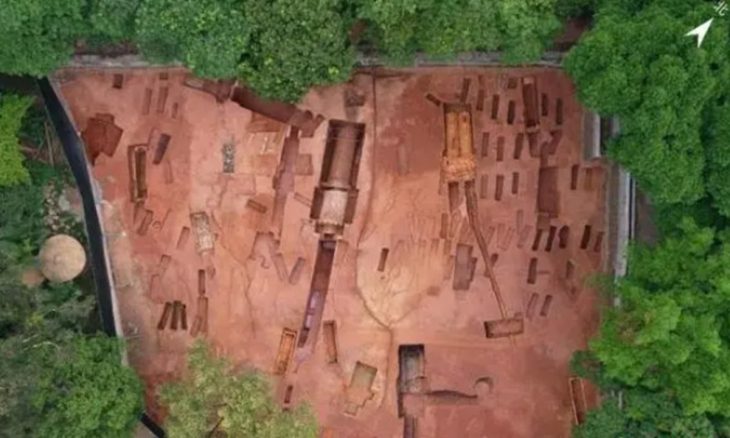
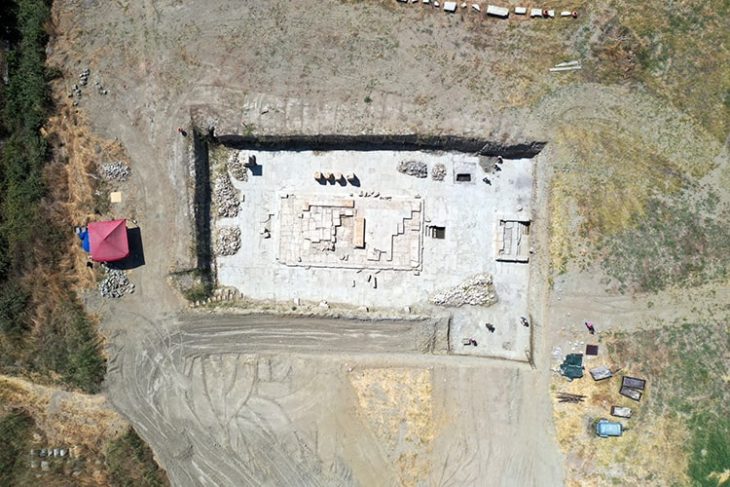
Researchers at the University of Cincinnati find evidence of cosmic cataclysm 1,500 years ago at 11 ancient sites in three states stretching across the Ohio River Valley.
This was home to the Ohio Hopewell, part of a notable Native American culture found across what is now the eastern United States.
The Ohio Hopewell Culture or Hopewell Culture was a widely dispersed set of Native American population connected by a common network of trade routes from 100 BC to AD 500 in the Middle Woodland period.
The comet’s glancing pass rained debris down into the Earth’s atmosphere, creating a fiery explosion. UC archaeologists used radiocarbon and typological dating to determine the age of the event.
The airburst affected an area bigger than New Jersey, setting fires across 9,200 square miles between the years A.D. 252 and 383. This coincides with a period when 69 near-Earth comets were observed and documented by Chinese astronomers and witnessed by Native Americans as told through their oral histories.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
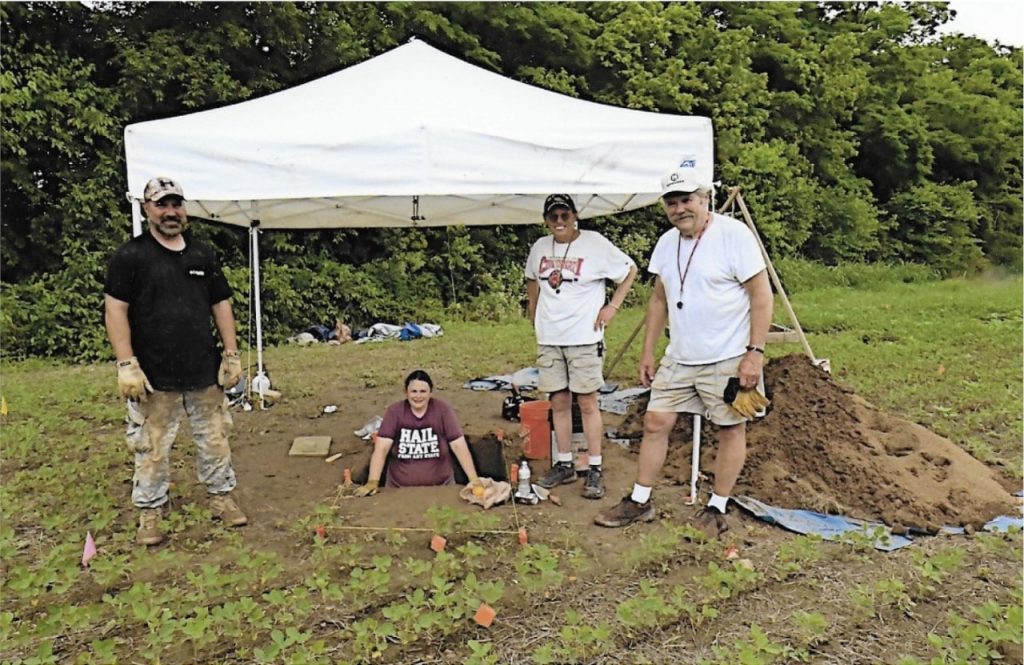

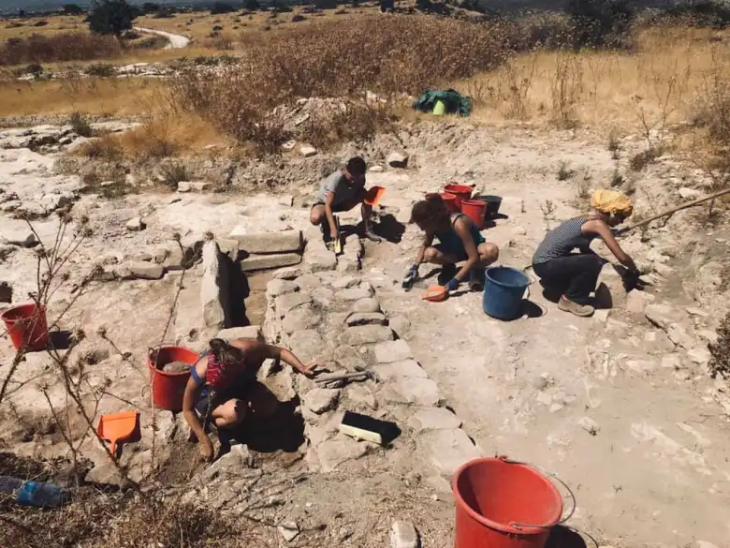
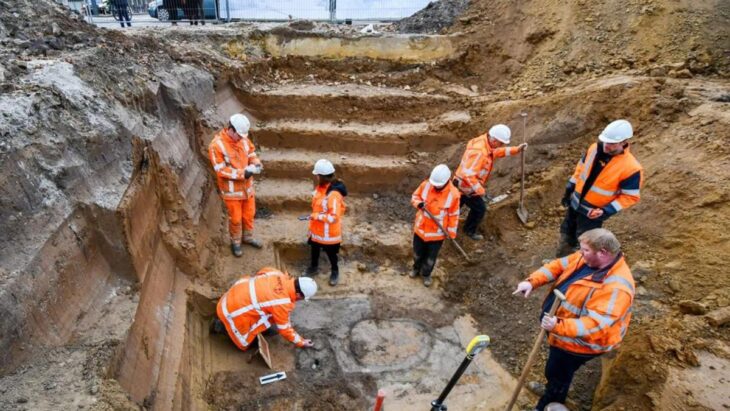
The study, published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports found an unusually high concentration and diversity of meteorites at Hopewell sites compared to other time periods. The meteorite fragments were identified from the tell-tale concentrations of iridium and platinum they contained. They also found a charcoal layer that suggests the area was exposed to fire and extreme heat.
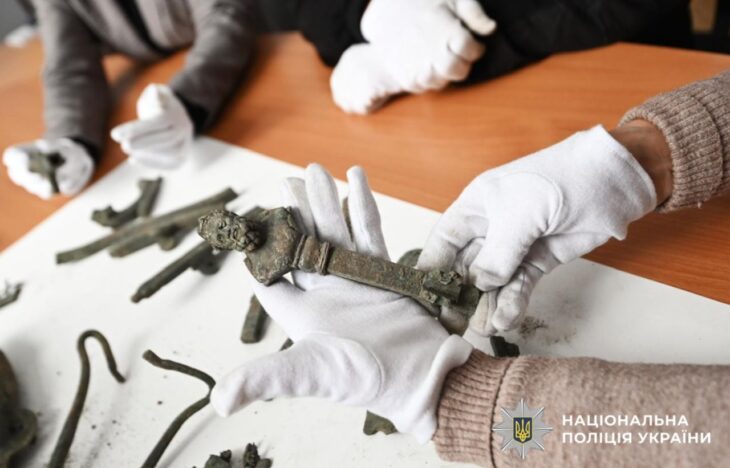
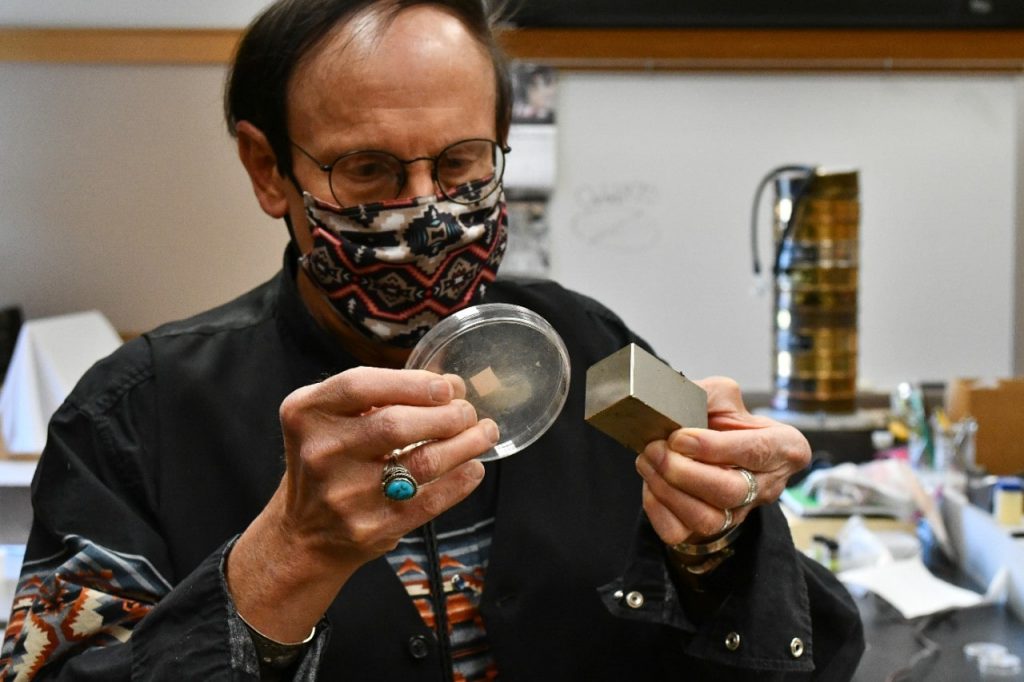
In his lab, lead author Kenneth Tankersley, a professor of anthropology in UC’s College of Arts and Sciences, held up a container of tiny micrometeorites collected at the sites. A variety of meteorites, including stony meteorites called pallasites, were found at Hopewell sites.
“These micrometeorites have a chemical fingerprint. Cosmic events like asteroids and comet airbursts leave behind high quantities of a rare element known as platinum,” Tankersley said. “The problem is platinum also occurs in volcanic eruptions. So we also look for another rare element found in nonterrestrial events such as meteorite impact craters — iridium. And we found a spike in both, iridium and platinum.”
The Hopewell people collected the meteorites and forged malleable metal from them into flat sheets used in jewelry and musical instruments called pan flutes.
Beyond the physical evidence are cultural clues left behind in the masterworks and oral histories of the Hopewell. A comet-shaped mound was constructed near the epicenter of the airburst at a Hopewell site called the Milford Earthworks.
Various Algonquin and Iroquoian tribes, descendants of the Hopewell, spoke of a calamity that befell the Earth, said Tankersley, who is Native American.
“What’s fascinating is that many different tribes have similar stories of the event,” he said.
“The Miami tell of a horned serpent that flew across the sky and dropped rocks onto the land before plummeting into the river. When you see a comet going through the air, it would look like a large snake,” he said.
“The Shawnee refer to a ‘sky panther’ that had the power to tear down forest. The Ottawa talk of a day when the sun fell from the sky. And when a comet hits the thermosphere, it would have exploded like a nuclear bomb.”

And the Wyandot recount a dark cloud that rolled across the sky and was destroyed by a fiery dart, Tankersley said.
“That’s a lot like the description the Russians gave for Tunguska,” he said of a comet airburst documented over Siberia in 1908 that leveled 830 square miles of forest and shattered windows hundreds of miles away.
“Witnesses reported seeing a fireball, a bluish light nearly as bright as the sun, moving across the sky. A flash and sound similar to artillery fire was said to follow it. A powerful shockwave broke windows hundreds of miles away and knocked people off their feet,” according to a story in EarthSky.
UC biology professor and co-author David Lentz said people who survived the airburst and its fires would have gazed upon a devastated landscape.
“It looks like this event was very injurious to agriculture. People didn’t have good ways to store corn for a long period of time. Losing a crop or two would have caused widespread suffering,” Lentz said.
And if the airburst leveled forests like the one in Russia, native people would have lost nut trees such as walnut and hickory that provided a good winter source of food.
“When your corn crop fails, you can usually rely on a tree crop. But if they’re all destroyed, it would have been incredibly disruptive,” Lentz said.
UC’s Advanced Materials Characterization Center conducted scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectrometry of the sediment samples. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry was employed at the University of Georgia’s Center for Applied Isotope Studies. The U.S. Geological Survey provided stable carbon isotope analysis.
Despite what scientists know, there is still much they do not, Lentz said.
“It’s hard to know exactly what happened. We only have a few points of light in the darkness,” he said. “But we have this area of high heat that would have been catastrophic for people in that area and beyond.”
Now researchers are studying pollen trapped in layers of sediment to see how the comet airburst might have changed the botanical landscape of the Ohio River Valley.
Co-author Steven Meyers, a UC geology alumnus, said their discovery might lead to more interest in how cosmic events affected prehistoric people around the world.
“Science is just a progress report,” Meyers said. “It’s not the end. We’re always somewhere in the middle. As time goes on, more things will be found.”