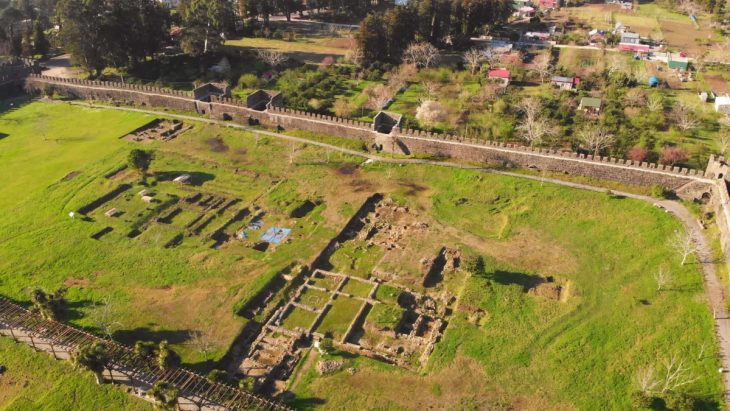
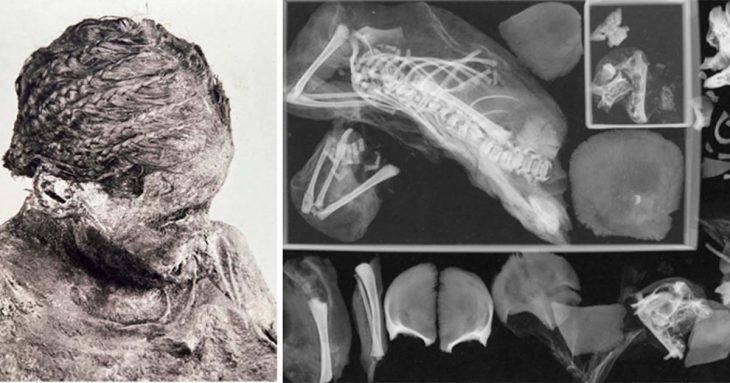
Archaeologists have uncovered a pre-Dong Son settlement in northern Vietnam dating back nearly 3000 years.
Researchers from the Institute of Archaeology have uncovered important Bronze Age finds at the Vuon Chuoi Archaeological Site in Lai Xa Hamlet, Kim Chung Commune, Hoai Duc District, Hanoi. These findings shed light on the organized society that once existed in northern Vietnam.
Dong Son culture is named for a village in northern Vietnam (named for the modern village Đông Sơn, a village in Thanh Hóa, Vietnam) where many of its remains have been found. It was a Bronze Age culture centered at the Red River Valley of northern Vietnam from 1000 BC until the first century AD.
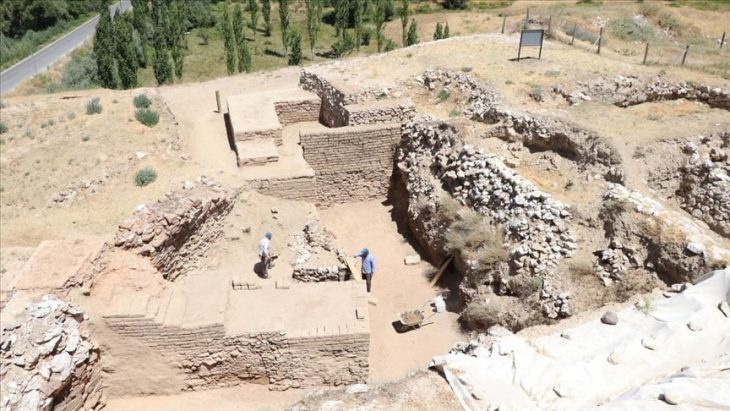
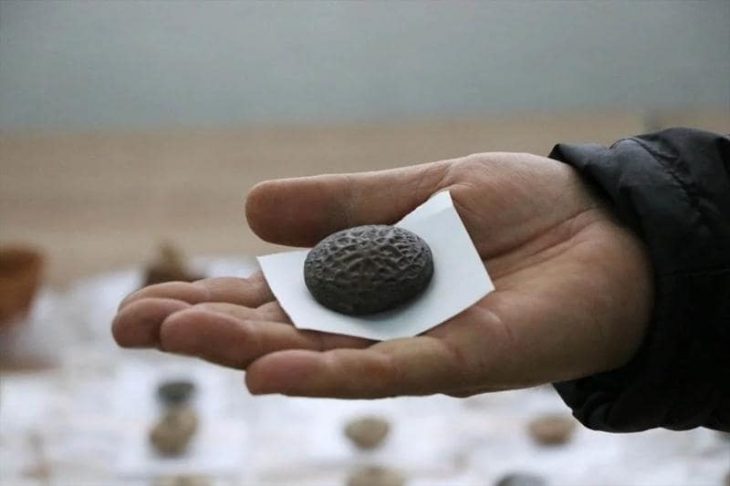
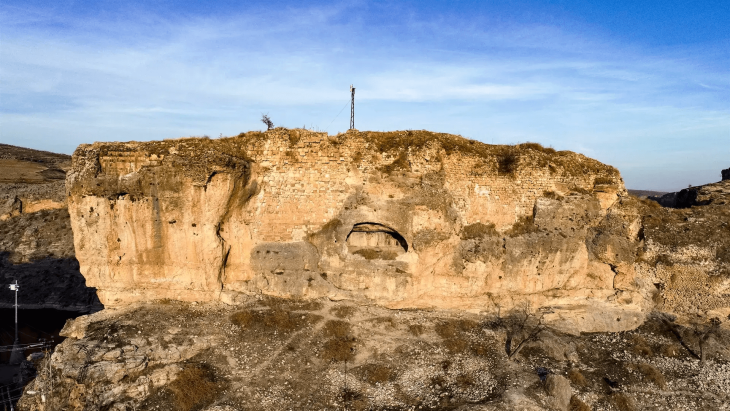
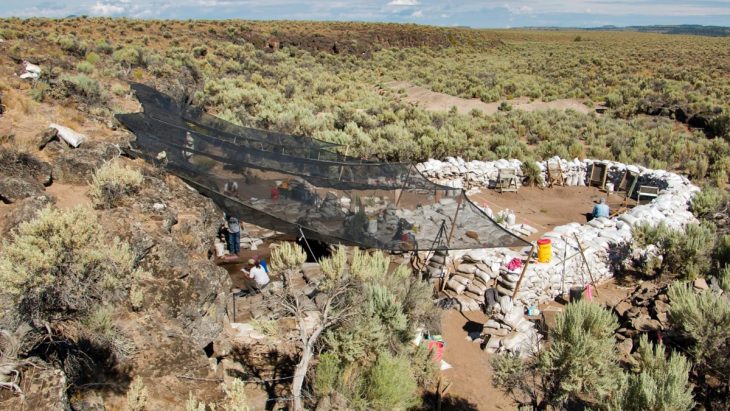
The excavation on the western side of the Vuon Chuoi site spanned 6,000 square meters, according to Dr. Nguyen Ngoc Quy, a researcher at the Institute of Archaeology. Numerous pits, each measuring roughly 100 square meters, were dug up, yielding important preliminary results.
“The initial discoveries revealed a settlement area from the pre-Dong Son period,” said Dr. Quy. “The site is situated on the highest point of the Vuon Chuoi mound, featuring a basin-like structure with the outer edges elevated by about 0.5 meters compared to the center. It appears that ancient people took advantage of both natural elevated and lower terrain to create a settlement, surrounded by a protective moat about 10 meters wide and 2.5 to 3 meters deep.”

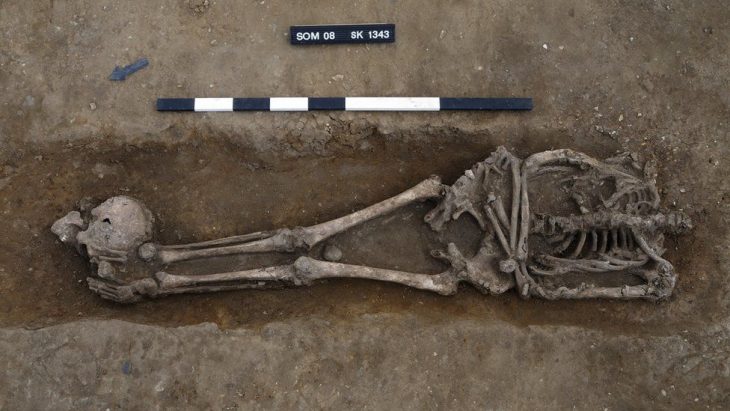
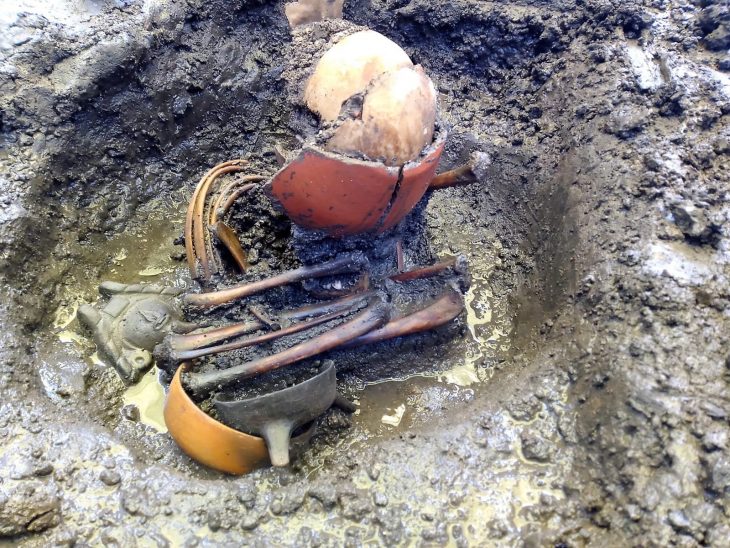
Based on observations, the building material was probably yellow-brown clay that was taken from nearby natural mounds. The site’s outer slopes contain burial sites, while the interior displays remnants of pre-Dong Son cultural periods. A dense burial area that formed a necropolis from at least two overlapping periods was found in the northwest corner in particular.
“These discoveries are pivotal for understanding the Bronze Age in Northern Vietnam,” Dr. Quy noted. “They provide deeper insights into how ancient communities managed their living spaces to address challenges posed by both natural and social environments. The scale of construction at this site also indicates a well-organized society with a high level of labor division.”
Despite these important results and the near completion of the excavation at Vuon Chuoi, conservation work is progressing very slowly. To guarantee the site’s protection, the Institute of Archaeology and other pertinent organizations have been submitting paperwork to authorities since 2019. The only portion of Vuon Chuoi that has been designated as a heritage site under inventory is the eastern portion, which was permitted to be preserved.
Hanoi Museum representatives have promised, that the Heritage Management Department will collaborate closely with the Hoai Duc District’s Cultural Department to expedite the process of recommending Vuon Chuoi’s designation as an officially recognized archaeological site.
Cover Image Credit: Vietnam Institute of Archaeology