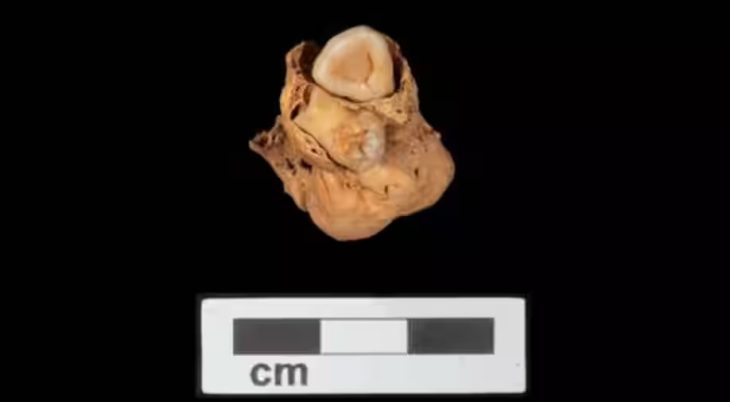
An elite class of ancient Anglo-Saxon women were buried with hundreds of ivory rings, and the origin of these ivory rings has long remained a mystery. Ivory rings found in England have origins from African elephants according to a new study.
In a new study, published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, researchers were able to use biomolecular analysis to trace the origin of hundreds of ivory bag rings found at dozens of ancient burial sites of Anglo-Saxon women.
Long thought to be the ivory from mammoth or walrus specimens, the new research shows that the ivory, in fact, came from Africa around the fifth or sixth century CE. This means that the ivory was actually sourced nearly 4,000 miles (6,400 km) away from the cemeteries in which the Anglo-Saxon ivory rings were found.
Given what is known about travel and trade in the first millennium AD, this is an extraordinary distance for ivory to have been transported. Despite the incredible distance, this remarkable discovery suggests that a trading network connecting Eastern Africa and Western Europe must have existed at the time.
“Through a multi-methodological approach, we have established that the ivory used for the Scremby bag rings came from elephants living in an area of young volcanic rocks in Africa at some point during the 5th and 6th centuries AD,” the researchers write. “This preliminary evidence allows us to consider the networks and socio-economic factors that facilitated the distribution of ivory from Africa to the British Isles at this time.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
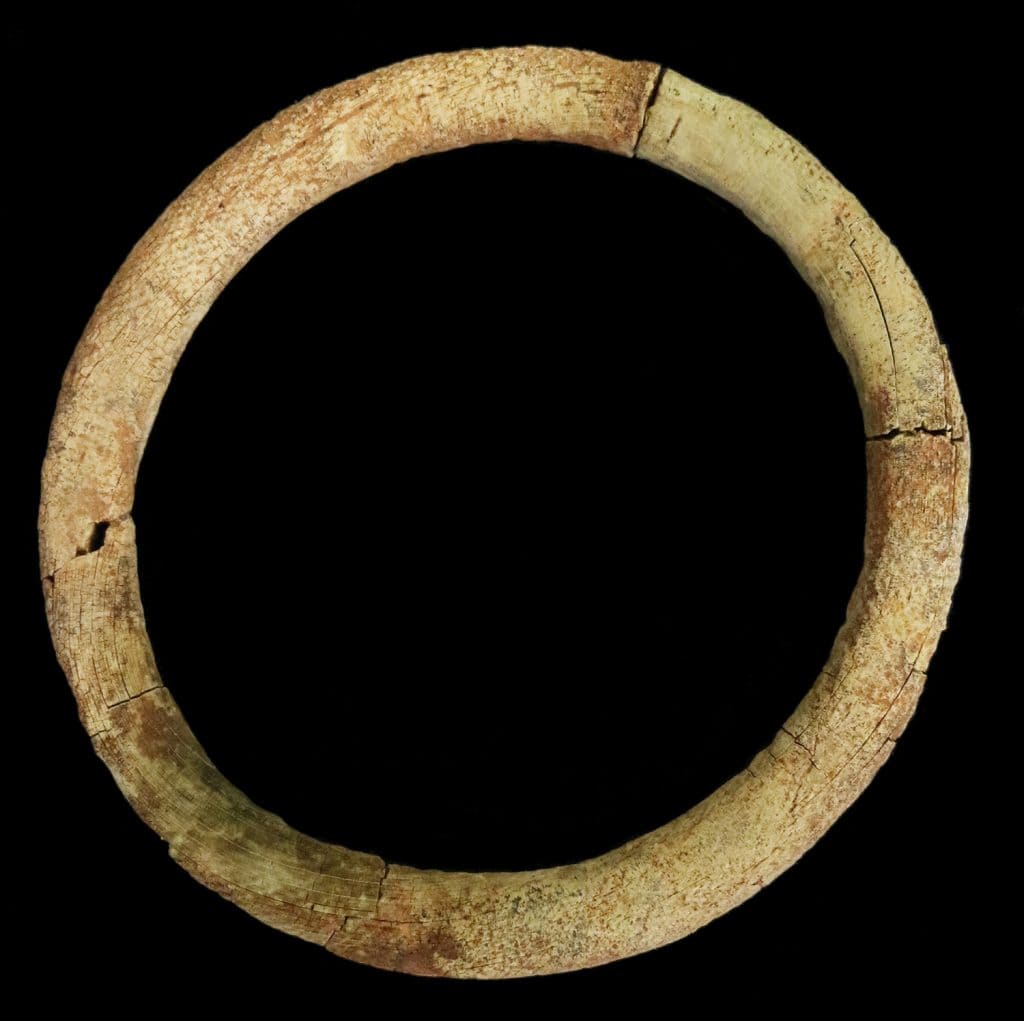

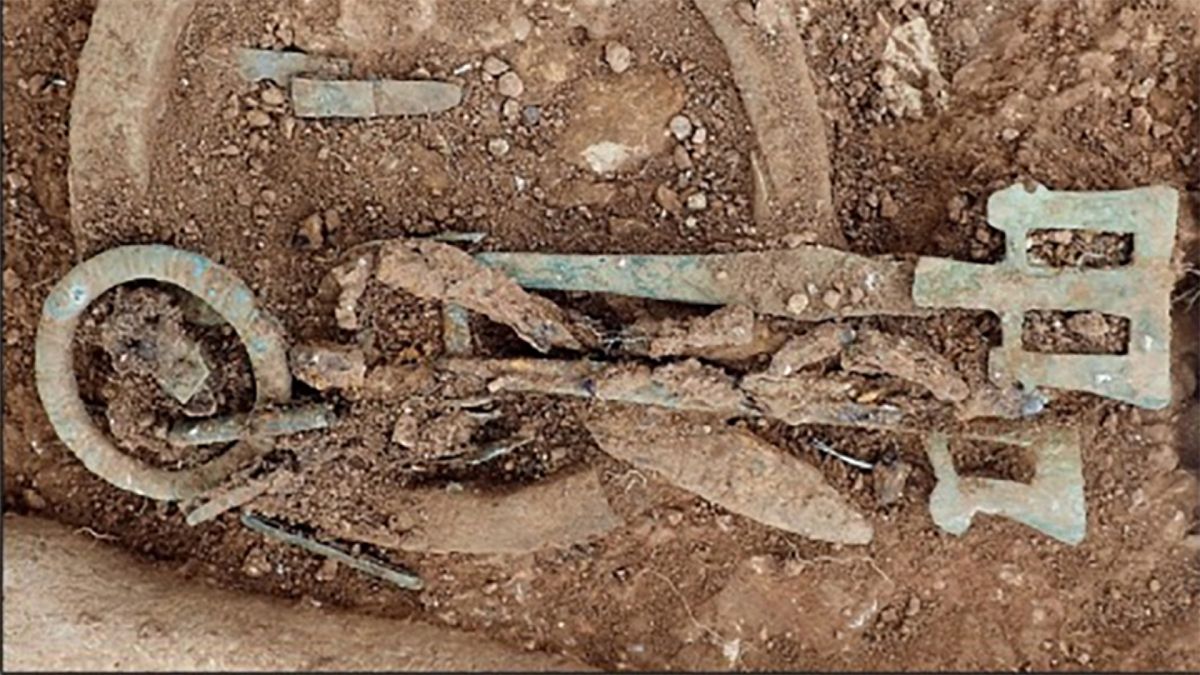
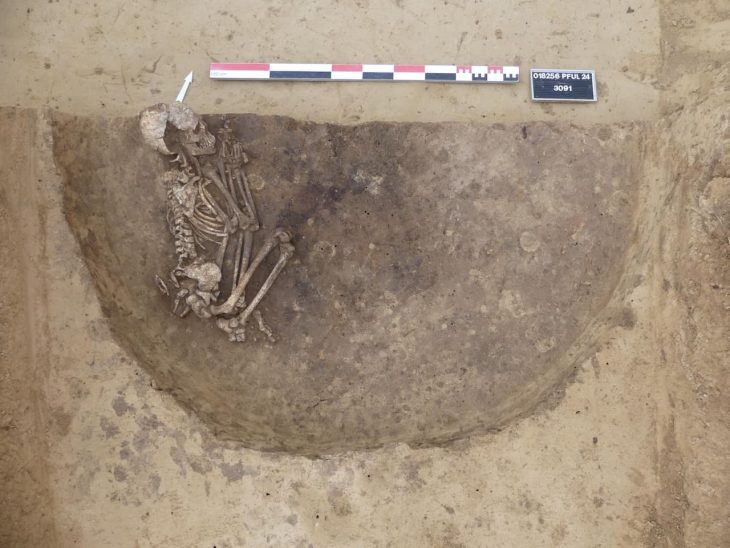
The ivory rings were found in the graves of women as part of the assortment of grave goods left in the grave with their bodies.
The rings themselves are somewhat enigmatic, as they resemble rings worn on fingers in shape but are much too large to have fulfilled that purpose. This indicates they were not jewelry and must have been used for something else. The rings are believed to have been part of bags that were hung from the women’s hips.
“Since most rings have been recovered near the hip, it is thought that the bags were suspended from the waist alongside other objects such as iron knives, pairs of copper alloy girdle hangers, and iron ‘latch lifters’,” the authors write.
A single bag ring that was taken from an early Anglo-Saxon burial and discovered in an old cemetery close to the village of Scremby in Lincolnshire was subjected to a thorough analysis by a team of UK researchers. This cemetery was in use from the late fifth through the early sixth centuries, and the ring was one of seven removed from excavated Anglo-Saxon graves.
North Africa and a large part of Great Britain were both part of the Roman Empire for centuries, so it would make sense that there would be some residual trade ties even after the fall of Rome. Why the trade appeared to end in the 700s isn’t known.