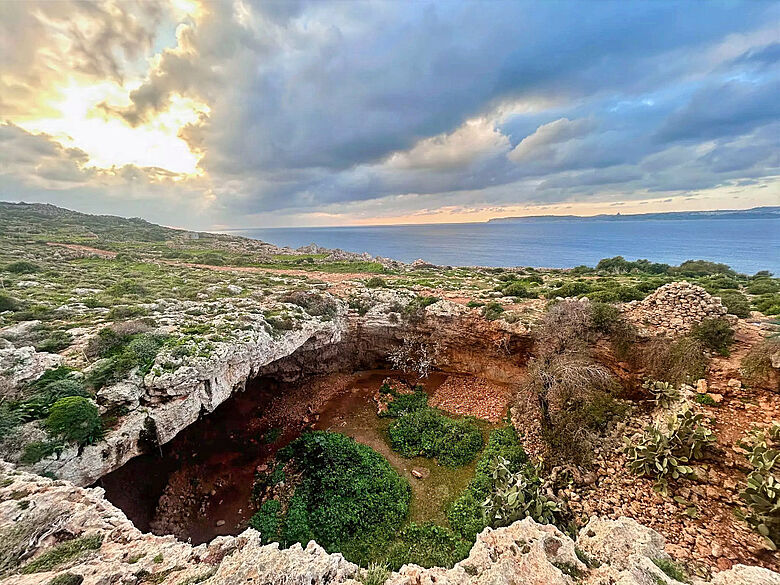
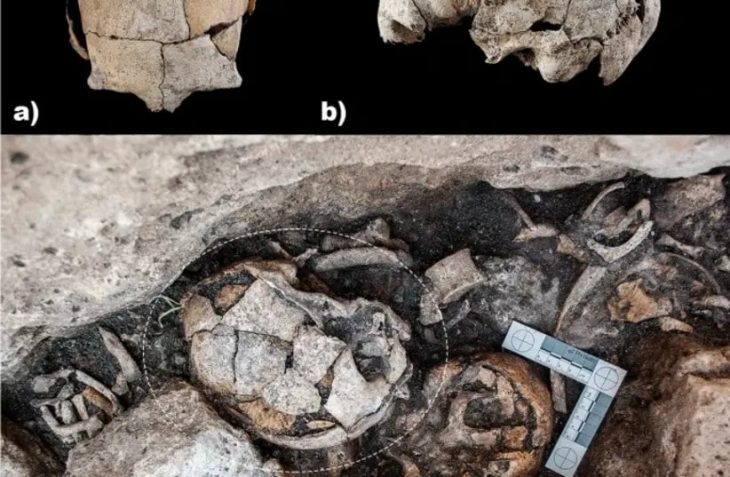
Recent archaeological findings have dramatically reshaped our understanding of human history in the Mediterranean, revealing that hunter-gatherers were capable of long-distance seafaring as early as 8,500 years ago—1,000 years before the advent of agriculture. This groundbreaking research, published in Nature, highlights the remarkable navigational skills of these early humans, who traversed at least 100 kilometers of open water to reach the island of Malta using simple dugout canoes.
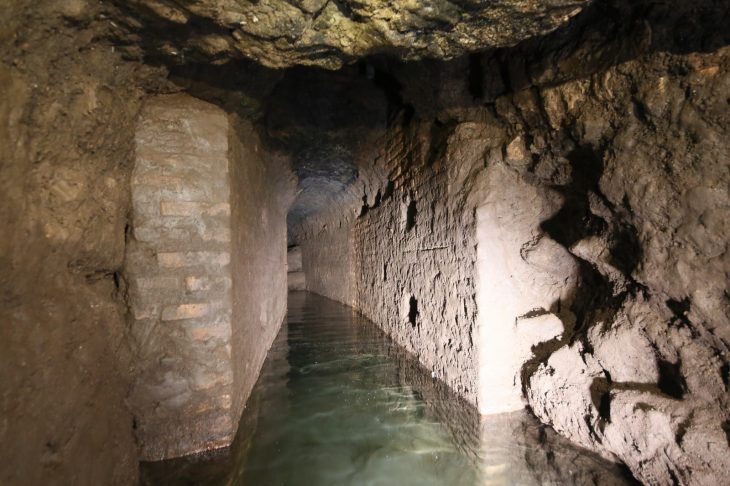
Led by Professor Eleanor Scerri from the Max Planck Institute for Geoanthropology (MPI-GEA) and the University of Malta, the research team uncovered significant evidence at the Latnija cave site in northern Malta. Among the findings were stone tools, hearths, and remnants of cooked food, indicating a rich and varied diet that included a range of wild animals. Notably, the remains of red deer—previously thought to be extinct by this time—were discovered alongside evidence of hunting and cooking of turtles and large bird species that are now extinct.
The study also revealed extensive use of marine resources, with remains of seals, various fish species, and thousands of cooked marine gastropods, crabs, and sea urchins found at the site. Dr. James Blinkhorn, a corresponding author of the study, emphasized the significance of these findings in understanding the dietary practices of these ancient communities.
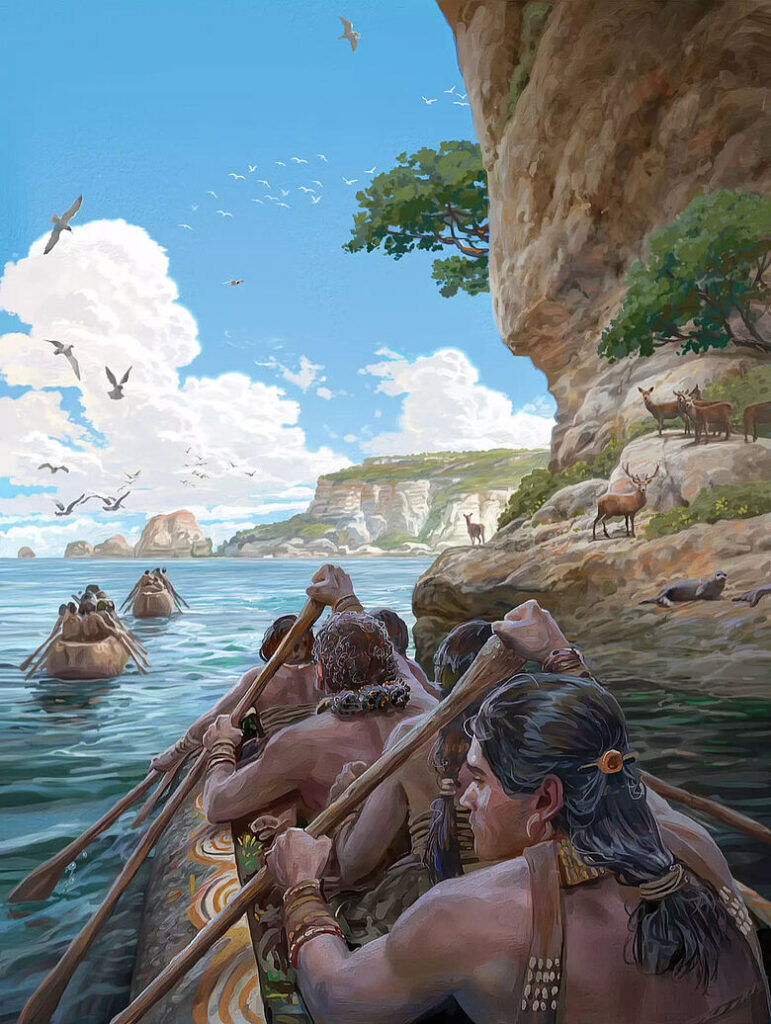

The implications of this research extend beyond dietary habits; they challenge long-held beliefs about the capabilities of prehistoric hunter-gatherers. Professor Nicholas Vella of the University of Malta explained that these early seafarers relied on natural elements such as sea currents and winds, as well as navigational techniques involving landmarks and celestial bodies, to undertake their maritime journeys. He noted that even during the longest days of the year, these journeys would have required several hours of navigation in darkness.
This new evidence not only extends the timeline of Maltese prehistory by a millennium but also prompts a reevaluation of the connections between Mesolithic communities across the Mediterranean. The findings raise intriguing questions about the extinction of endemic species on Malta and other small islands, suggesting that these hunter-gatherers may have played a role in shaping early ecosystems.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research was supported by Malta’s Superintendence of Cultural Heritage and funded by the European Research Council and the University of Malta’s Research Excellence Award. As scholars continue to explore the maritime capabilities of ancient hunter-gatherers, this study marks a significant milestone in our understanding of human adaptation and innovation in prehistoric times.
Cover Image Credit: Latnija Cave in northern Malta. Credit: Huw Groucutt
Eleanor M.L.Scerri, James Blinkhorn, Huw S. Groucutt, Mathew Stewart, Ian Candy, Ethel Allué, Aitor Burguet-Coca, Andrés Currás, W. Christopher Carleton, Susanne Lindauer, Robert Spengler, Kseniia Boxleitner, Gillian Asciak, Margherita Colucci et al. Hunter-gatherer sea voyages extended to remotest Mediterranean islands. Nature. 9.4.2025
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08780-y