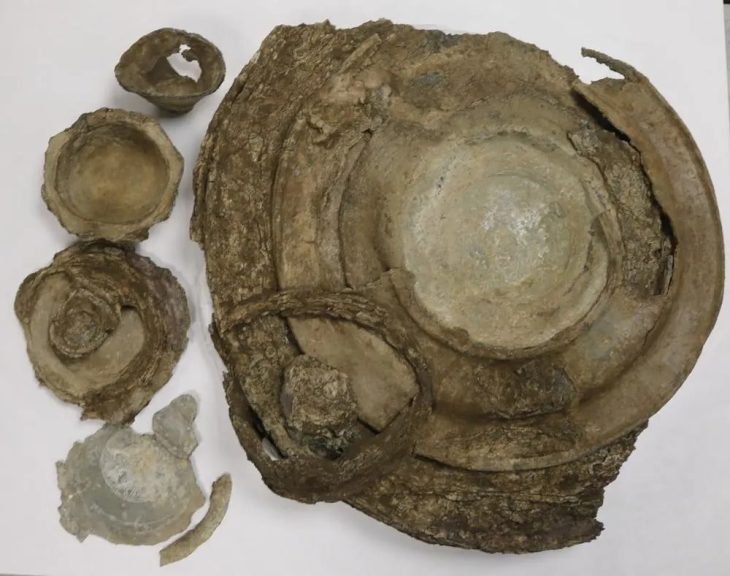
A previously undiscovered wreck has been found outside of Fjällbacka on the Swedish west coast. Analysis of wood samples shows that it is the oldest shipwreck ever found in the province of Bohuslän. This is also one of the oldest cogs that have yet to be found in Europe.
“The wreck is made from oaks cut between 1233 and 1240, so nearly 800 years ago,” says Staffan von Arbin, a maritime archaeologist at the University of Gothenburg.
This wreck from the Middle Ages was found by the island of Dyngö outside of Fjällbacka in the Swedish municipality of Tanum. This last autumn, the University of Gothenburg conducted archaeological diving inspections along the coast of Bohuslän to find out more about known wrecks on the seafloor.
“We collected wood samples to determine the age by dating the tree rings – known as dendrochronology,” says Staffan von Arbin.
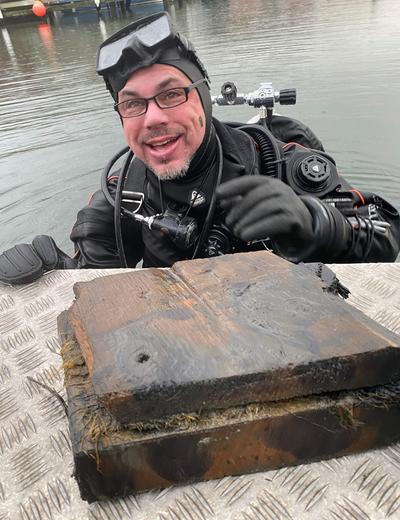

It was during this work that the maritime archaeologists came upon the wreck outside of Fjällbacka which has been given the name “Dyngökoggen”. This limited survey of the wreck shows that it is a cog, a type of ship that was widely used from around the 12th century onward.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The bottom planking is flush-laid (carvel), while the side planks are overlapping (clinker). Seams between planks are also sealed with moss, which is typical for cogs. The surviving hull section is about 10 metres long and 5 metres wide. Staffan von Arbin believes, however, that originally the ship would have been up to 20 metres long.
Was the ship attacked by pirates?
Analysis of the wood samples shows the ship was built of oaks from north-western Germany. How did it end up outside of Fjällbacka?
“Cogs are mentioned often in written sources about the medival Hanseatic League, but ships of this type were common throughout the Middle Ages in northern Europe.” Staffan von Arbin argues that the find also points to the importance of Bohuslän as a transit route for international maritime trade during this period.
This is also one of the oldest cog that has yet to be found in Europe.
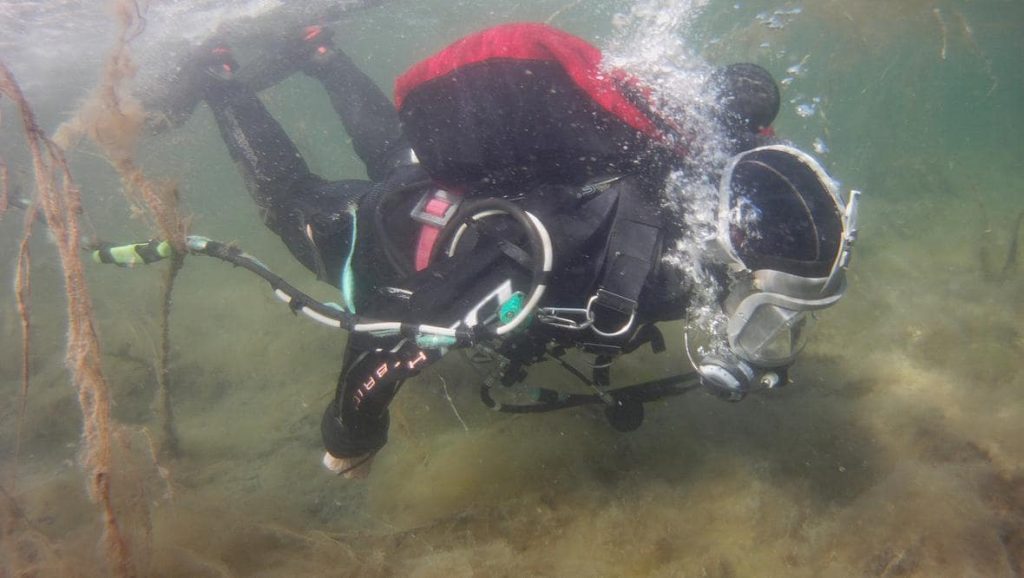

It is not yet known why the ship sank but that would likely be an exciting story. The survey of the ship clearly shows indications of an intense fire.
“Perhaps the ship was attacked by pirates? Written sources tell us that Norway’s southern coast, including Bohuslän, had periods with intense pirate activity during the Middle Ages.”
But it might also have been a simple accident, perhaps a fire spread while the ship was docked. Or the ship was sunk in battle? The first decades of the 12th century were a turbulent time in Norway, which Bohuslän was a part of, with intense internal struggles for the Norwegian crown.
What happens now?
There are currently no plans for more surveys of the wreck. However, they hope to conduct new dives of the wreck in the future. But this requires both a permit from the county administrative board and extensive external funding that is currently unavailable. The results and observations by the marine archaeologists are currently being analyzed for a larger scholarly article.
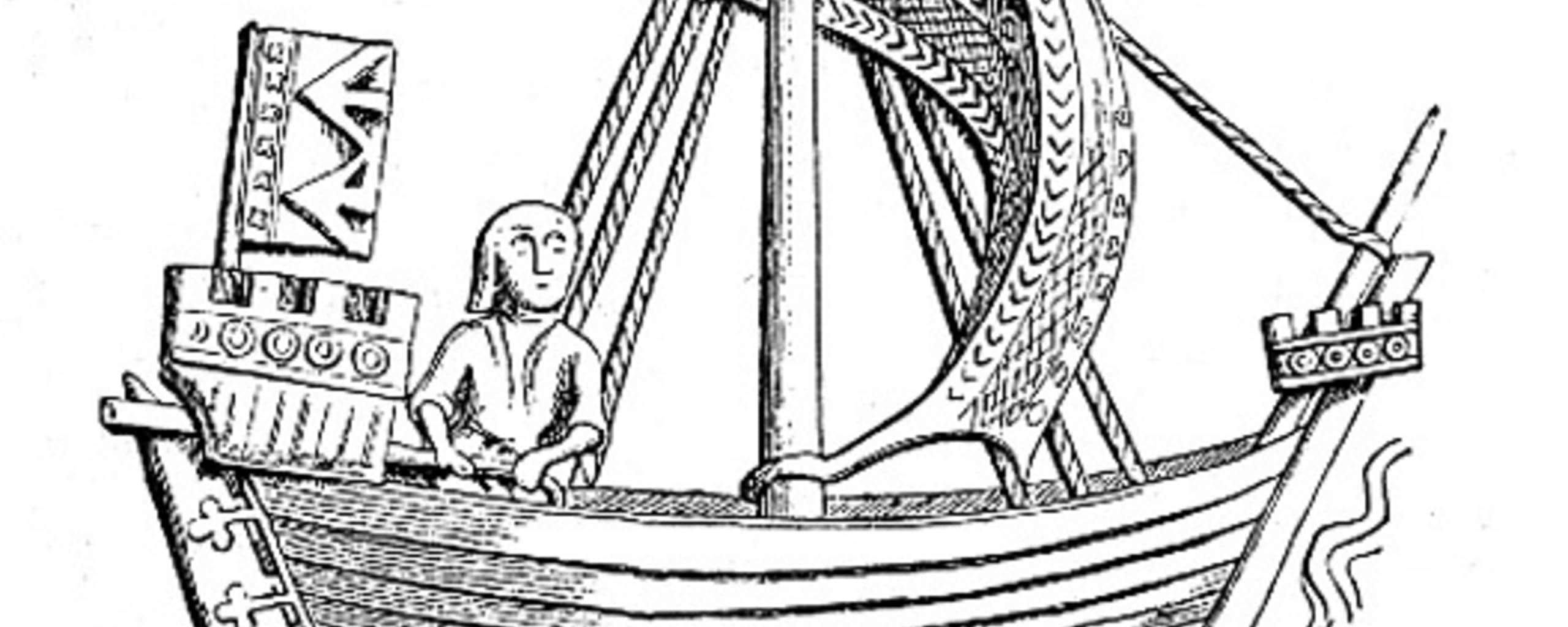
Cover Photo: A cog ship on the town seal of Stralsund dated to 1329. Even if the depiction is nearly 100 years later than the Dyngö cog ship, it provides a good idea of what cogs may have looked like.