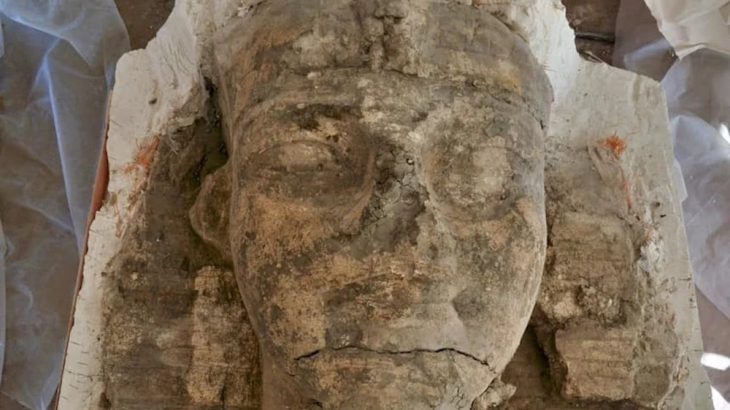
An international team of scientists found that Children and adults buried next to each other in one of the oldest cities in the world, Catalhoyuk, are not related.
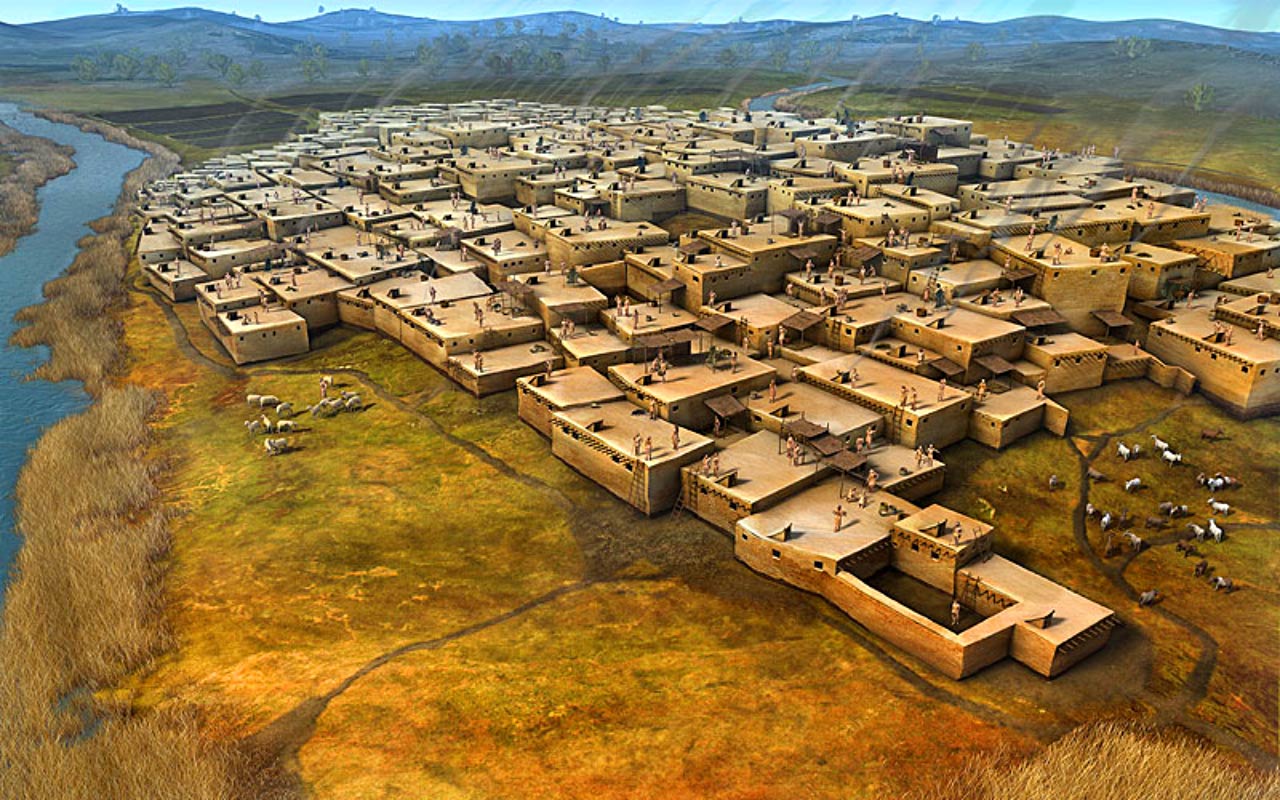
Between 7100 and 5950 BC, the archaeological site of Çatalhöyük in central Turkey was continuously inhabited for nearly 1,200 years. It is estimated that at its peak of growth, the heavily built-up city with an area of several hundred hectares was home to approximately 6,000 people.
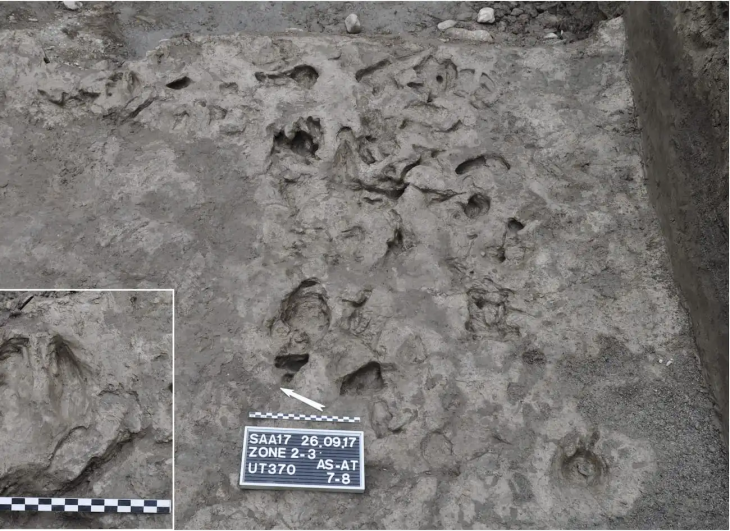
The dead were buried under the floors of their homes, prompting historians to ask whether they were linked.
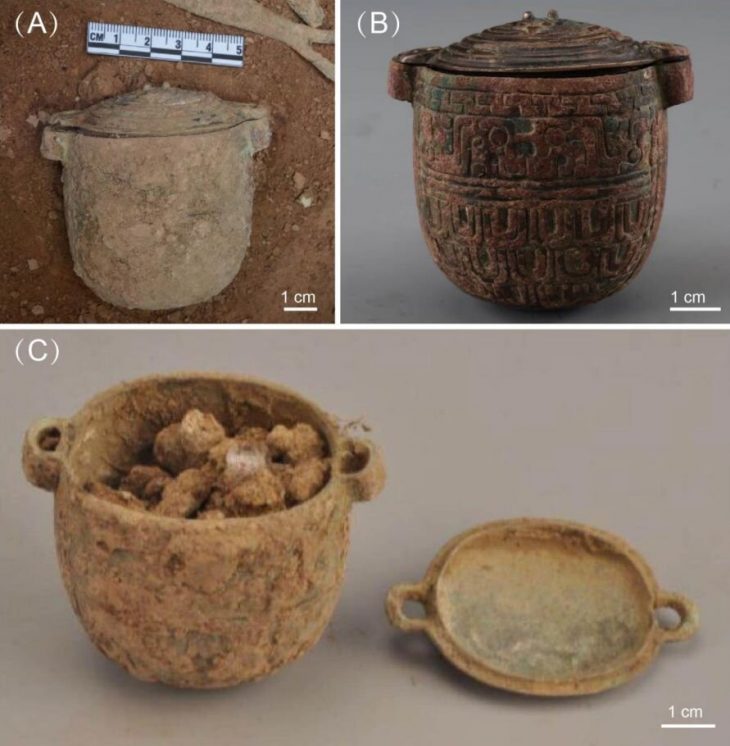
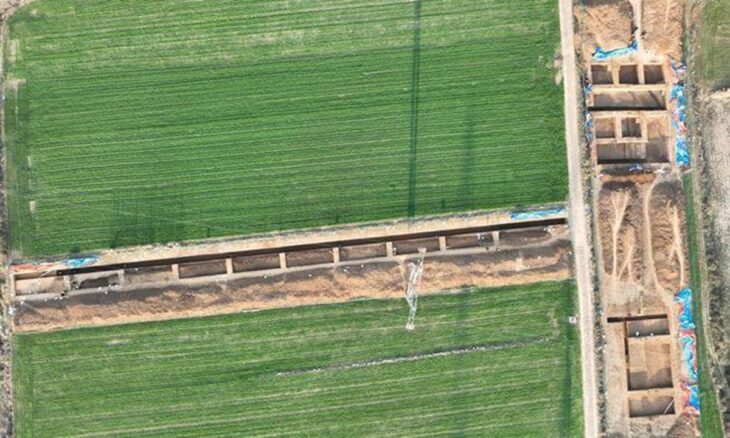
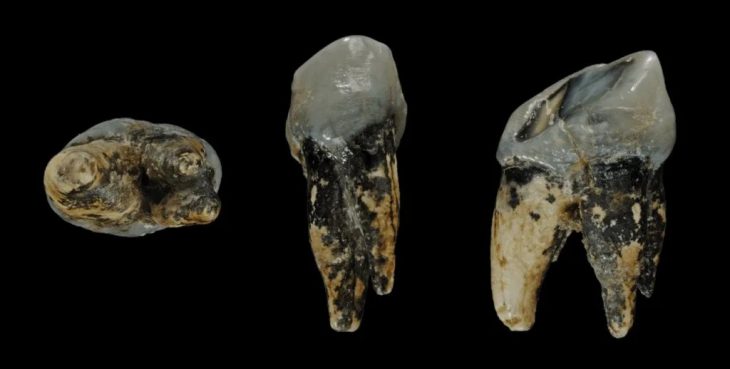
The international team of scholars, which included scientists from the Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznań, analyzed 22 genomes collected from the deceased buried in Anatolia’s prehistoric cities of Aşıklı Höyük and Catalhöyük.
According to the researchers, houses acted as burial places for members of relatives’ communities in some prehistoric settlements, while adults and children buried under one house in other sites, such as Çatalhöyük, were not related to each other. The study’s findings were published in Current Biology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to archaeologists, the people who lived in the Middle East during the Neolithic period were the first settled farming groups who not only constructed permanent homes but also buried their dead beneath them.
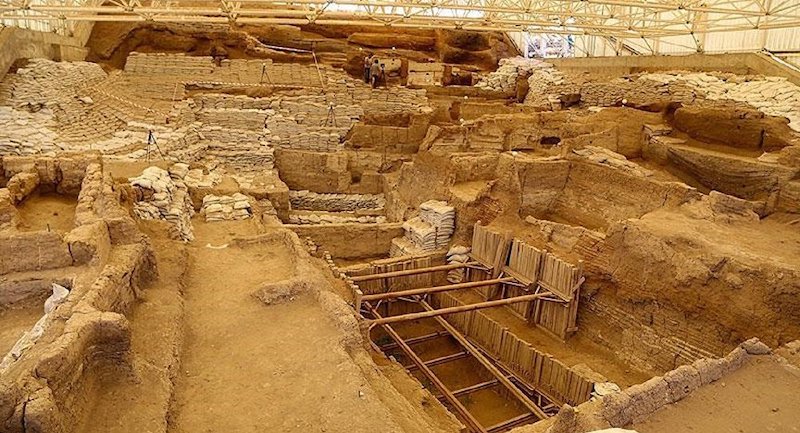

The researchers said: “This custom has been known for a long time, but the way it was related to the social organization of the residents of these settlements was a matter of guesswork. Some researchers assumed that the buried persons were members of biological families, while others considered more complex structures, not based on genetics.”
To solve the issue, the researchers examined scores of burials from various Neolithic settlements. Dr. Maciej Chyleski of the Institute of Human Biology and Evolution at the Faculty of Biology at Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznan was one of the leading researchers. In 2019, he demonstrated the absence of maternal ancestry among people buried beneath the floors of houses in çatalhöyük using mitochondrial genomes.
The researchers said: “In the continuation of the project, it was important to extend the research to other sites from the region, but most of all to use nuclear DNA, which enables research in much higher resolution, even despite the poor preservation of genetic material in the tested samples. We analyzed more than 60 samples from two sites, Aşıklı Höyük and Çatalhöyük, but genetic material of adequate quality could be obtained only for 22 samples, most likely due to unfavorable environmental conditions.”

The researchers applied these results to genomes collected from the deceased at three other Anatolian sites: Boncuklu Höyük, Barcın, and Tepeciftlik, and then used them to approximate the degree of kinship between people buried inside or near individual houses.
According to the researchers, the later settlements Çatalhöyük and Barcın yielded more intriguing findings (approx. 8,500 years old). Human populations greatly expanded and stabilized during that period. Researchers were able to collect DNA mostly from the burials of children and babies in these two villages.
The researchers said: “It turned out that in buildings with several such burials, biological relationships between the buried children were relatively rare.”
The findings back up Dr. Chyleski’s earlier findings that there is no proof that these individuals belonged to biological families based on mitochondrial genomes. According to the researchers, the social system in Çatalhöyük, as well as probably other settlements from the time span, was not dependent on genetic relatedness.
The publication’s co-author Professor Arkadiusz Marciniak said: “We are still far from fully understanding the early Neolithic communities, but their organization was certainly significantly different from the structure based on biological kinship or patriarchal kinship relations. The basis of social organization was probably a complex system of socially regulated dependencies and connections linking individuals and groups of people living in individual households.”
Source: PAP