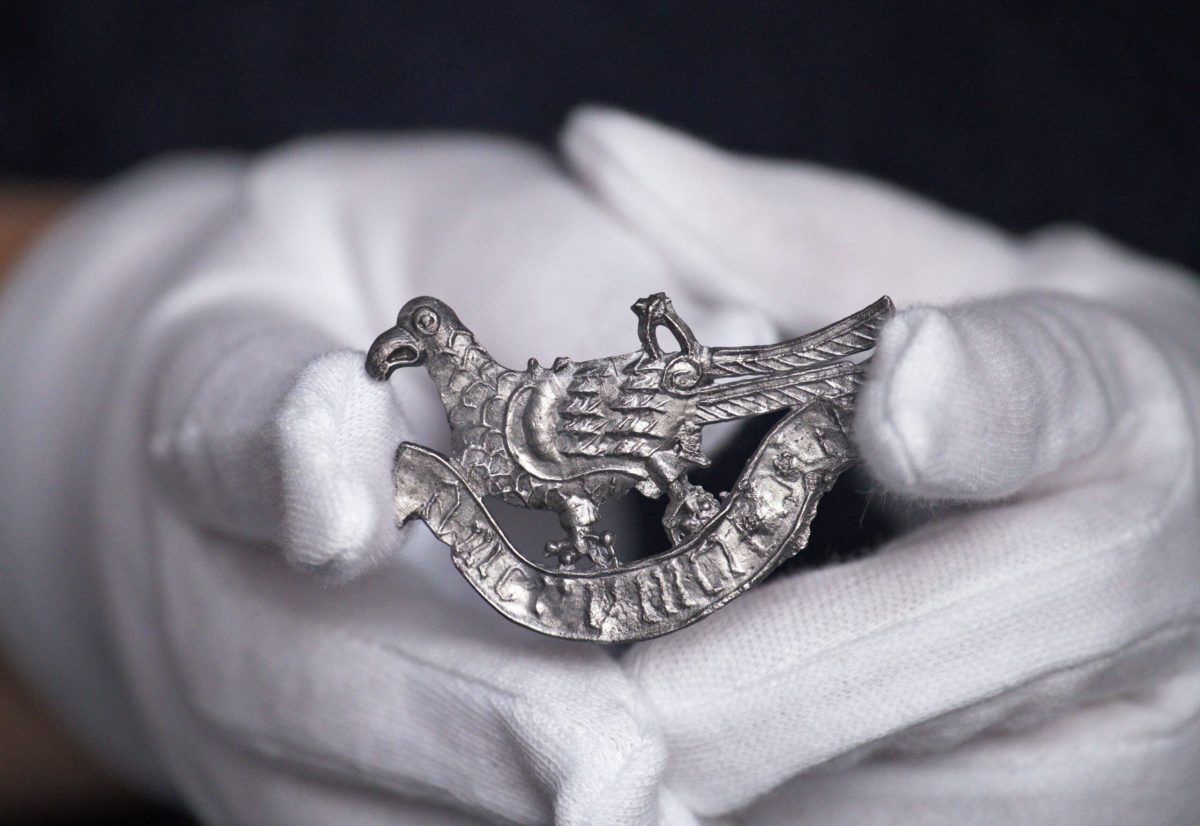
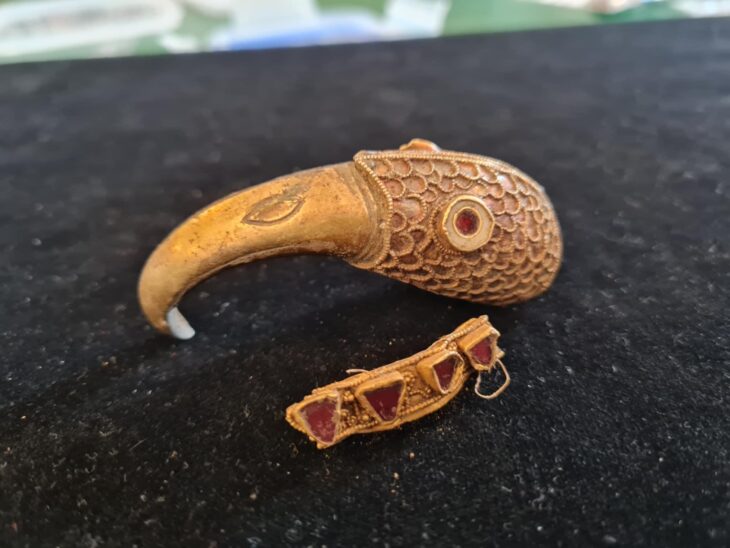
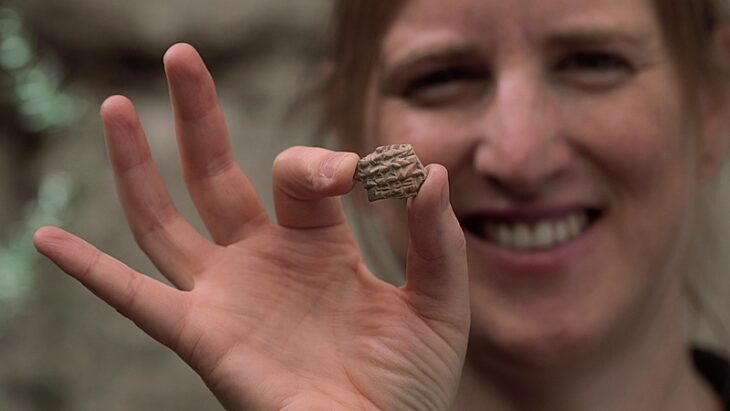Polish archaeologists have discovered a late medieval badge: a piece of tin shaped into a turtle dover and with the Latin inscription: “AMOR VINCIT OMNIA” – “Love conquers all”.
The beautiful find was announced in a news release of the Gdańsk National Maritime Museum on 13 February. The tin artifact was shaped like a turtle dove perched on a ribbon, the museum said.
The turtle dove badge includes the remains of two detached handles that would allow it to be hanged from a chain or attached to clothing.
To early Greeks and Romans, doves symbolized love, devotion, and caring. The dove was the sacred animal of Aphrodite and Venus the goddesses of love.
When you think of birds and love, a pair of doves is probably the most likely image that springs to mind. Their reputation as symbols of love is so strong that many love potion recipes popular during medieval times required the heart of a dove.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Their loyalty and care towards their partner and offspring make them an ideal symbol of love and family,” adds Dr. Anna Rembisz-Lubiejewska, an archaeologist from the National Maritime Museum in Gdańsk.
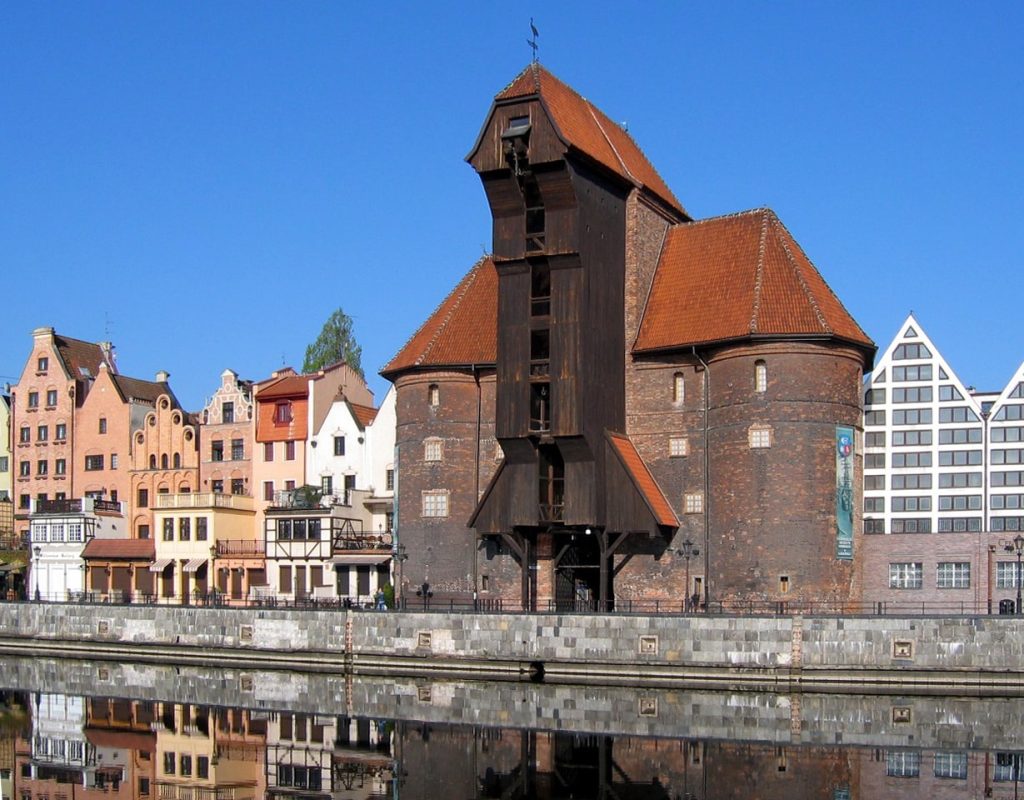

The museum said that similar ornaments were popular in Gdańsk between the 14th and 15th centuries and that this fashion came from Western Europe, especially from the Netherlands and England.
The artifact was discovered during archaeological work at The Crane, a 15th-century port crane sandwiched between two defensive towers.
The original structure, which was first mentioned in 1367, burned down in 1442 before its current design was created between 1442 and 1444. As a working crane, it was used to transfer cargo and raise ship masts.
This was once the world’s largest working crane, but it also served as a defensive structure and one of the city’s gates. It had a lifting capacity of 4 tonnes to a height of 11 meters, which was achieved by two massive wooden wheels at its heart, each with a diameter of 6 meters.
Since 2020, restoration efforts have been underway to restore The Crane, which was severely damaged during WWII. The restoration will allow visitors to see parts of the original 15th-century walls and return the crane’s appearance to how it looked in the 17th century. The renovation and modernization of the Crane is scheduled to be completed on 30 April 2024.
Gdańsk National Maritime Museum
Cover Photo: Hanna Borkowska /NMM