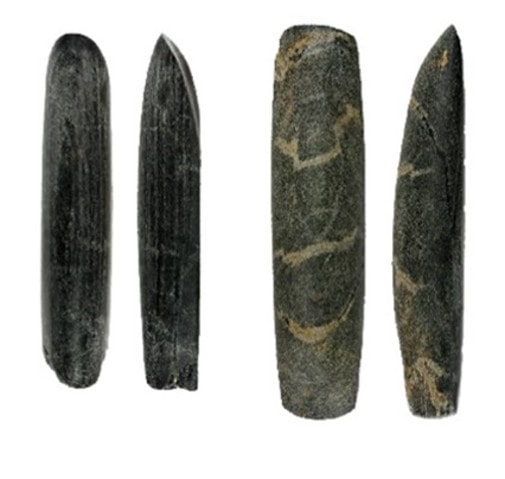
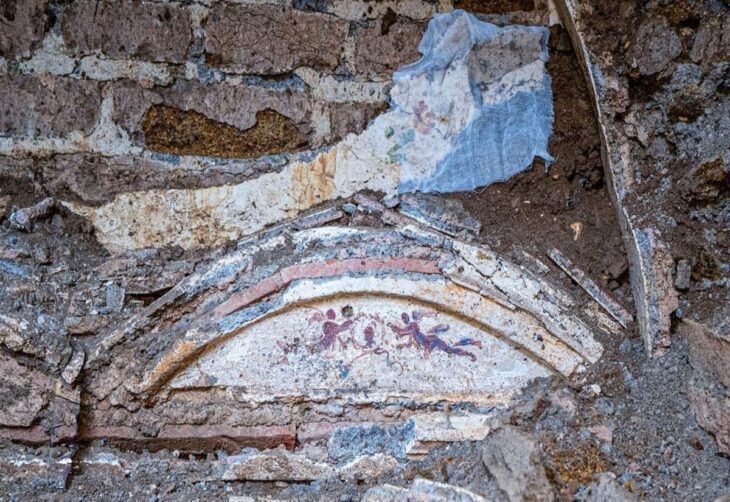
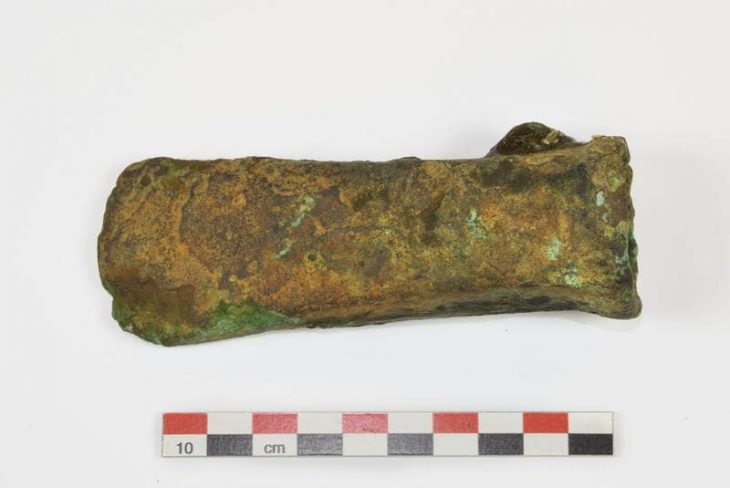
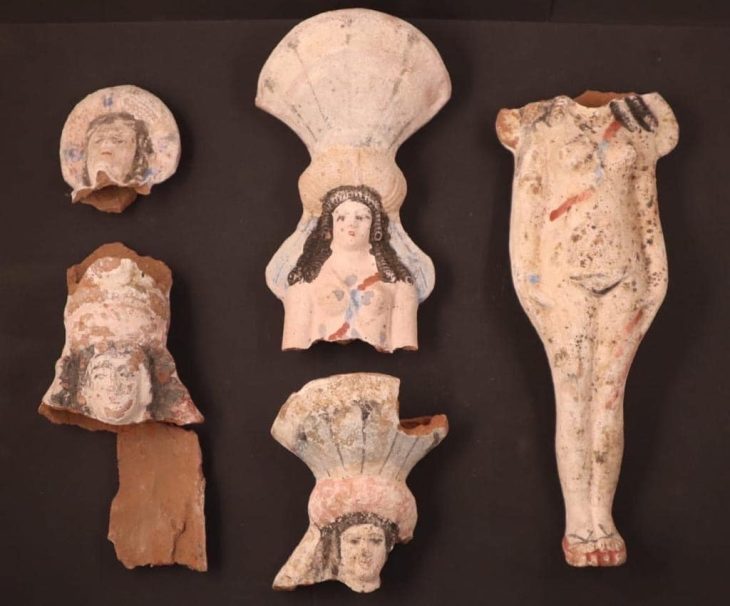
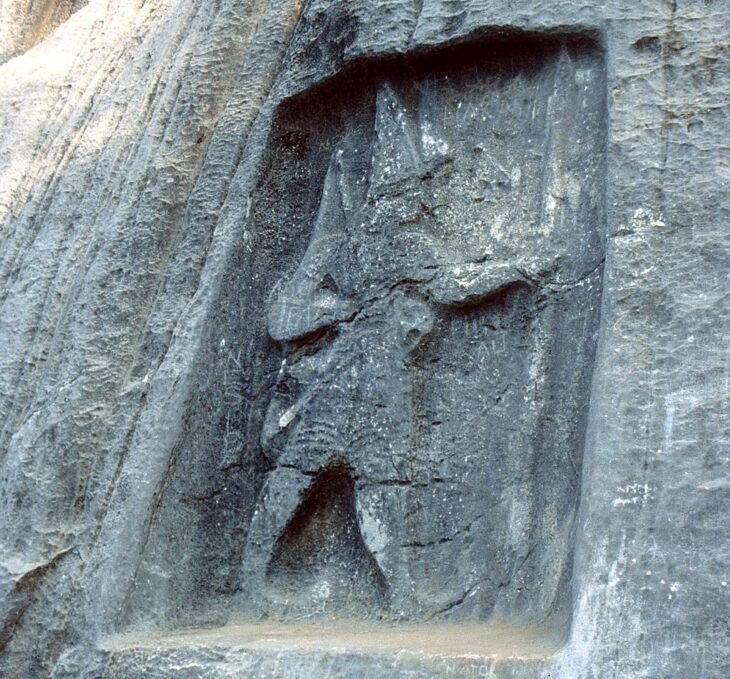
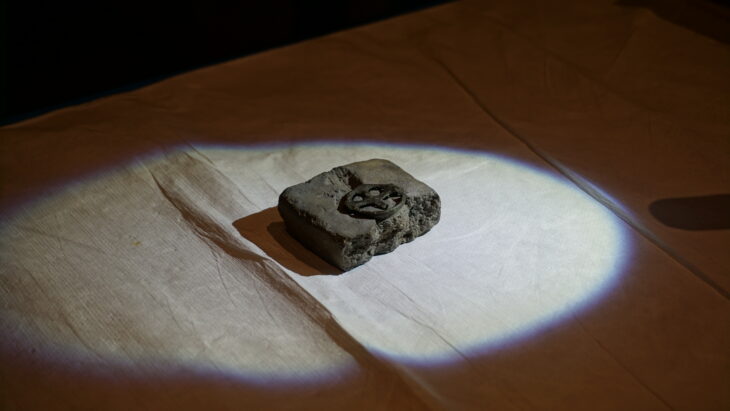
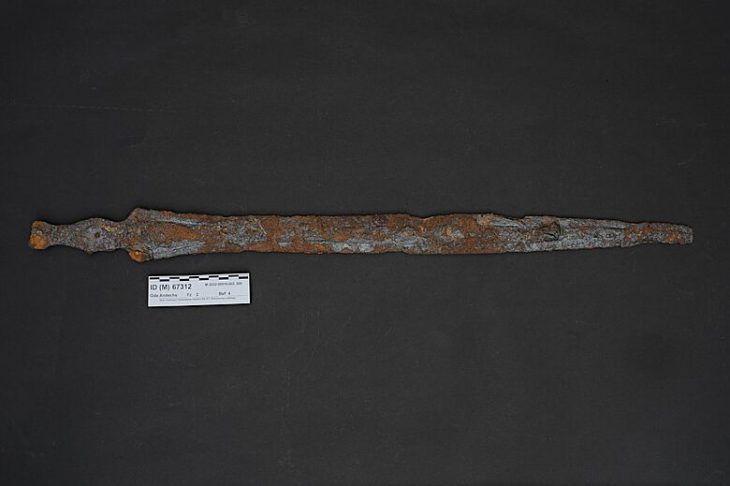
Grave goods, such as stone tools, have revealed that Neolithic farmers had different work-related activities for men and women.
Researchers at the University of York analyzed 400 stone objects found in graves at cemetery sites across Europe and noted there were differences in size, weight, and raw material dependent on whether the body was a male or a female.
Archaeologists had previously thought that polished stone tools in this period were used for woodworking, but analysis now shows a much wider range of tasks, with different activities for men and women.
The tools found in female graves were most likely used for the working of animal skins and hide, and tools for the men were associated with hunting and potential conflict. The researchers concluded that the different roles of men and women were a crucial part of the transition to farming in human societies.
Dr. Penny Bickle, from the University of York’s Department of Archaeology, said: “The gendered roles, far from being a sign of early gender inequalities, actually shows how dynamic farming societies were and how aware they were of the different skills of members of their community.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The tasks attributed to women were difficult manual work and complimented the work of the men as equal contributors to their community. The fact that you see these objects in the graves of men and women, demonstrates how marked out and valued they were for these jobs.”

The evidence also demonstrated that these roles would have varied depending on where the community was from. In eastern areas, there is evidence to suggest women moved around more than men, and regardless of sex, shell ornamentation and jewelry were carried in their graves. In the west, men moved around more and had tools more associated with hunting than women.
Alba Masclans Latorre, a postdoctoral researcher from Barcelona and the lead on the study, said: “Women’s roles and contributions to these very early human societies are often downplayed, but here we show that they took an active role in shaping early farming communities.
“So important was their role that these activities were chosen to mark them out in death, but we see the same in the graves of men, suggesting that there were indeed specific gendered roles, but all of these jobs were hugely significant to the proper functioning of their society.”
Source: UNIVERSITY OF YORK