Over 249 hectares of land for sale on Facebook Marketplace has sparked controversy in Yucatan and across Mexico.
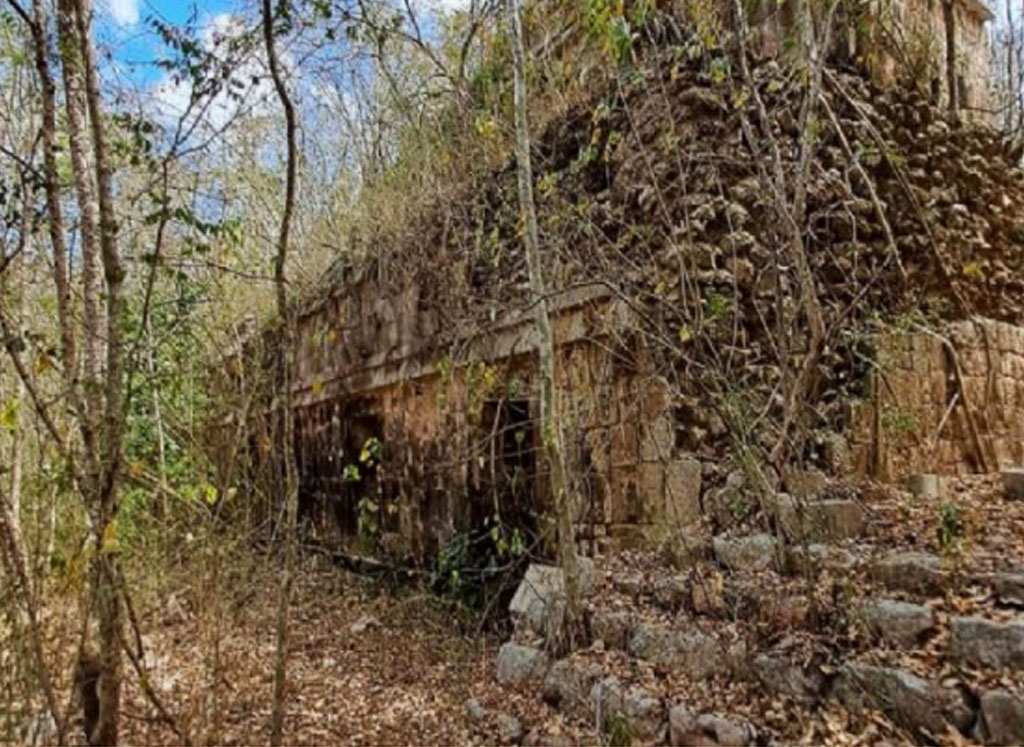
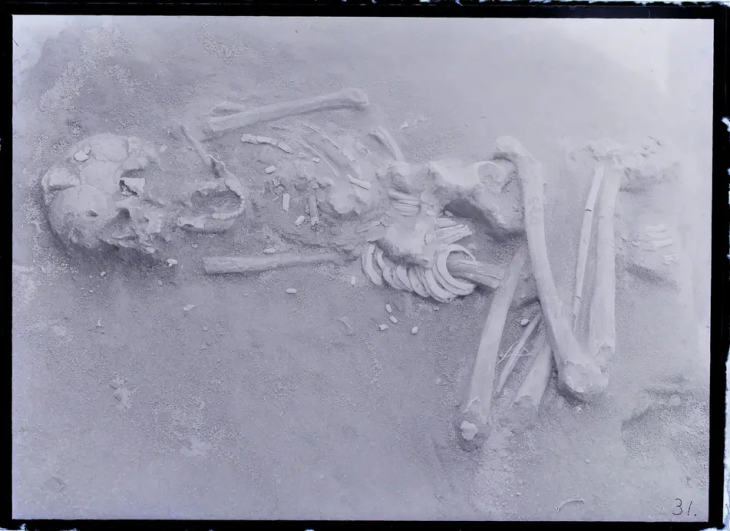
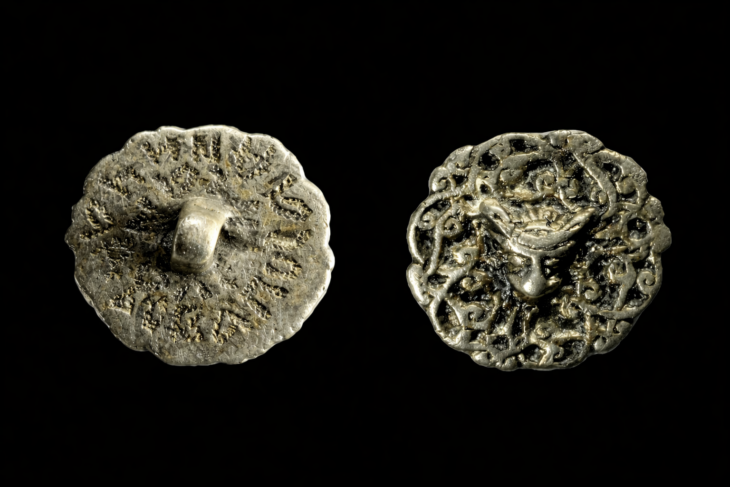
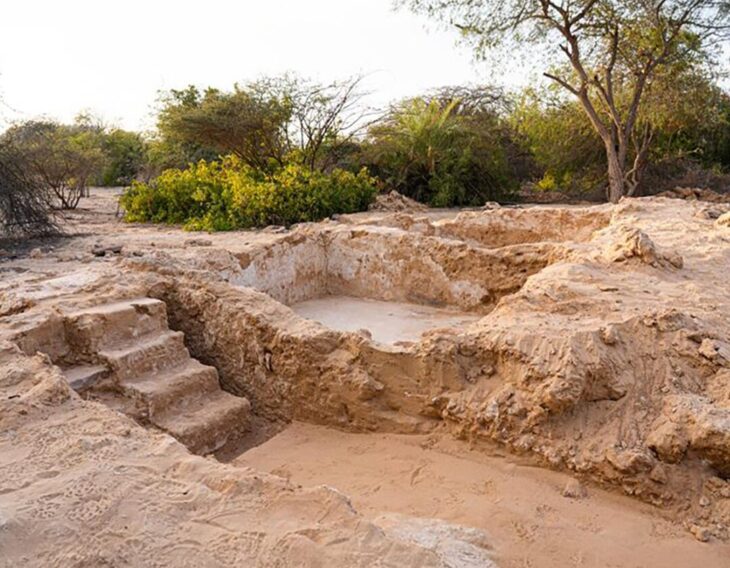
The property, which was advertised on social media, contains the remains of ancient Maya structures within the Xkipche Archaeological Zone, a registered monument in the Archaeological Atlas of the state of Yucatán.
In response to this sale, the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) is taking legal action against the private sale of the land containing the Mayan monuments of Mexico’s Yucatan.
The present owners of the land posted an advert on a Facebook group, stating that the site is being sold as a “ranch” with “18 paddocks”, and is “located ten minutes from the archaeological zone of Uxmal and has pyramids”.
They also stated that the land had previously been investigated by academic institutions between 1990 and 1997, as well as archaeologists from Bonn University in Germany working in collaboration with INAH from 2002 to 2004.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
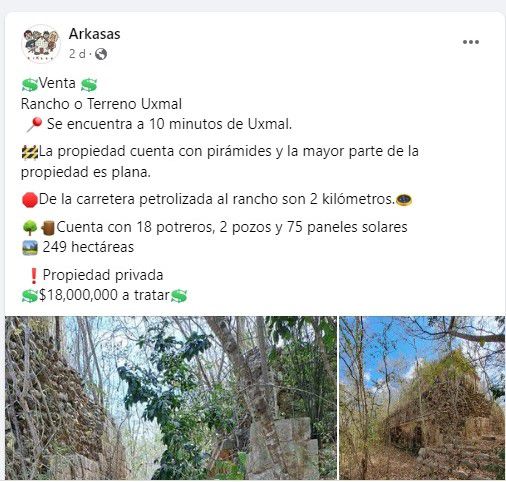
The property is listed for sale at a price of 18 million pesos or roughly one million USD.
According to Yucatán Magazine, the INAH is now preparing to take legal action to avoid the sale and perhaps even expropriate the property.
José Arturo Chab Cárdenas, Director of the INAH Yucatán Center, stated that a criminal complaint will be filed against the owners of said land for commercialization of archaeological monuments
The advert sparked outrage on social media and made national headlines across Mexico, stating that the sale would set a precedent, allowing private sales of archaeological sites for profit, and endangering the nation’s cultural heritage.

Owning property with archaeological remains on it is not illegal under Mexican law, but all archaeological remains are constitutionally the property of the federal government, making their sale impossible. The same goes for pieces of land with rivers, lakes, or cenotes, as all waterways are also government property under Mexican law.
The Puuc region is home to dozens of well-known archaeological sites open to the public, including Uxmal, Kabah, Sayil, and Labna, but it also has a plethora of others, the majority of which are on private or ejido land.
















