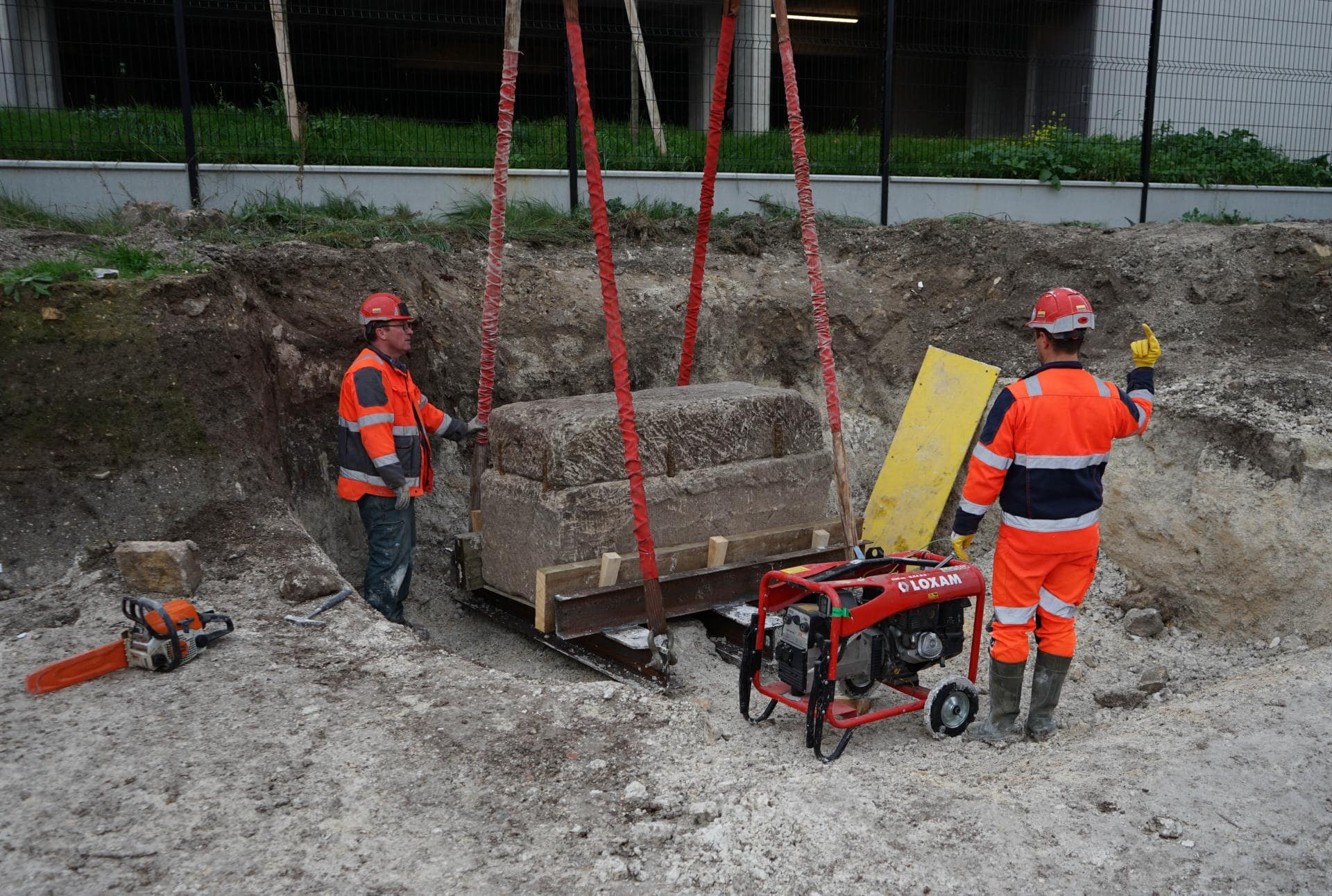
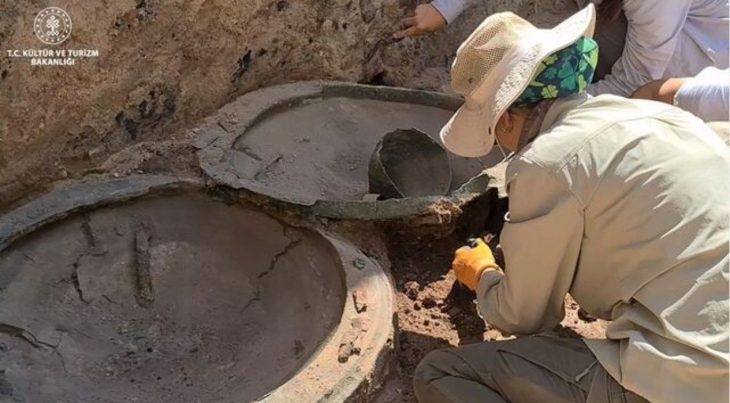
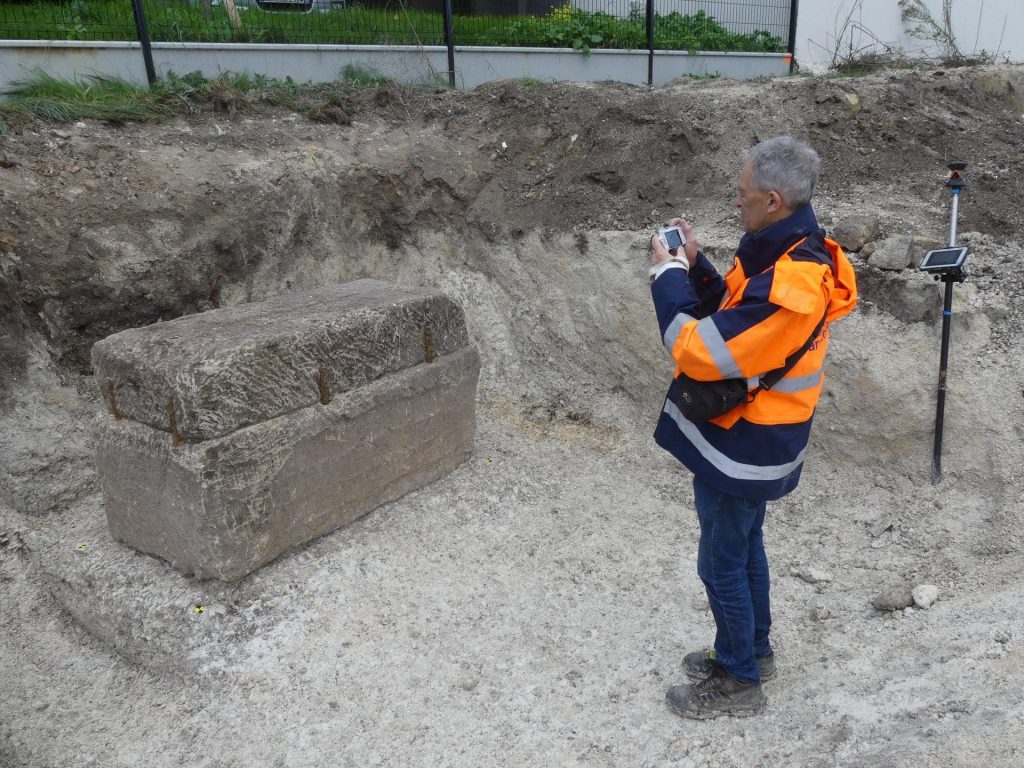
Archaeologists from France’s National Institute of Preventive Archeology (INRAP) have unearthed an unlooted ancient stone sarcophagus in the vast ancient necropolis on Rue Soussillon in northeastern France.
It’s not often that archaeologists find an unlooted Roman sarcophagus, so when it does happen, it becomes the perfect opportunity to learn more about the past.
The ancient Durocortorum was the capital of the province of Gaul Belgium and was one of the largest cities in the Roman Empire. The city extended over 600 hectares and was delimited by a powerful wall. It was in the second half of the 19th century, during extension work in Reims, that the contours of this so-called “Augustan” enclosure were highlighted as well as the extra muros necropolises, located around the seven main access routes. (towards Boulogne, Soissons, Paris, Lyon, Trier, Cologne and Bavay). In 22 years of research, 5,000 tombs have been explored and added to the museum’s collections.
The First World War destroyed the museum as well as a large part of its collections and documentation. Apart from knowledge of the topography of the funerary spaces, very little remains from the excavations of these ancient necropolises. The layout of the “great enclosure” has been little explored by archeology and presents areas of uncertainty that each discovery completes. In this context, the discovery of a portion of the intact necropolis on Rue Soussillon constitutes an exceptional discovery for Reims archaeologists.

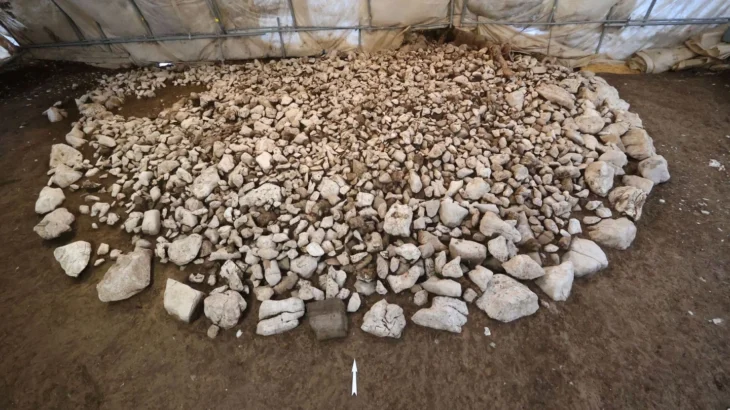
On Rue Soussillon, researchers have uncovered 1,200 m2, which is just a portion of a sizable ancient necropolis. The high concentration of tombs in this area of the city is especially intriguing because it has long been thought of as a swampy area unfit for any kind of settlement.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
During the recent excavation, scientists discovered a lime sarcophagus limestone that measures 3.3 feet high, 5.4 feet long, and 2.6 feet wide, with a 1,700-pound lid held in place by iron pegs sealed with lead. The archaeologists first did X-rays on the sarcophagus then used an endoscopic camera. They found a skeleton of a woman inside, alongside a number of other objects, including a mirror.
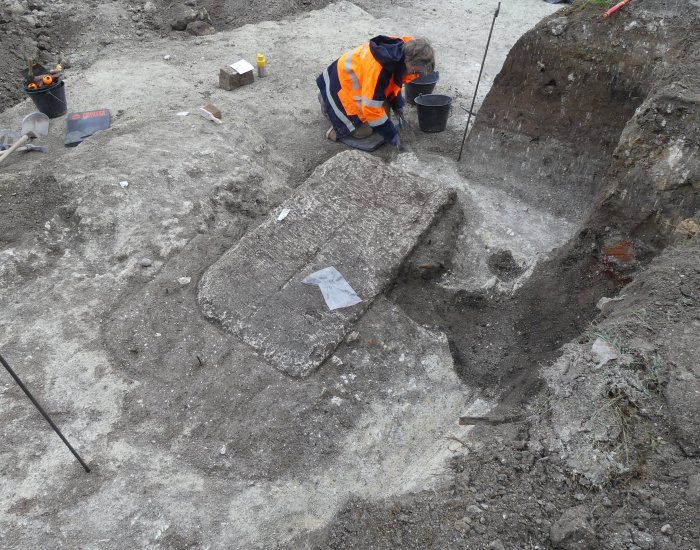

“It’s quite exceptional, it’s the first time that we have found a tomb intact and which has not been looted. It was sealed by eight iron staples, and we were the first to explore it,” Agnès Balmelle, deputy scientific and technical director at Inrap Grand Est, told local news Le Parisien.
“The skeleton occupied the entire space of the [5-foot] tank, the individual must have been around 40 years old and had a special status. Four oil lamps were found near her legs and shoulders, as well as a small mirror, an amber ring and a comb,” Balmelle added.
Inside the sarcophagus were also two glass containers possibly containing perfumed oils.
The unearthed items indicate that the burial occurred in the 2nd century A.D. Samples of the sediment on the bones and on the bottom of the tank will make it possible to determine if there are plant remains or products linked to the treatment of bodies.
Cover Photo: France’s National Institute of Preventive Archeology (INRAP)