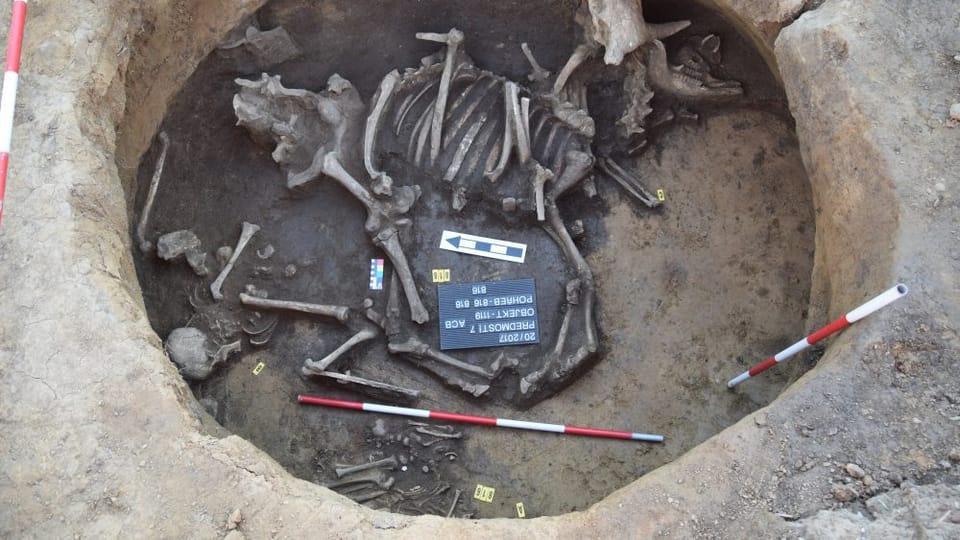
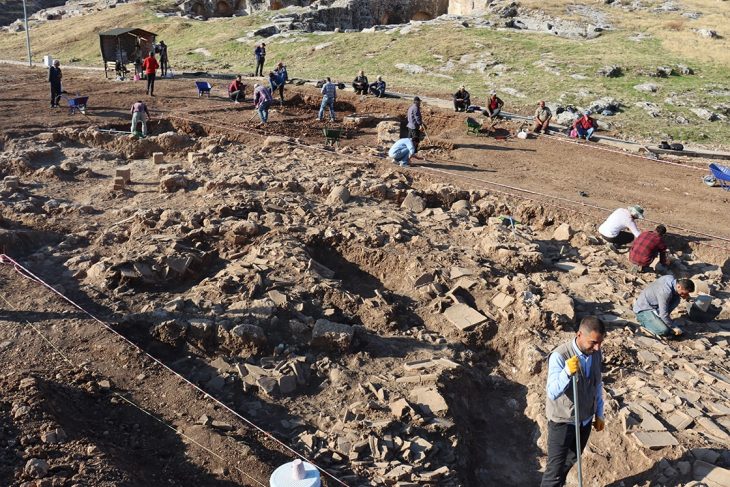
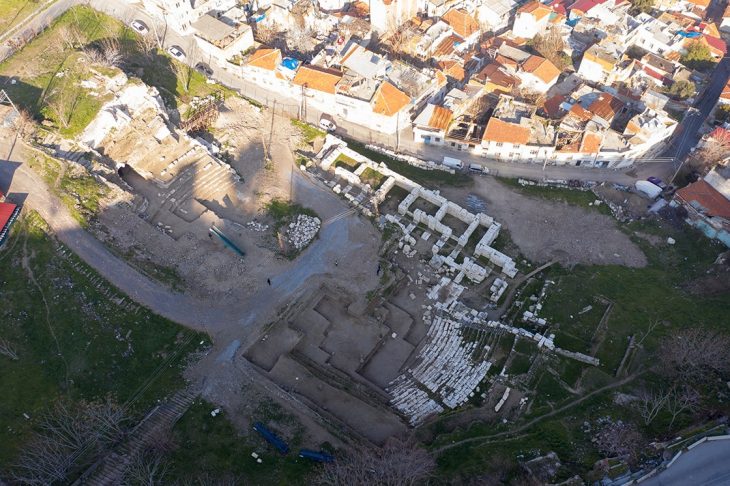
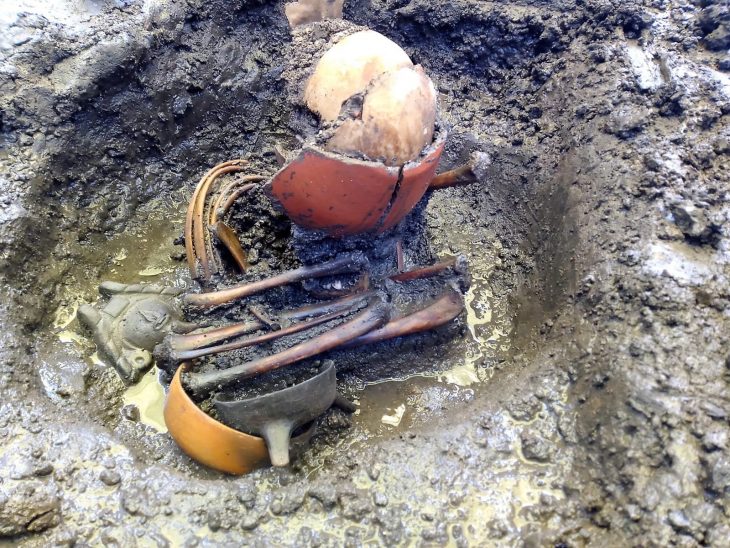
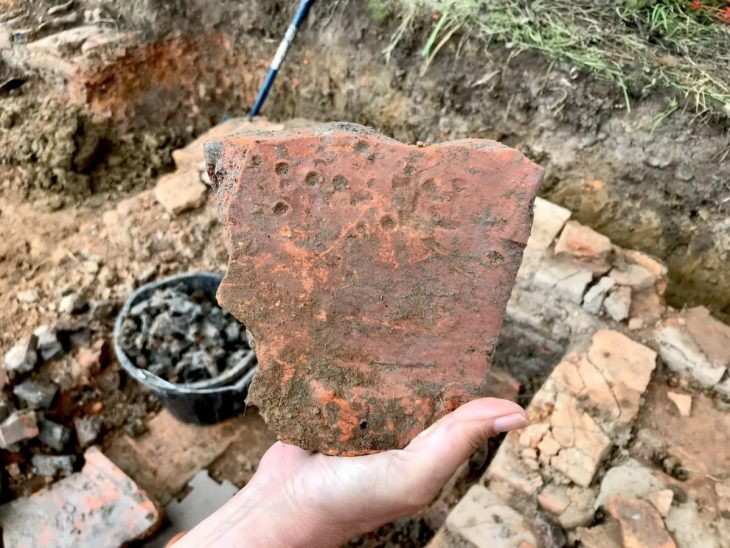
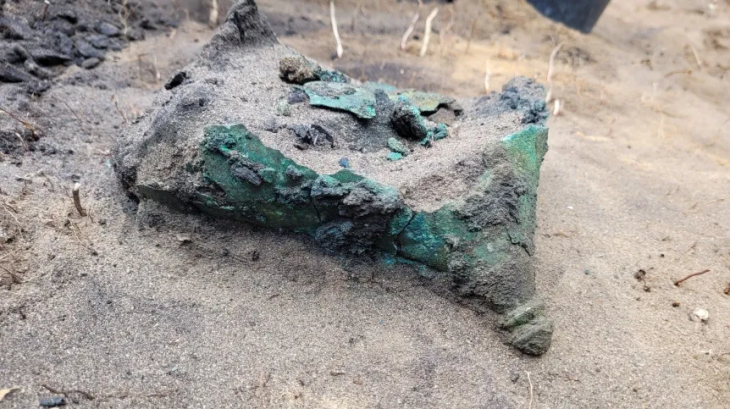
During a four-year dig in the Moravian city (Czech Republic) of Perov, rare gems, mysterious burial places, and divine thrones were discovered. New settlements from a variety of prehistoric periods, including the Neolithic and early Bronze Age, were discovered by archaeologists.
Excavations near Perov began in 2017, ahead of the anticipated building of a highway, and were completed this June. Archaeologists say they uncovered approximately 4,700 items and 150 burial sites in the region, which will now be thoroughly examined.
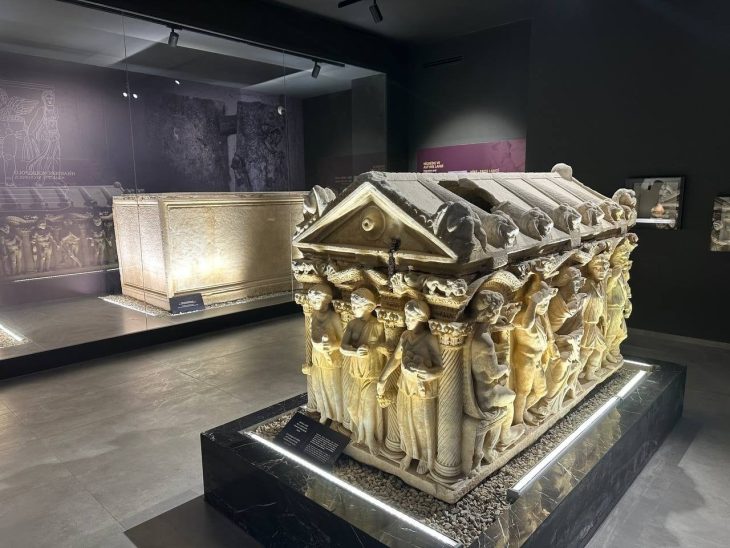
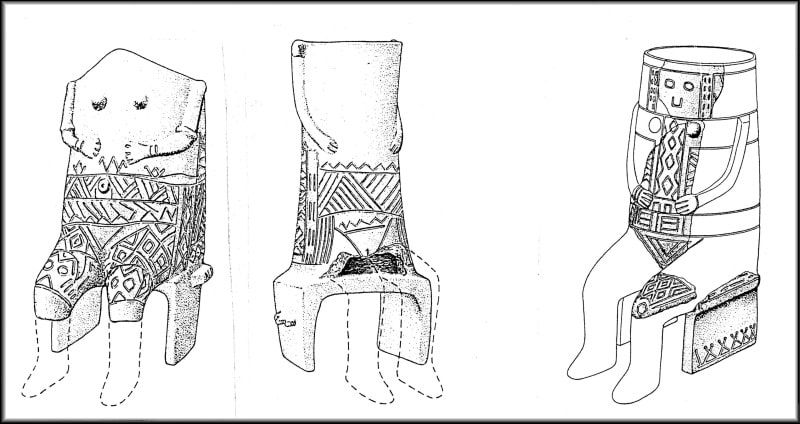
Parts of enthroned deity sculptures, which were prevalent in late Stone Age Neolithic art, are among the finds.
The excavations were supervised by the Olomouc Archaeological Centre.
Dr. Jaroslav Peška said about the excavations, “I have to say that our archaeological digs in the area exceeded our expectations. We now know that at least three pieces of enthroned god statues were found around Přerov, ” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“One is from the Linear Pottery culture period, which is the name for the oldest farmers who settled on our territory sometime around 6,000 BCE. We were able to date the throne by its decorations, which carry signature features of that period. “The two other thrones are also from the Neolithic period but are a bit younger. We believe they are connected to the Lengyel culture (5,000 to 3,400 BCE). This culture’s art in the Moravian region is known for its richly painted pottery. In one case, we managed to also find a leg belonging to the god who sat on the throne, which is quite rare.”

Dr.Peška says the indigenous civilizations of the Neolithic period frequently portrayed their gods in a seated, enthroned pose. These were usually female representations, although they may sometimes include male gods, as more complete discoveries in neighboring Hungary have proven.
Ceramic thrones are rarer artifacts in the Lengyel culture. They are thought to be related to with seated statues found not only in Moravia (Střelice-Bukovina, Brno-Ivanovice, Nitrianský Hrádok, Wetzleinsdorf, Jaroměřice nad Rokytnou, Otaslavice, Hrotovice, Hejčín, Komjatice-Tom, etc.).
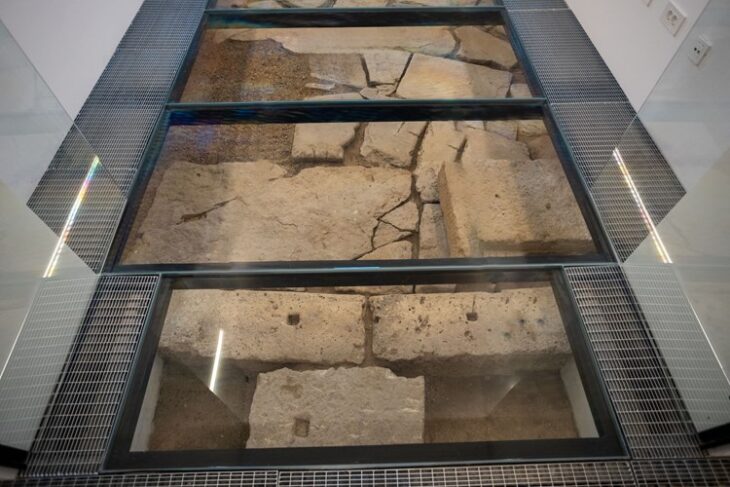
A fortified settlement from the eight-millennia-old Linear Pottery period was also discovered. According to Dr. Peska, the site has a ditch and a wall.
Dr. Peška, “If we are able to identify any connections between the enthroned deity fragment and the settlement, this site could become quite special,” he said.
Dr. Peška stated that the defensive structures are known from this period, but they seem to be quite rare and this settlement is one of the 4 or 5 most interesting places for Morovia.
The finding of unique burial sites in the Neolithic Lengyel culture excavations is also noteworthy. According to Dr. Peška, they resemble long trenches rather than tombs and are packed with large amounts of pottery, which he claims is an archaeological first in Moravia.
The Lengyel culture is an archaeological culture of the turn of the Neolithic and Eneolithic (sometimes between 4400 and 4300 BC) prevalent in the ancient settlement of central and northeastern Bohemia. It belongs to a large cultural complex that spread from the Balkans to Central Europe (Slovakia, Moravia, Austria, Bohemia) at the end of the Neolithic. Its name comes from a paid housing estate near Lengyel in southern Hungary. The Lengyel culture was created by mixing influences from the southeast, Moravian painted ceramics – MMK and spiked pottery culture. It was therefore a mixture of influences from the southeast and west.
Over Photo: Archeological Center in Olomouc