Chinese archaeologists revealed fresh important finds at the Sanxingdui Ruins site in southwest China’s Sichuan Province on Thursday, from pits No. 3, No. 4, No. 7, and No. 8.
In recent months, more than 500 artifacts have been unearthed in the renowned Sanxingdui Ruins site in southwest China’s Sichuan Province.
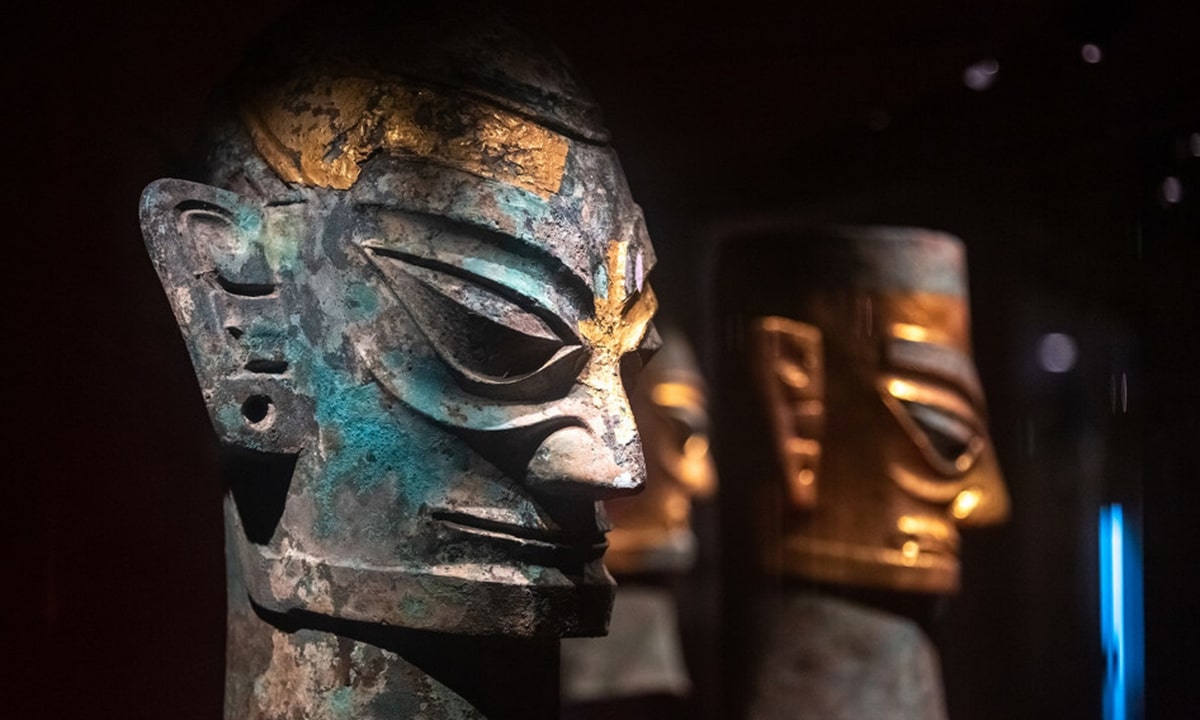
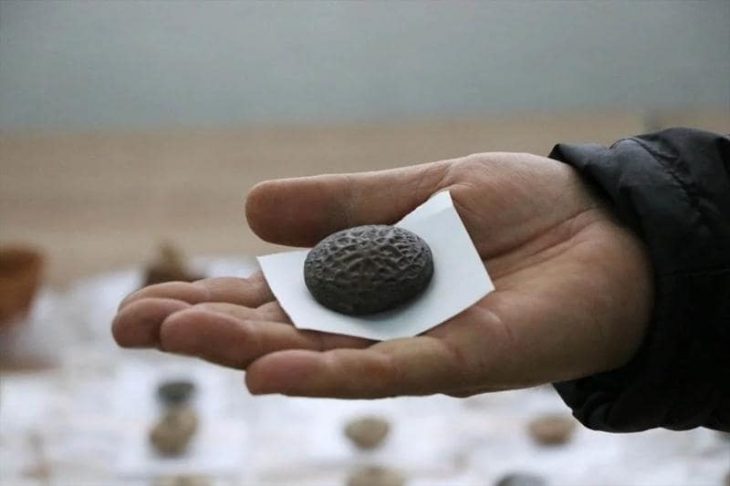
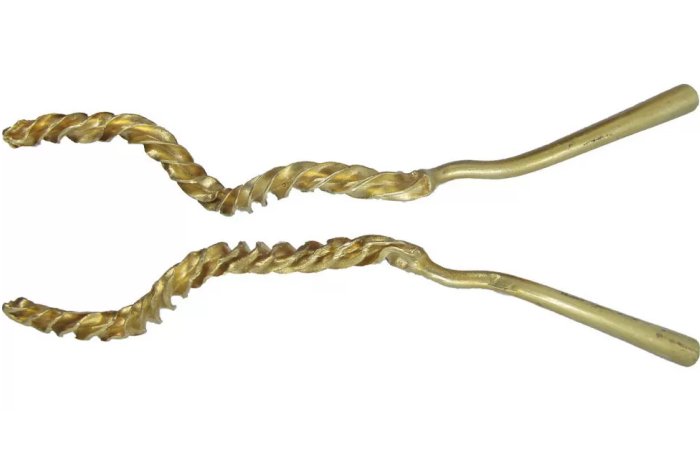
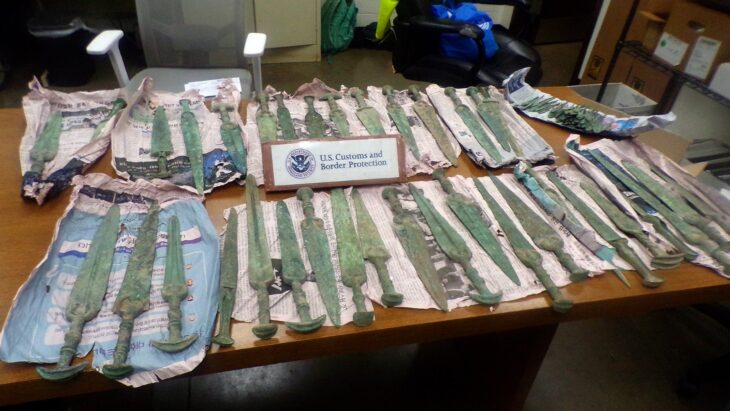
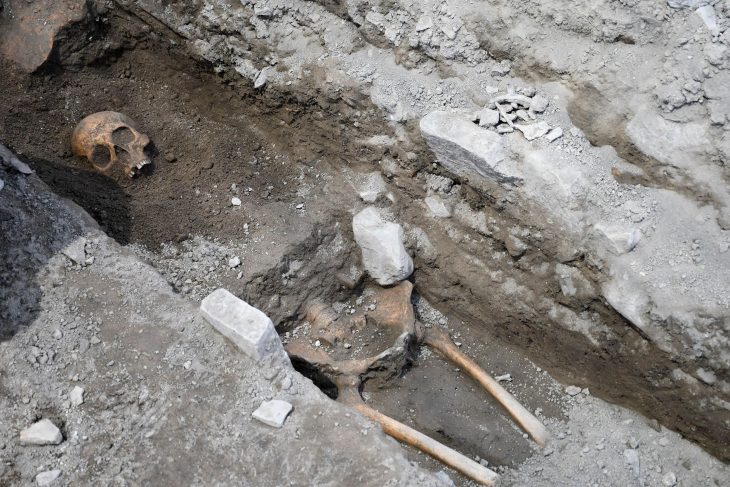
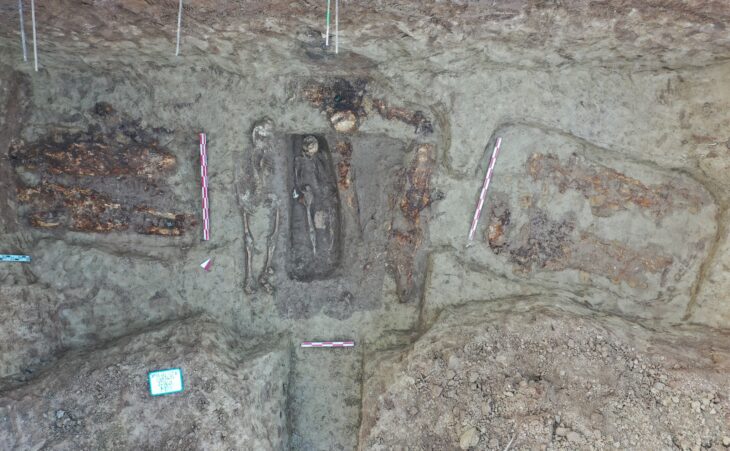
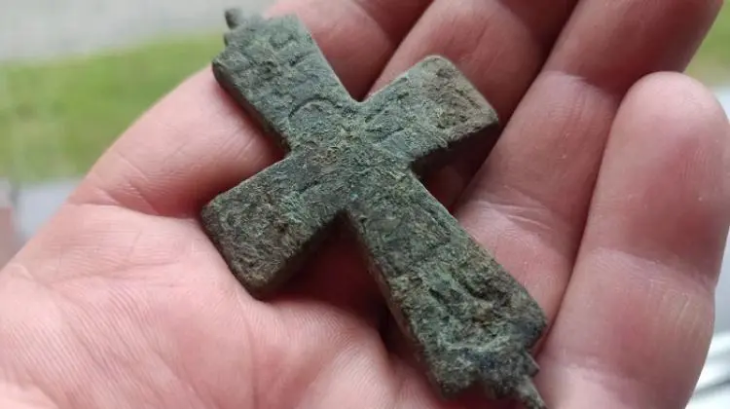
The treasures unearthed at the ruins’ six new sacrifice pits include golden masks, jade and ivory items, and bronze goods that were finely constructed and uniquely formed, according to the Sichuan Provincial Cultural Heritage Administration on Thursday.
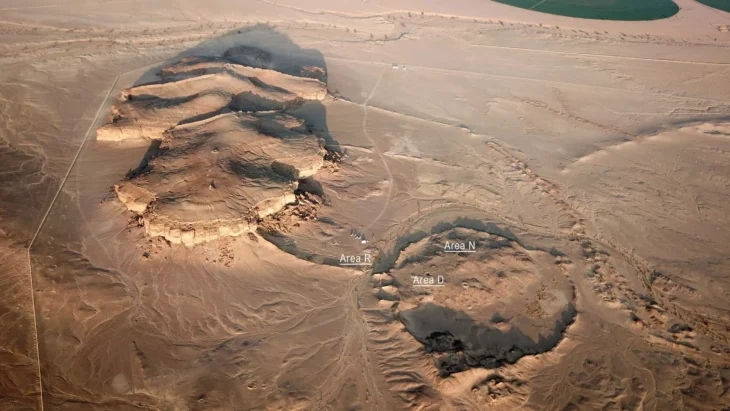
Since the site reported the discovery of six additional pits in March, the much-anticipated archaeological excavation of the Sanxingdui Ruins site has been continuing, with almost 10,000 cultural relics dating back around 3,000 years unearthed so far.

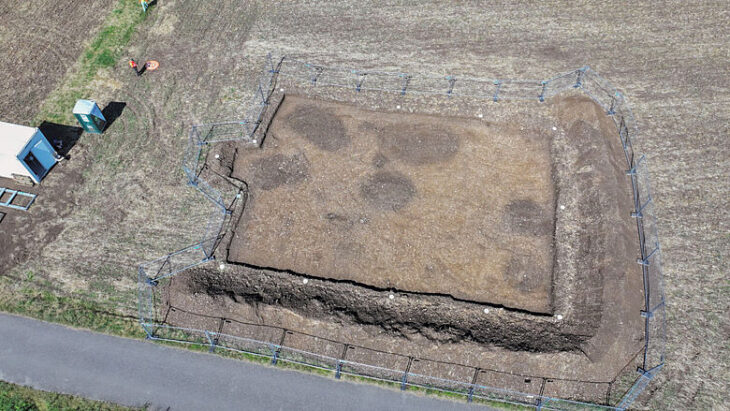
The No. 8 sacrifice pit at the archaeological site’s southwestern corner is the biggest, measuring 5.1 meters in length and 3.8 meters in breadth. It has a surface area of almost 20 square meters, which is five times that of pit No. 5.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
After the archaeological team cleared the topsoil and ash, a significant number of ivory objects were found in the vessel layer covering almost the entire pit, and large bronze vessels were discovered in some corners.
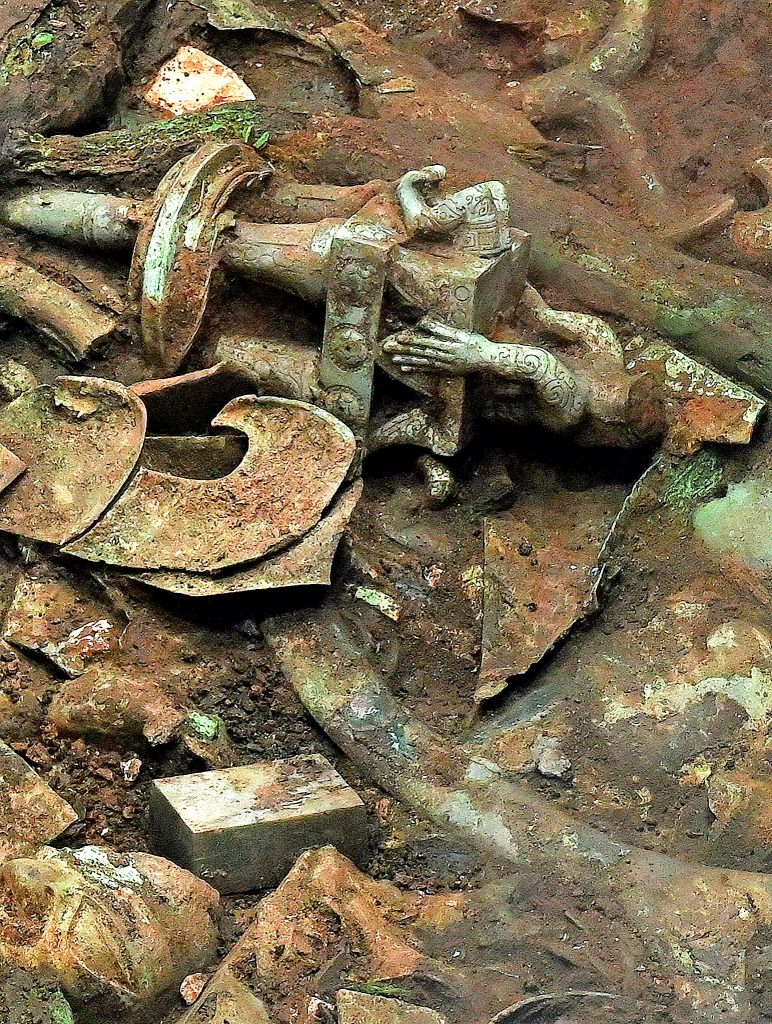

According to the archaeologists at the site, it could be distinguished from the exposed parts that these bronze items are unique in shape and have never been seen before.
“The new discoveries demonstrate once again that imagination and creativity of the ancient Chinese far surpassed what people today had expected,” said Tang Fei, chief of the Sichuan Provincial Cultural Relics and Archaeology Research Institute.
Tang added that the excavation of the new pits has entered a critical stage, with more items yet to be unearthed and expected to defy the conventional wisdom of archaeologists.

The Sanxingdui Ruins, found in the late 1920s, have been considered one of the world’s greatest archaeological discoveries of the twentieth century. The ruins, which occupy an area of 12 square kilometers and are located in the city of Guanghan, some 60 kilometers from the provincial capital Chengdu, are thought to be the relics of the Shu Kingdom, dating back 4,500 to 3,000 years.
Sichuan Provincial Cultural Relics and Archaeology Research Institute