Excavations at Haldensleben in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt provide important information about a lost settlement.
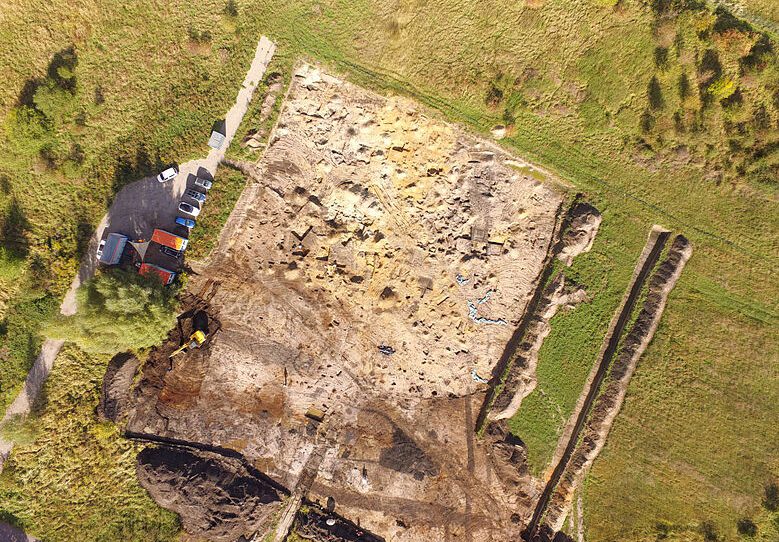
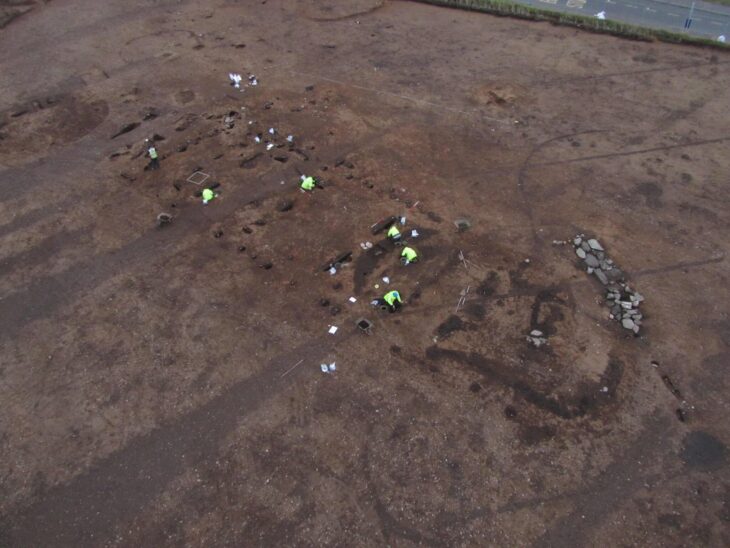
Since May 2024, the State Office for Monument Preservation and Archaeology (LDA) Saxony-Anhalt has been conducting archaeological investigations on the site of the Hermes Fulfilment GmbH shipping center in Haldensleben. The excavations are taking place in an area immediately east of an extraordinary castle complex from the High Middle Ages (from AD 1000 to 1300) that was excavated in 2010/11. As part of the renewed investigations, significant settlement findings from the Bronze and Iron Ages as well as the Middle Ages were archaeologically documented.
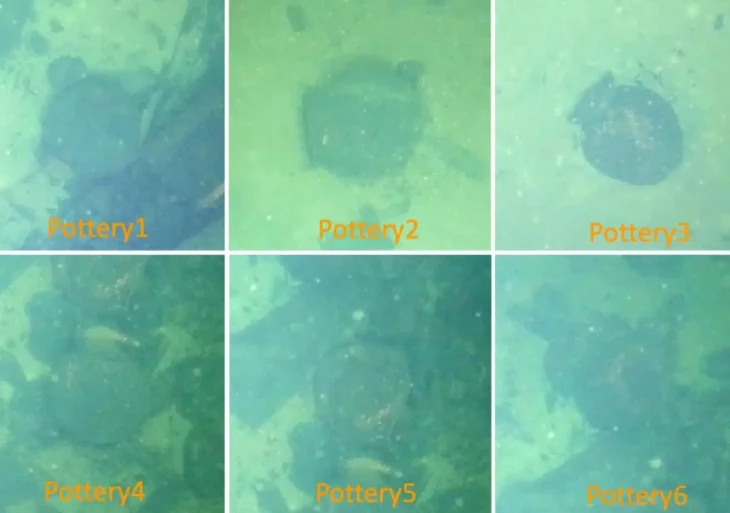
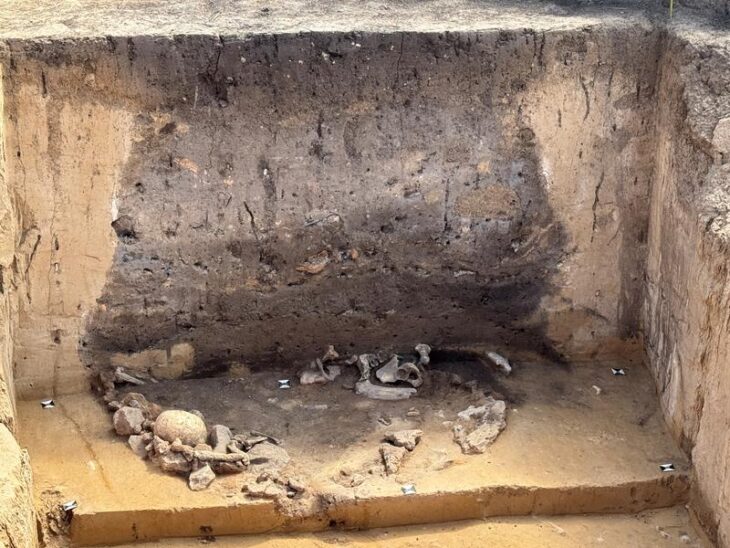
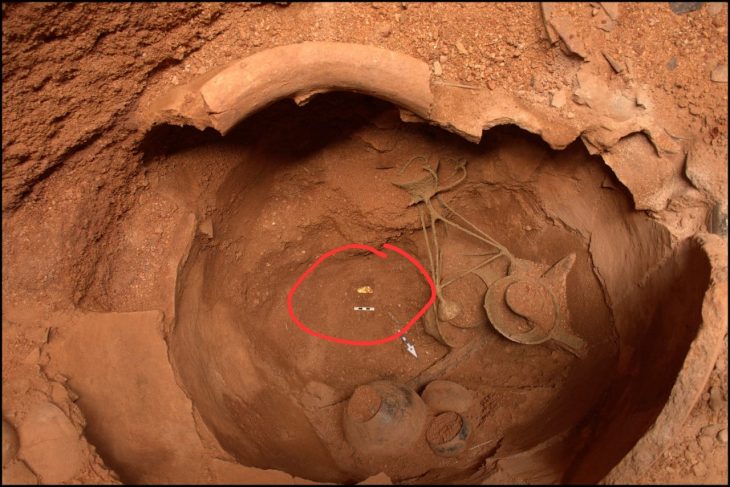
The earliest phase of settlement dates from the Bronze Age (circa 2200 BC to 750 BC), where the researchers found various settlement pits, ceramics, animal bones, and a well containing a fully intact vessel.
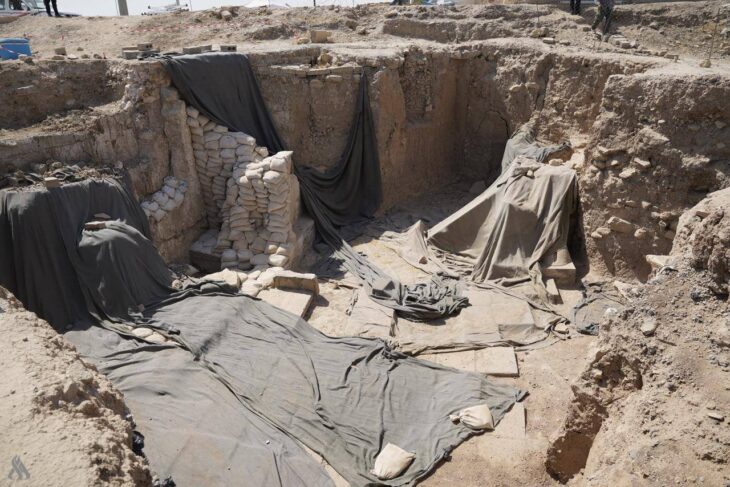
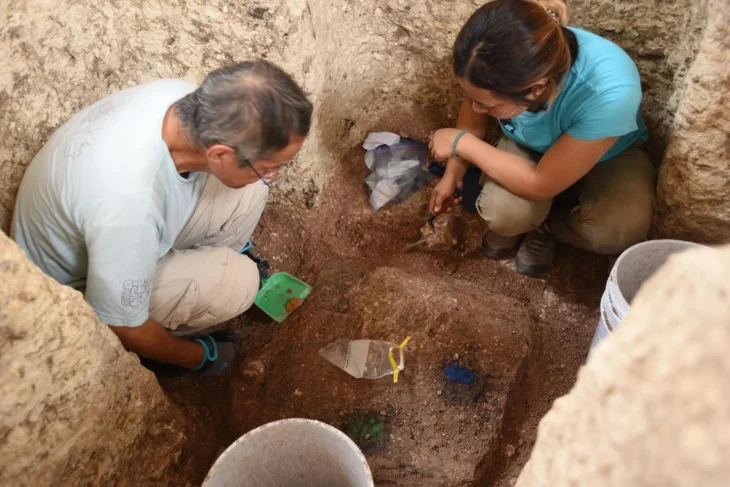
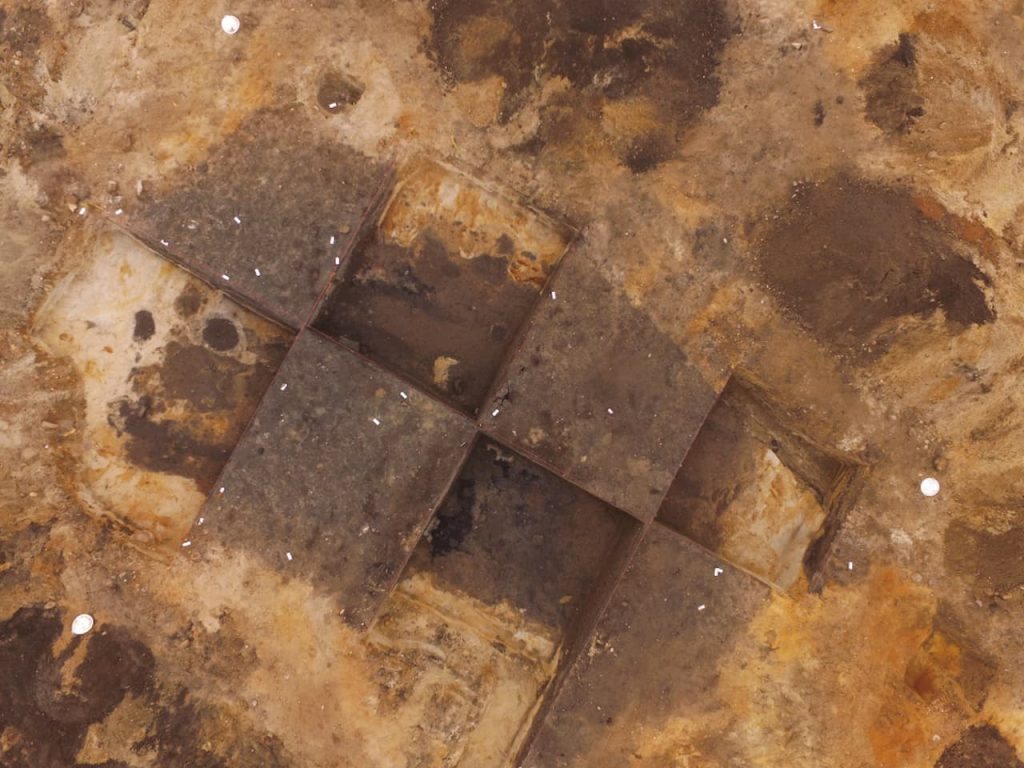
Undoubtedly, the most interesting discoveries of the excavation were the remains of looms from the 11th and 12th centuries and a large underground structure where remnants of looms and numerous weaving-related items, such as loom weights and spindle whorls, were found.

Prehistoric and early historical settlement
The excavation site is located on a flat sand/gravel terrace that juts out into the Ohre lowlands. Due to the extremely favorable location of the site on the river in terms of traffic and settlement topography, it is not surprising that it was already in use before the Middle Ages.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Numerous findings suggest intensive settlement during the Bronze Age (around 2200 BC to 750 BC). In addition to settlement pits, a well into which a completely preserved vessel had fallen was uncovered and numerous settlement finds such as ceramics and animal bones were recovered.
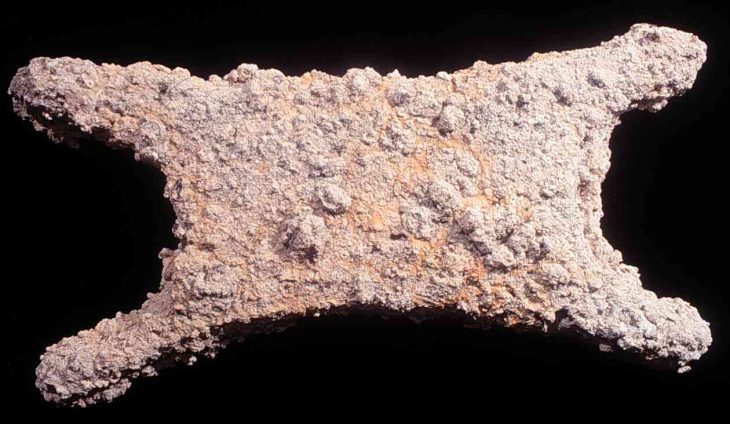
The most interesting find from this era is a bronze eyelet headpin from the Aunjetitz culture. Numerous settlement finds from the Iron Age (approximately from 750 BCE to the beginning of the Christian era) were also uncovered. A lime kiln is particularly noteworthy from this period.

The medieval settlement at the castle
Before the construction of the fortress found in the 2010-2011 excavations, which dates to the second half of the 11th century, the terrace along the Ohre River remained a significant occupation site during the early and high medieval periods, particularly in the 9th and 10th centuries. Excavations have uncovered twelve underground buildings and numerous posts of above-ground structures. This evidence suggests that the land was inhabited by a well-organized and active community long before the fortress was constructed.
Remains of small ovens were uncovered in some of the sunken buildings from this older phase. To the north and northwest, the settlement was bordered by the Ohre, to the southwest and south by a wide ditch, which probably served primarily to drain groundwater.
In the 11th/12th century, the settlement, which was now connected to the already known, mighty castle complex in the southwest, expanded southwards over the ditch. A pointed ditch was dug to secure the castle settlement. However, no remains of the assumed associated fortification wall have survived. Some of the pit houses in the settlement are unusually large.
Of particular importance is a larger pit house, in which traces of looms and numerous loom weights and spindle whorls provide evidence of textile production. This building appears to have been a textile production center, a characteristic feature of settlements around lordly fortresses in this era.
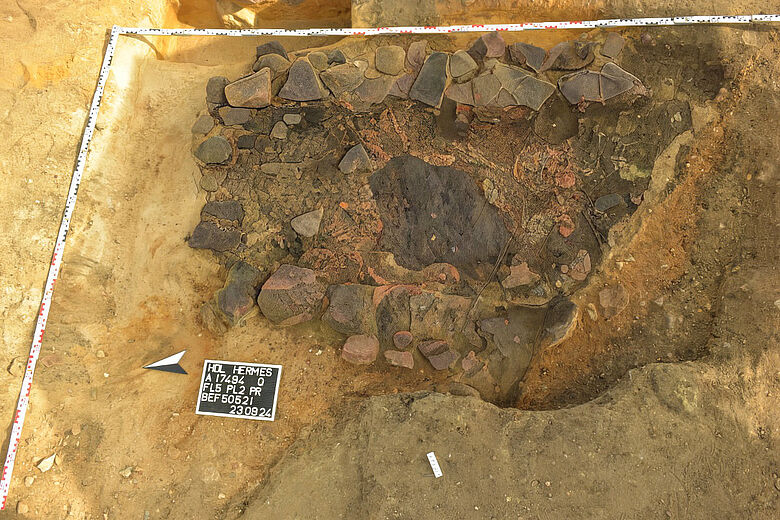

Some of the above-ground structures are notable for having sophisticated heating systems. The remains of complex stone ovens that, because of their design, enabled homes to be heated without emitting smoke were discovered by archaeologists. One building even featured a stone cellar, a unique element that suggests it may have served as a safe haven or as storage.
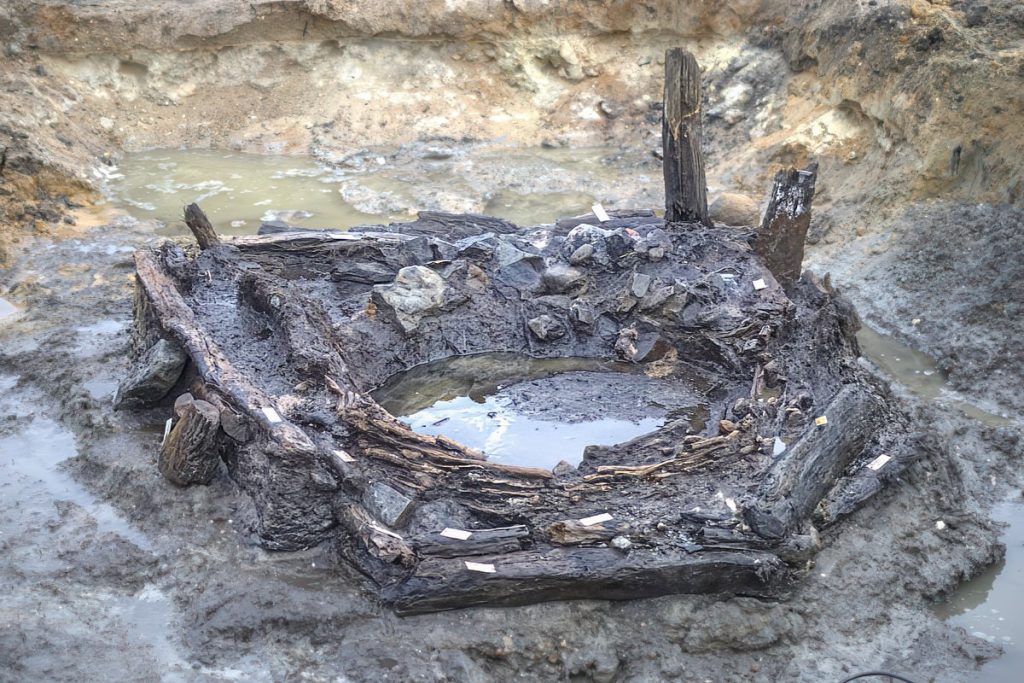
According to the finds, some of the houses were in use even after the destruction of the adjacent castle in 1167 until the end of the 13th century. This also applies to three very different wells or water extraction points in the southern part of the excavation area, which is characterized by strata water coming to the surface. A pentagonal wooden structure is unusual, in which a round wickerwork installation was located, separated by a stone packing. The inner construction probably served to purify water. Another well consisted of a wooden barrel used for secondary purposes.
Among the finds, in addition to characteristic spherical pots made of ceramic, iron knives, bronze fittings, an ornate bone comb, and bronze awls and needles deserve mention.
Cover Image Credit: State Office for Monument Preservation and Archaeology Saxony-Anhalt- Bodo Hänler