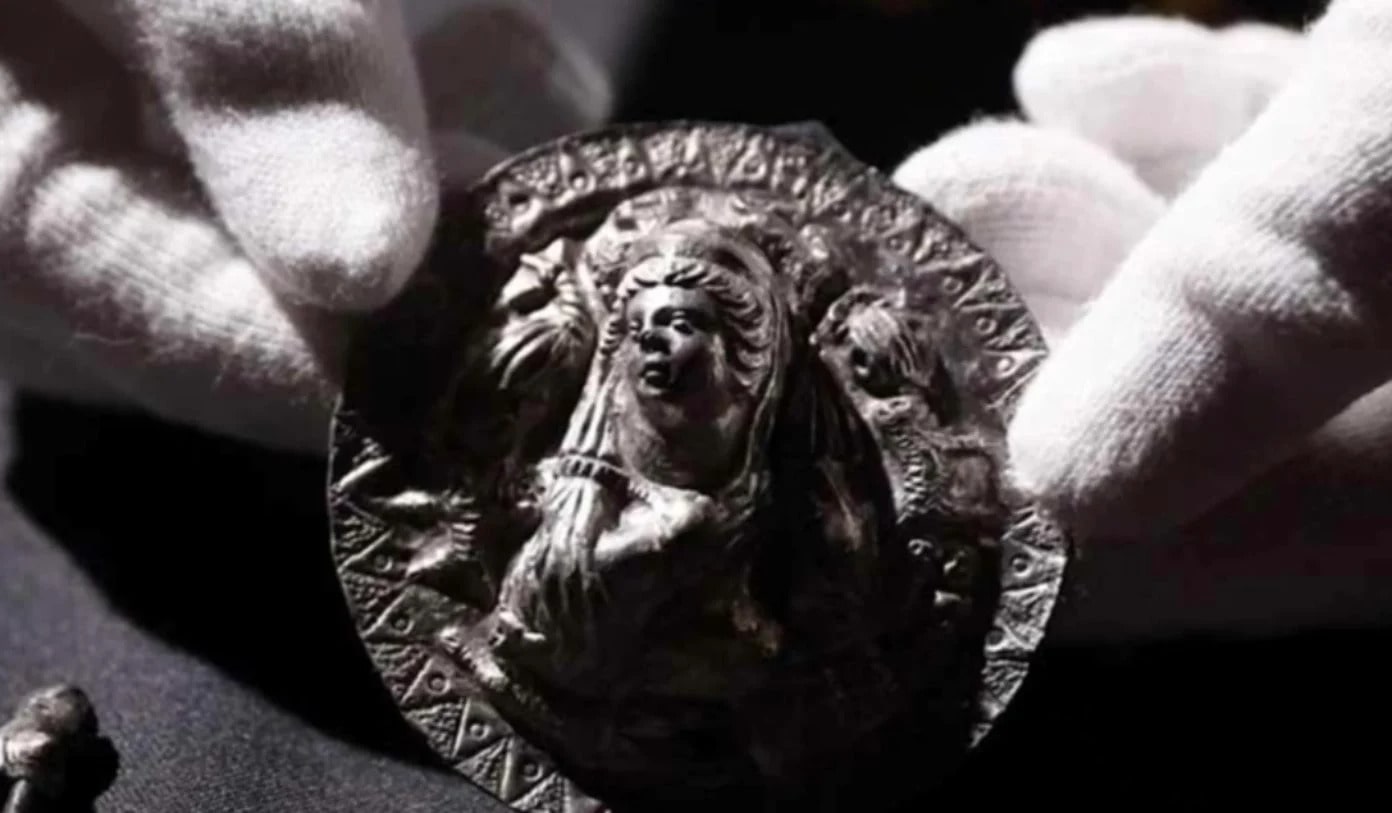
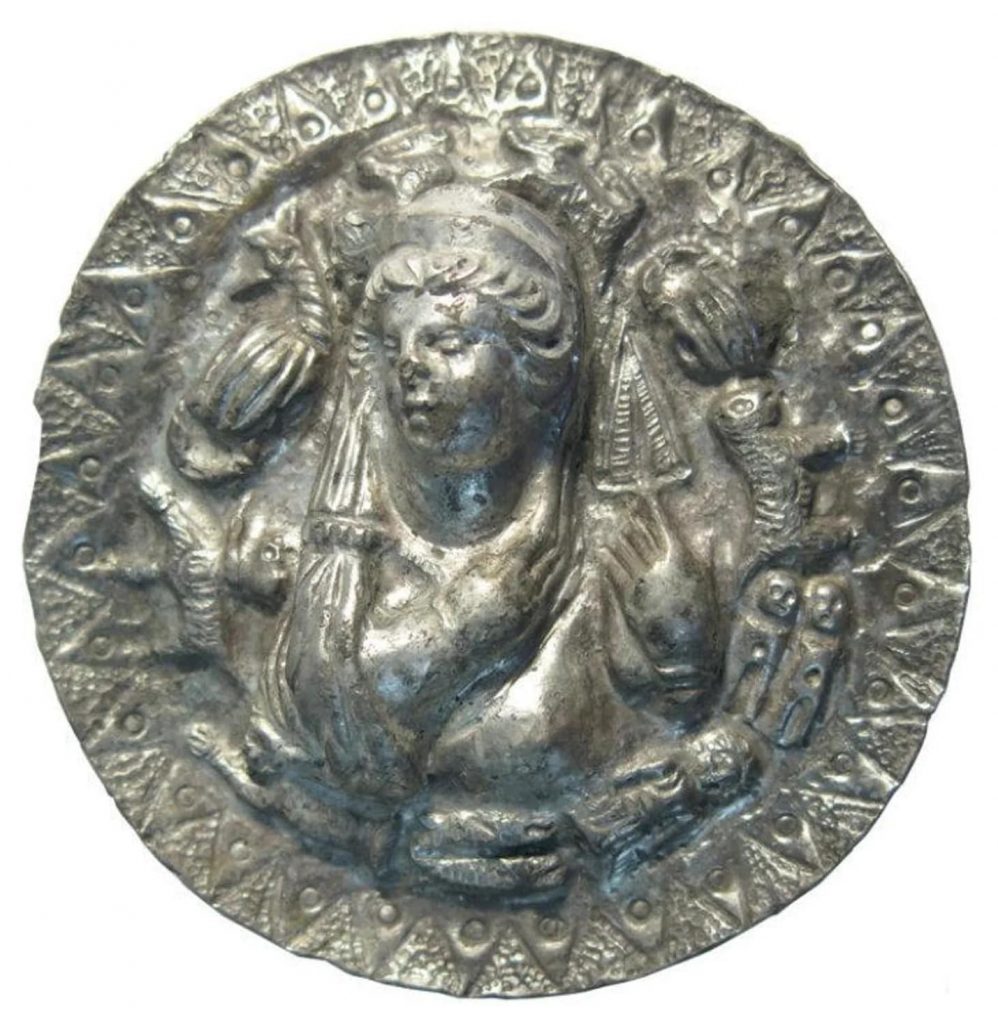
Archaeologists have unearthed a silver medallion depicting the Greek goddess Aphrodite (Roma Venüs) in a 2100-year-old grave of a priestess on the northeast coast of the Black Sea.
The unique medallion depicts ten rather than the known twelve signs of the zodiac and provides insight into religious practices at the time of its creation.
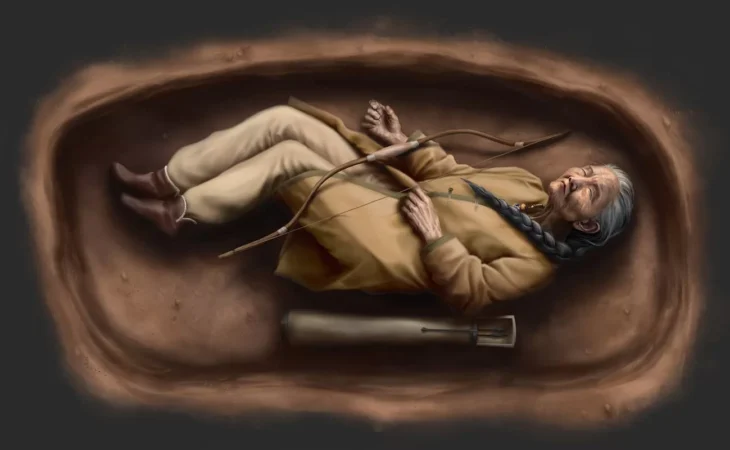
The discovery, in the opinion of archaeologists, raises the possibility that the buried woman was an Aphrodite priestess, the goddess of beauty and love. The rings, silver earrings, and other grave goods that were dedicated to the goddess led to these conclusions.
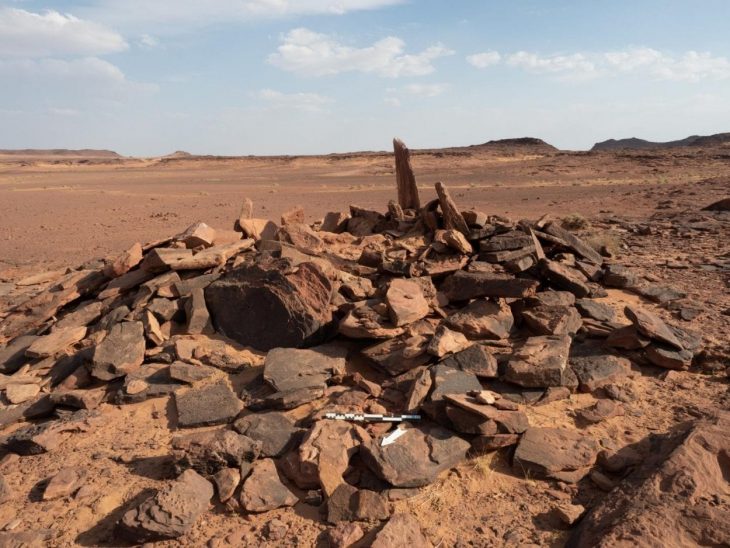
The grave is among a number of striking finds unearthed this summer at a site near the shore of the Taman Peninsula in southern Russia, east of the Crimean Peninsula and between the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov.
According to the Oleg Deripaska Volnoe Delo Foundation’s spokesman Ruben Bunyatyan, archaeologists Nikolay Sudarev and Mikhail Treister discovered the woman’s grave during the Phanagoria archaeological expedition’s 2022 summer season.

Greek historian, Hecataeus of Miletus, said that Phanagoria was founded in the sixth century B.C. by refugees from Teos, a Greek city on the coast of Anatolia now part of modern-day Turkey.
The Aphrodite medallion is surrounded by 10 embossed symbols that correspond to signs of the zodiac, including a lion for Leo, a bull for Taurus, and a scorpion for Scorpio. But the symbols for the zodiac signs Aquarius and Libra are missing, and the researchers don’t know why.
According to archaeologists, the inclusion of the zodiac indicates the medallion is a portrayal of “Aphrodite Urania” — the heavenly aspect of the goddess, as distinct from her Earthly aspect, “Aphrodite Pandemos.”
It also suggests a belief in astrology, the idea that the positions of celestial bodies can influence events on Earth, which was widespread throughout the ancient world.

The silver medallion found in the early first century B.C. grave shows the embossed head, shoulders, and hands of Aphrodite, based on other contemporary iconographic portrayals.
Such medallions were common in the territory of the Bosporan Kingdom as early as 2,300 years ago, said Maria Chashuk, senior research associate of the Phanagoria archaeological expedition.
The medallion is about 7 centimeters (2.75 inches) in diameter and 15 millimeters thick.
Medallions of the sort were used in many ways: as brooches, as headgear accessories, and as pendants.
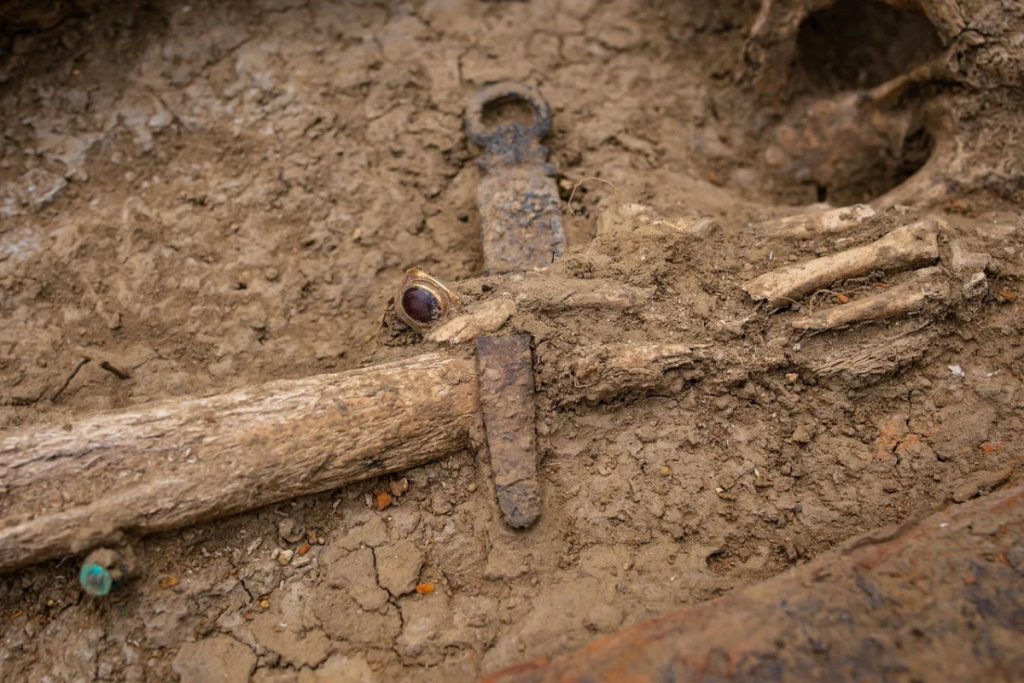
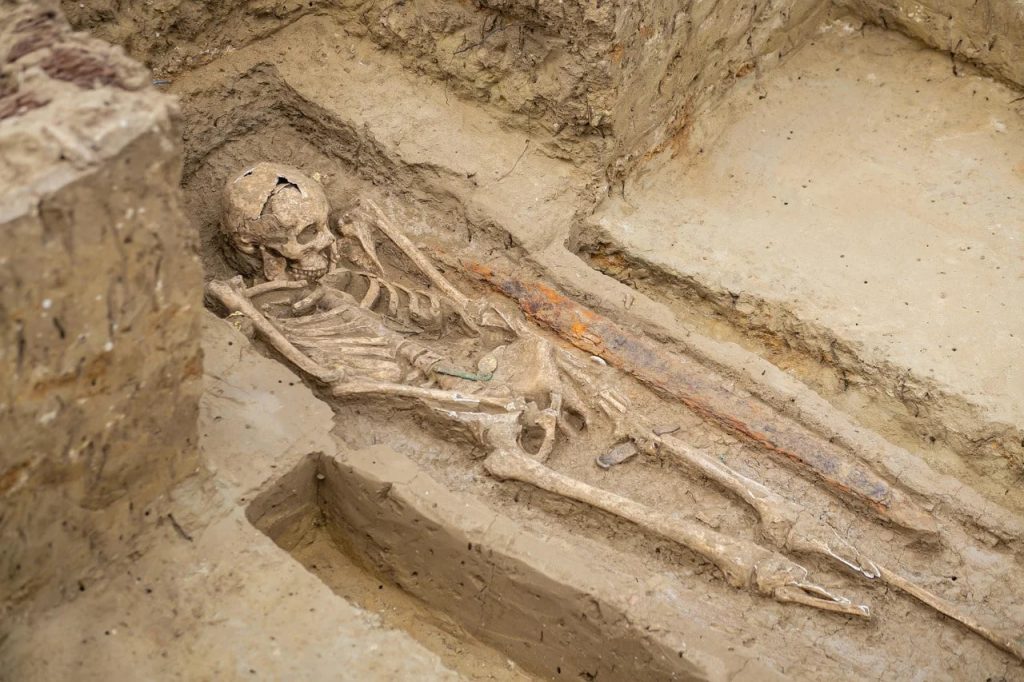
Another intriguing find at the Black Sea site was a warrior’s tomb featuring a sword that had been made in early medieval Iran.

The large iron sword was found in the style of swords from the Sassanid, or the second Persian Empire, which ruled the areas of modern-day Iran, Iraq, Turkmenistan, and much of Afghanistan. The researchers think that the sword may have been a diplomatic gift or that it may have been taken as a military trophy.
According to the statement from the Volnoe Delo Foundation, “this massive, expensive and prestigious sword was part of the equipment of the horsemen of the era of the Great Migration,” a period when much of Europe and Western Asia was threatened by invasions of peoples from Central Asia, such as the Huns. The unique find not only reflects the tastes of the late antique warriors of the Taman Peninsula, but also suggests that in the middle of the first millennium Phanagoria had close political and cultural ties with the [Sassanid] Empire,”
The warrior’s tomb (first century B.C.) also contained fragments of a horse’s harness, buckles, belt tips, glass jugs, utensils, and wooden boxes, as well as a pottery jug, beads, a brass mirror, and a pair of iron scissors.