According to a study published Thursday (July 6) in the journal Scientific Reports, the highest-status individual in ancient Copper Age society in Iberia was a woman, not a man as previously thought.
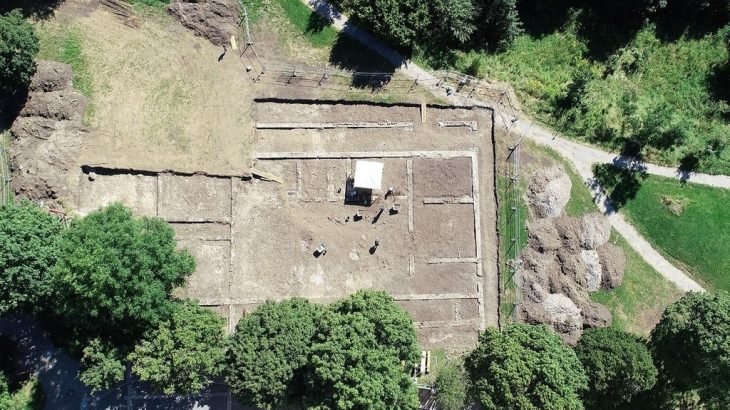
Since its discovery in 2008, the skeleton of a high-ranking individual buried inside a tomb in the Iberian Peninsula between 3,200 and 2,200 years ago was thought to be the remains of a man. However, a new analysis reveals that this person was actually a woman.
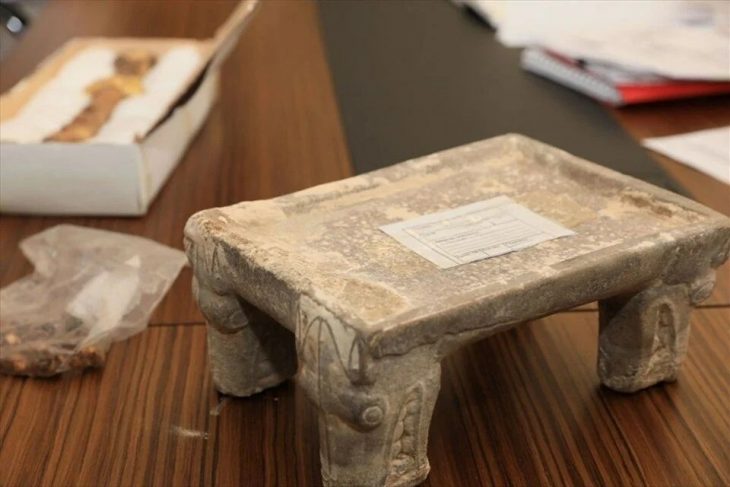
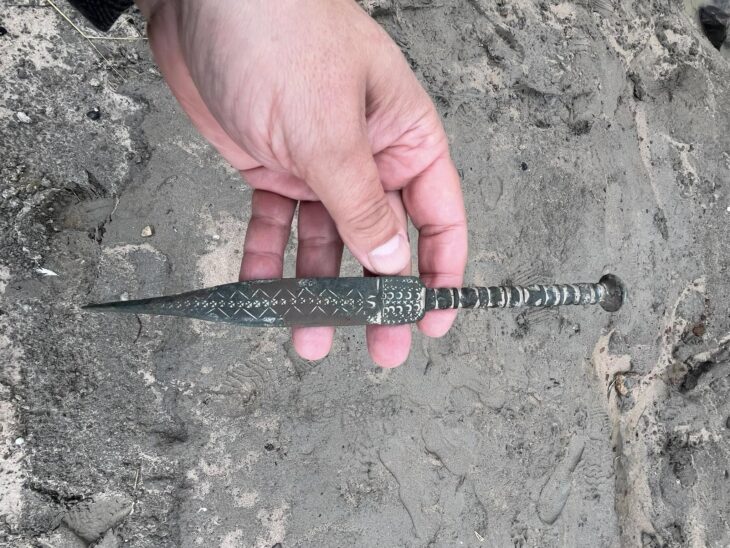
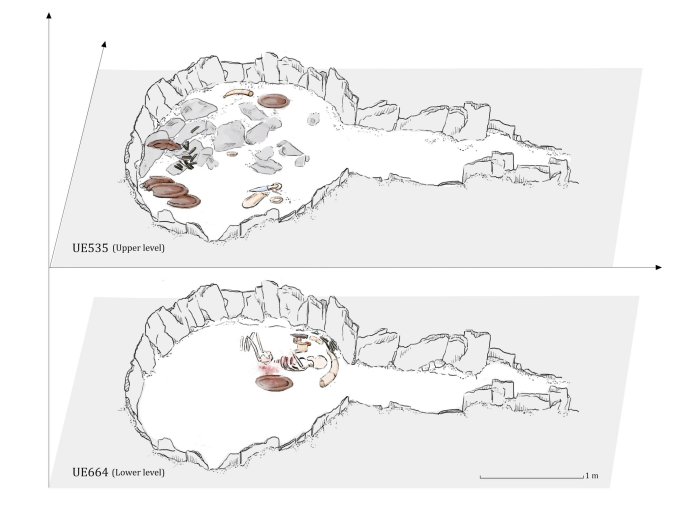
Archaeologists in Spain dubbed the woman the “Ivory Lady” based on the bounty of grave goods found alongside her skeleton, including an ivory tusk surrounding her skull, flint, an ostrich eggshell, amber, and a rock crystal dagger.
For more than a decade, archaeologists believed that this individual was a man, even nicknaming him the “Ivory Merchant.” As well as being a rare example of a single occupancy burial, the grave contained a large number of valuable goods, suggesting that this individual—originally thought to be a young male aged between 17 and 25 years. —held a high status within society.
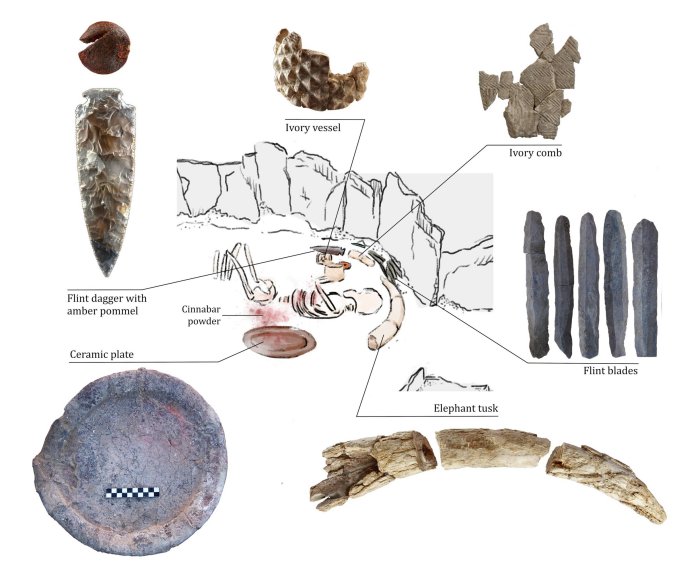
“She stands out as the most prominent person ever to have lived in that period” in this region, said University of Seville professor of prehistory Leonardo García Sanjuán, one of the authors of the research.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
While the researchers do not know precisely who she was or what societal role she played, they suspect she combined political and religious power and may have been viewed as the founder of an important clan.
Because the skeleton’s pelvic region wasn’t well preserved, this new group of researchers used a different method to analyze the remains: They conducted an amelogenin peptide analysis of the skeleton’s tooth enamel to see if it contained the AMELX gene. Analysis of a molar and an incisor detected the presence of the AMELX gene—which produces amelogenin and is located on the X chromosome—indicating that the individual was female rather than male.
“This analysis told us precisely that the skeleton was female,” García Sanjuán said.
“During this time period, we were starting to see new forms of leadership in Western European societies,” he said. “She was a leader who existed before kings and queens, and her status wasn’t inherited, meaning that she was a leader based on her personal achievements, skills and personality.”
No male of similarly high status has been found at the site. Located nearby was a similarly lavish tomb containing the bodies of at least 15 women – thought to have been built by people claiming descent from the “Ivory Lady.”
Other burials in southern Spain, particularly those of infants interred without grave goods, show that birthright did not determine social status during the Copper Age. According to the study, the location of her tomb also provides insight into the ancient society that once lived there.
The “Ivory Lady” shows that women may have held high leadership positions during the Copper Age, a transitional period between the Stone Age and the more technologically sophisticated Bronze Age.
doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36368-x
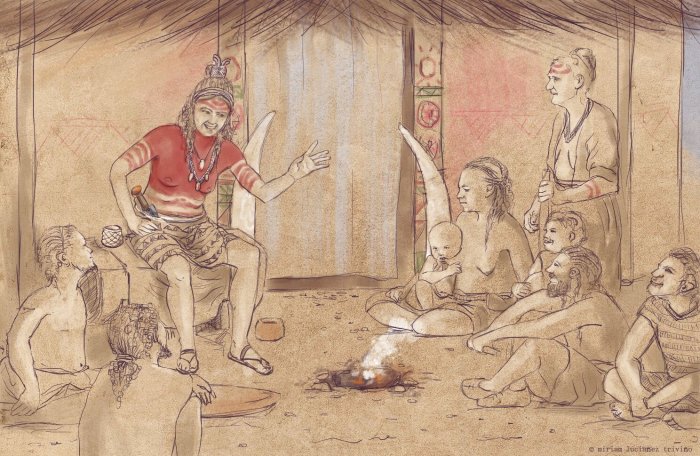
Cover Photo: Recreation drawing of ‘The Ivory Lady’. Miriam Lucianez Trivino.
















