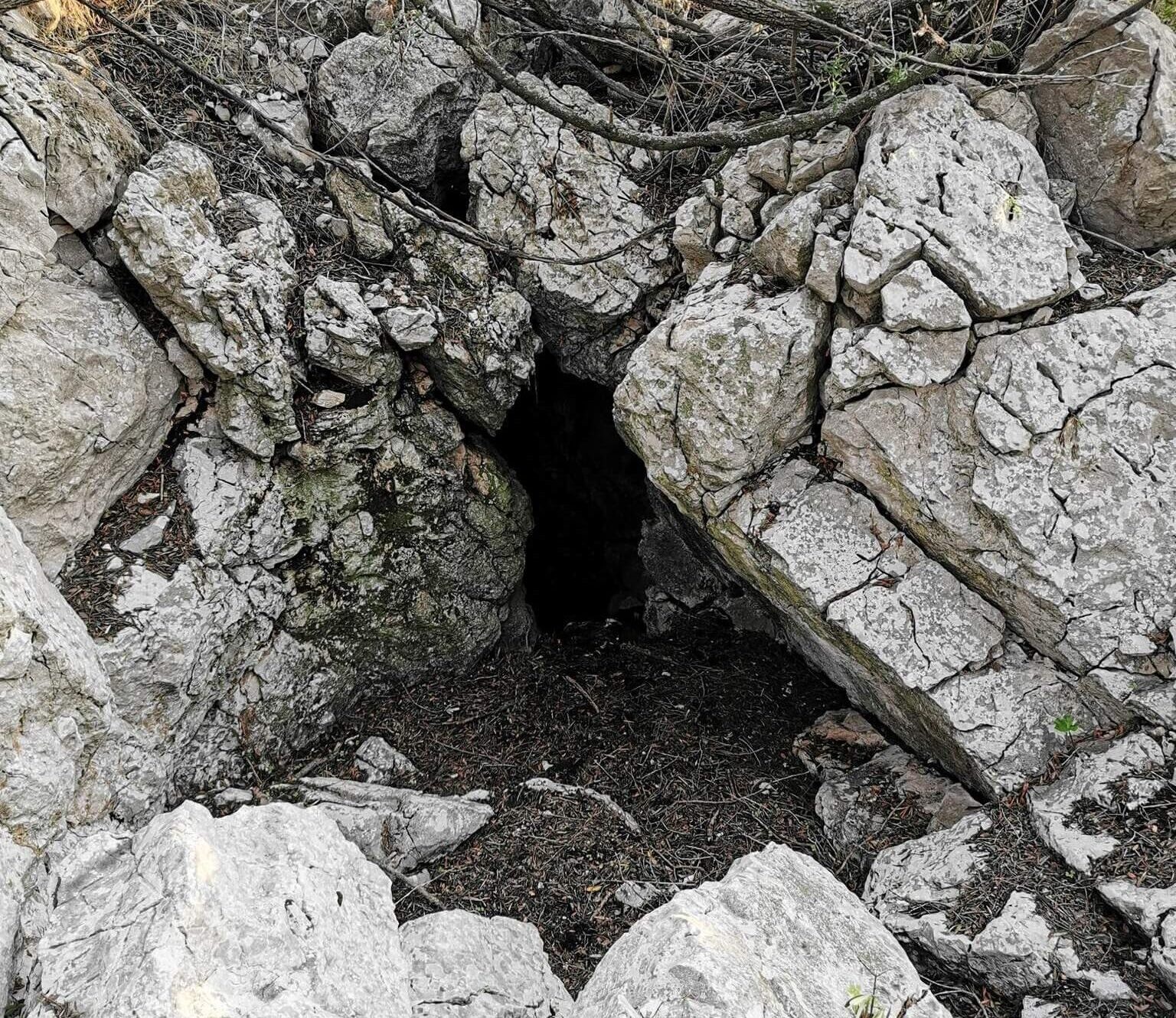
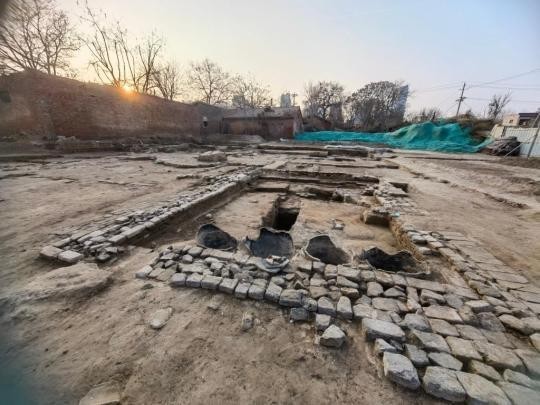
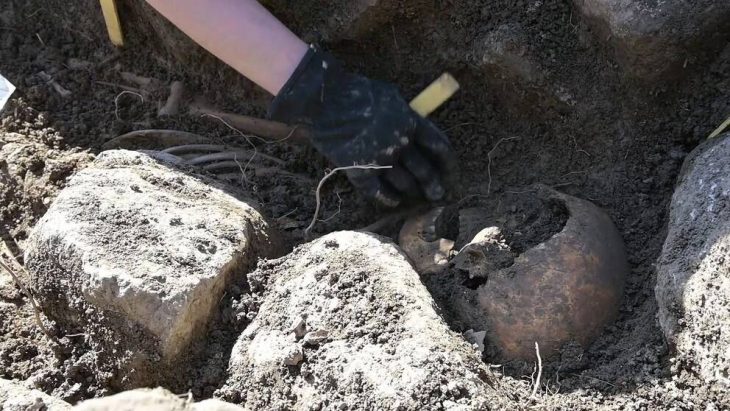
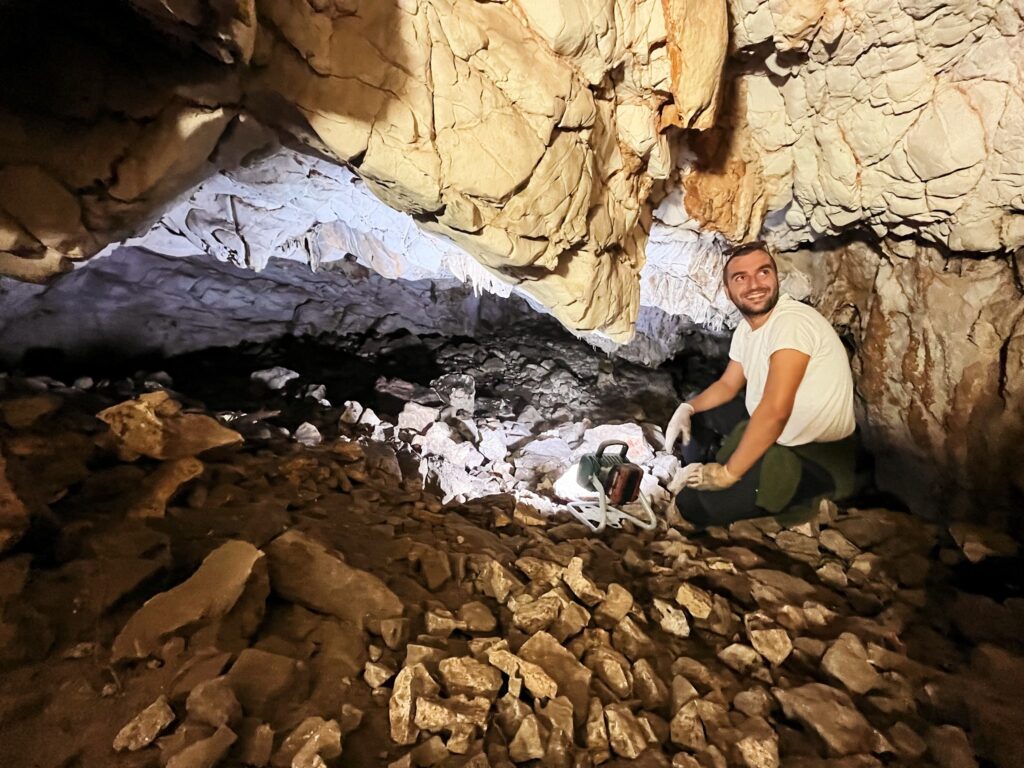
Recent archaeological excavations on Šćedro Island, located south of Hvar, have unveiled significant findings that challenge previous understandings of the island’s prehistoric past. The Ratina Cave, a site of interest since the early 20th century, has revealed evidence of human activity dating back to the late Neolithic period, approximately 3000 years earlier than previously believed.
In 1923, renowned archaeologist Grga Novak first identified traces of human presence in Ratina Cave, discovering ceramic fragments from the Iron Age. However, a recent excavation led by the company Kantharos doo, in collaboration with the Friends of the Island of Šćedra Association and the Municipality of Jelsa, has dramatically altered the narrative surrounding the island’s history.
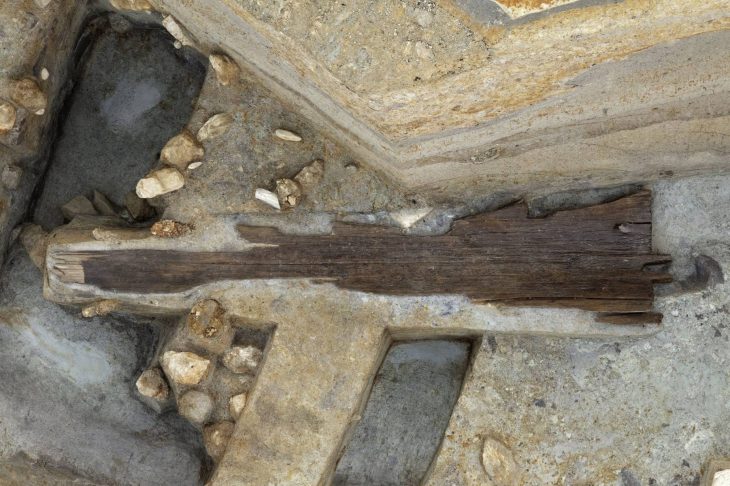
During a focused excavation of just 1.5 x 1.5 meters, researchers uncovered an impressive array of artifacts, including 250 ceramic fragments, 97 animal bone fragments, 109 shells and sea snails, and four flint tools. Charcoal samples have been collected for radiocarbon dating, which will help confirm the age of these significant finds.
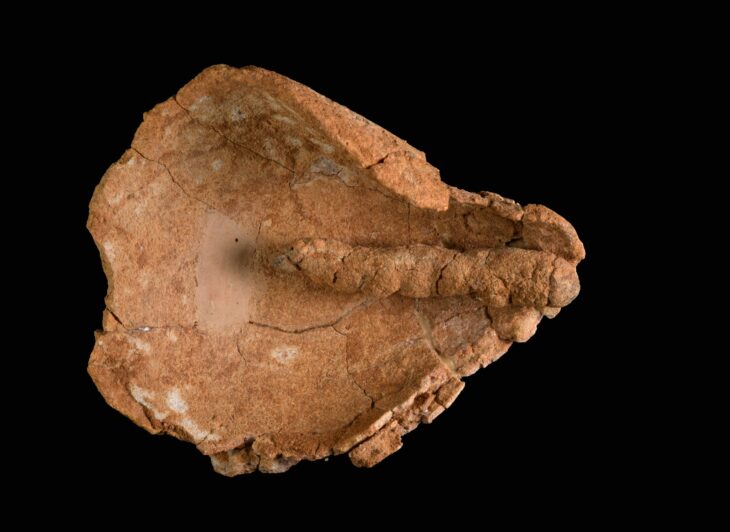
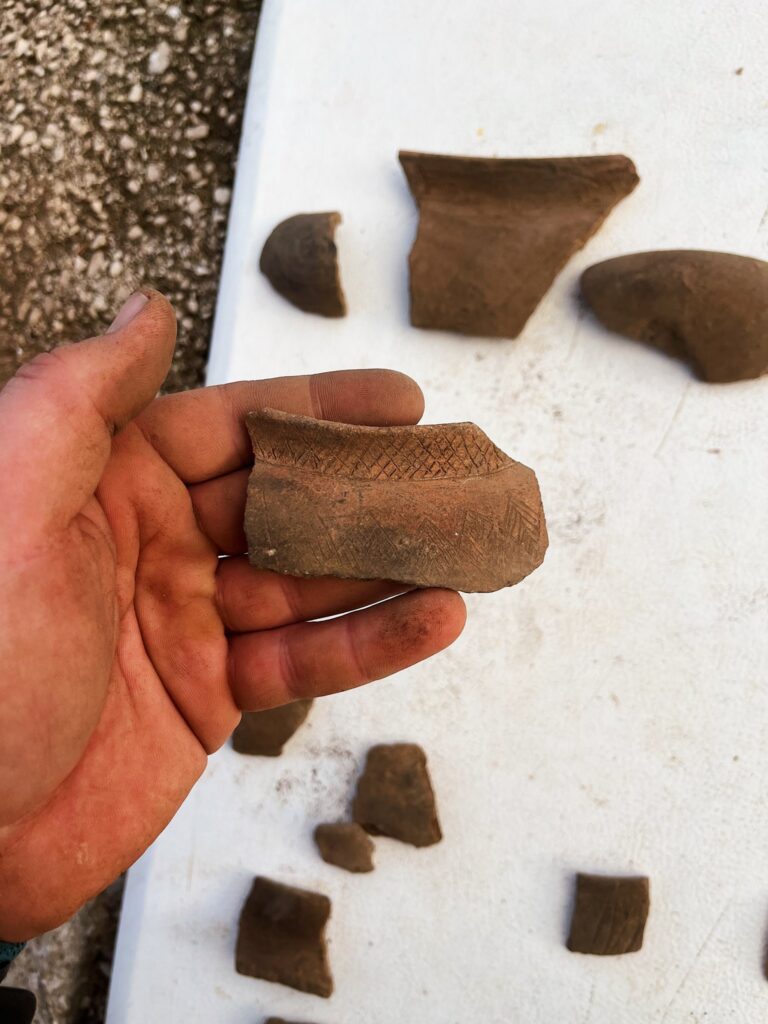
Among the most remarkable discoveries are the ceramic fragments, with 67 pieces exhibiting distinctive features indicative of hemispherical bowls with ring-shaped rims and partially smoothed walls. These vessels, adorned with incised geometric designs, are linked to the Hvar culture, specifically dated to the 5th millennium BC (between 5000 and 4300 BC).

The Hvar culture refers to a prehistoric cultural group that thrived on the island of Hvar and surrounding areas in the eastern Adriatic during the Neolithic period, particularly between 5000 and 4300 BC. This culture is characterized by its distinctive pottery, which often features geometric decorations and specific vessel shapes, such as hemispherical bowls with ring-shaped rims.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeological findings associated with the Hvar culture include not only ceramics but also tools made from stone and flint, as well as evidence of early agricultural practices. The Hvar culture is significant for its role in the development of trade networks in the region, as it indicates interactions between various communities across the Adriatic Sea. The Hvar culture is considered an essential part of the broader prehistoric narrative of the Adriatic region.
The shapes and decorations of these ceramics closely resemble those found in the Grapceva caves on Hvar, a key Neolithic site in the eastern Adriatic. This connection suggests that Ratina Cave was inhabited concurrently with some of the most important prehistoric settlements in the region, raising questions about its role in the broader network of trade and habitation.

Another intriguing aspect of the research is the origin of the materials used for the lithic artifacts. Preliminary analyses indicate that the stone and flint tools were likely sourced from other Adriatic islands and mainland areas, hinting at established trade and maritime networks that connected Hvar, Korčula, Pelješac, and the wider eastern Adriatic region during the Neolithic era.
Šćedro’s strategic location along vital maritime routes positions it as a significant hub for communication and trade among prehistoric communities. Although the current excavation has only explored a small section of the cave, the volume and importance of the findings suggest that the site was either continuously inhabited or utilized as a seasonal shelter and workspace.
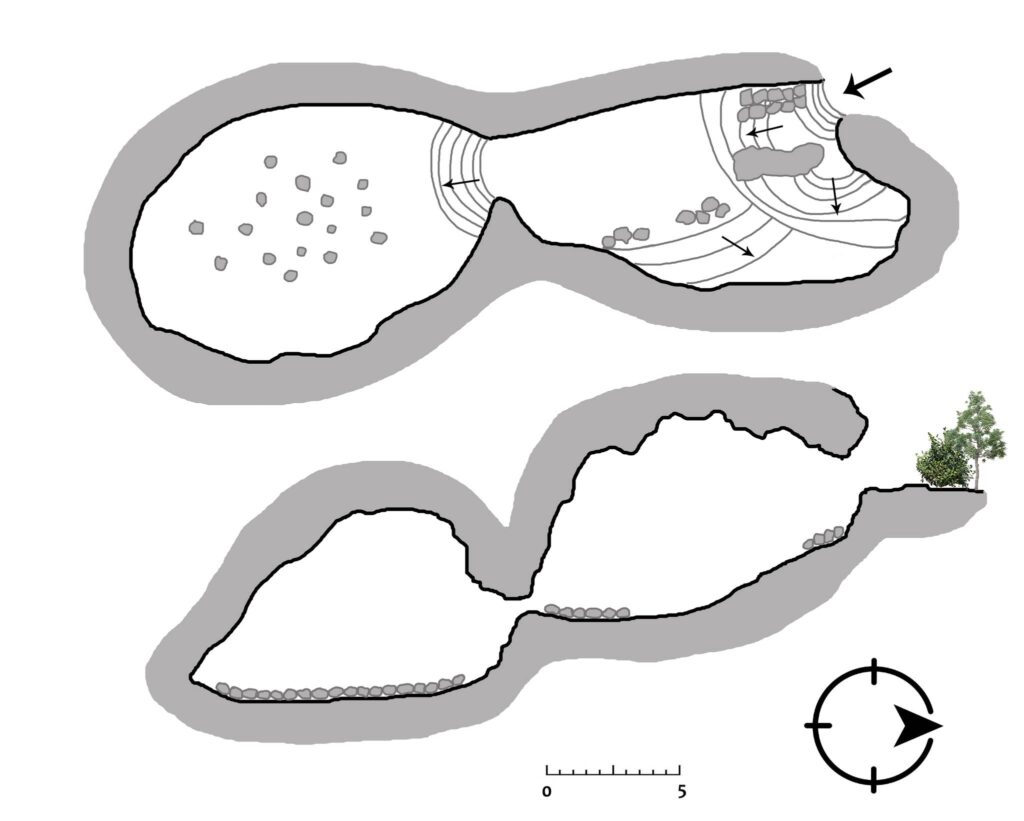
Future research will focus on expanding excavations to the surrounding plateau, which, along with the cave’s proximity to the sea and fertile soils, presents an ideal environment for prehistoric life. Additional studies may also uncover evidence of a later phase of the Hvar-Nakovan culture, which remains insufficiently explored.
This archaeological work not only enhances our understanding of Hvar culture but also offers valuable insights into the lives of prehistoric communities along the eastern Adriatic coast.
Prijatelji otoka Scedro / Friends of the Scedro island
Cover Image Credit: Friends of the Scedro island
















