Archaeologists in Mexico have discovered a 16th-century altar in Plaza Garibaldi, the center in Mexico City famous for its revelry and mariachi music.
After Hernan Cortes conquered the Aztec city of Tenochtitlan in modern-day Mexico City in 1521, one indigenous household that had survived the brutal Spanish assault set up an altar with incense and a container containing human ashes.
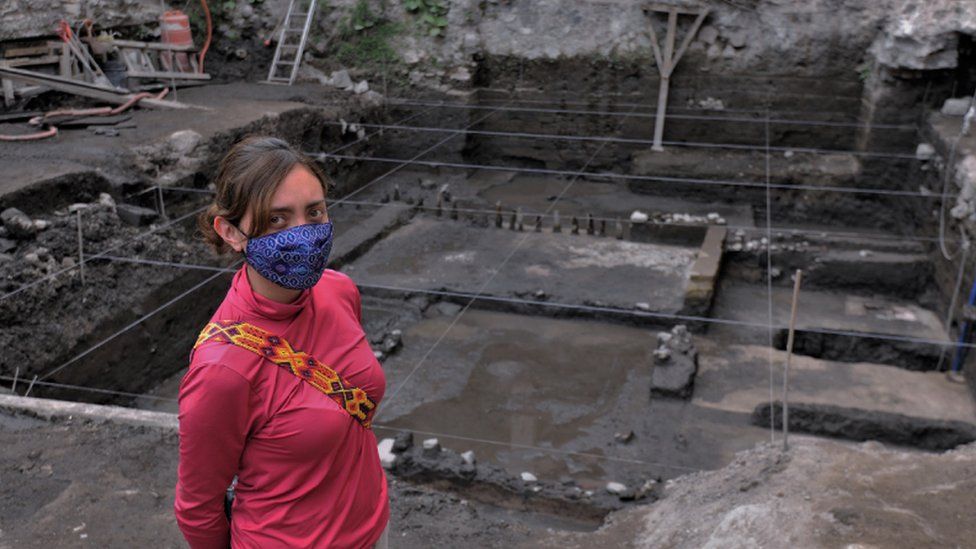
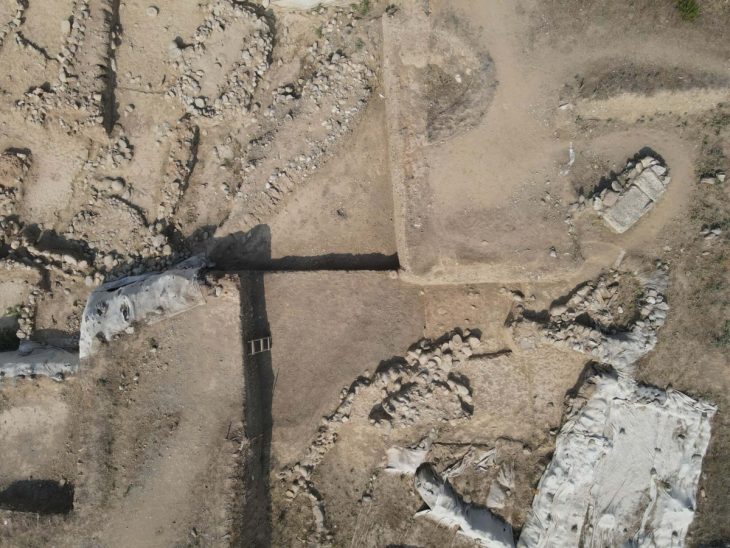
The discovery was made in August, but archaeologists spent three months investigating the site before it was publicized by Mexico’s National Institute for Anthropology and History (Inah) on Tuesday.
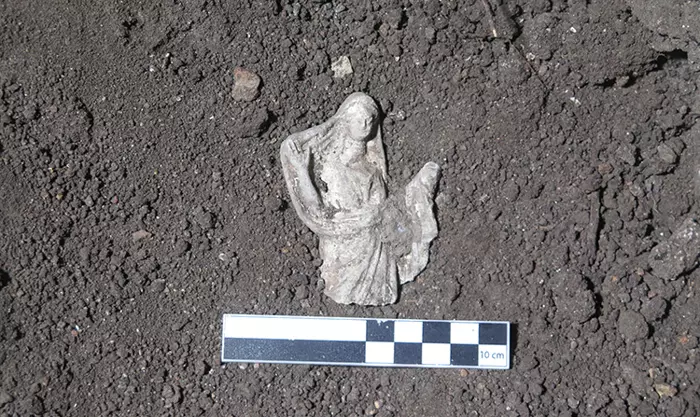
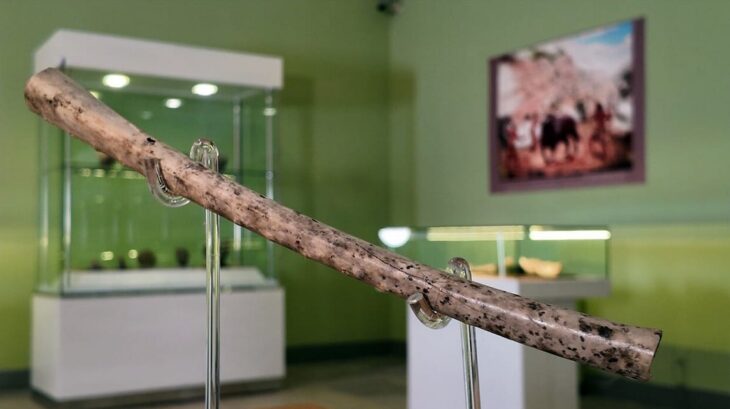
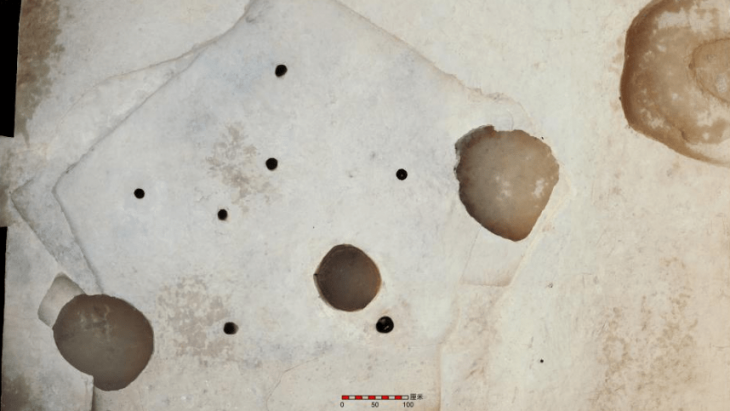
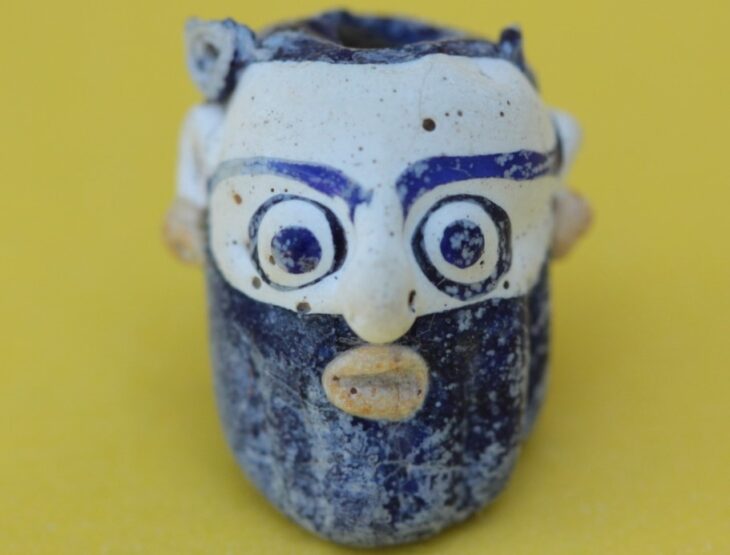
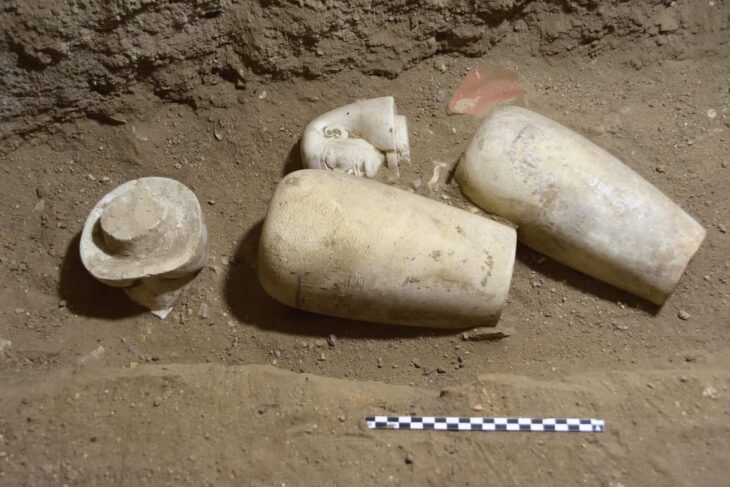
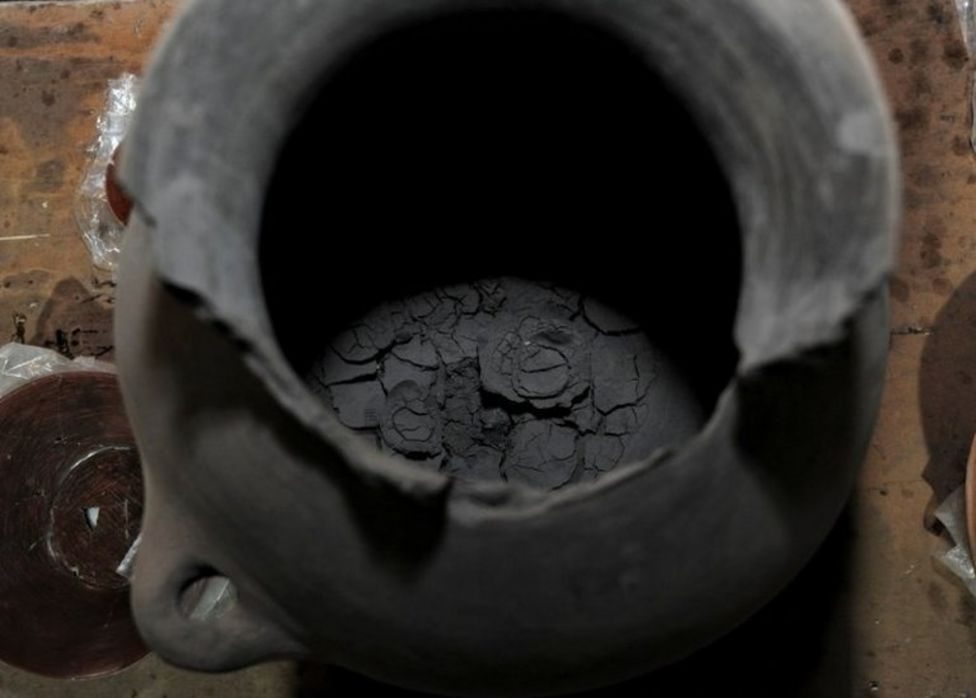
In honor of this fading world, the inhabitants of this former home unit performed a ritual in the 16th century, probably between 1521 and 1610 AD, to witness that this was the end of a cycle of their lives and civilizations. Between the songs and the smell of copal, the residents held an offering in the courtyard, which included various elements, including a pot with bone remains (human ashes) and 13 multicolored incense burners, about one meter long, used to burn the resin.

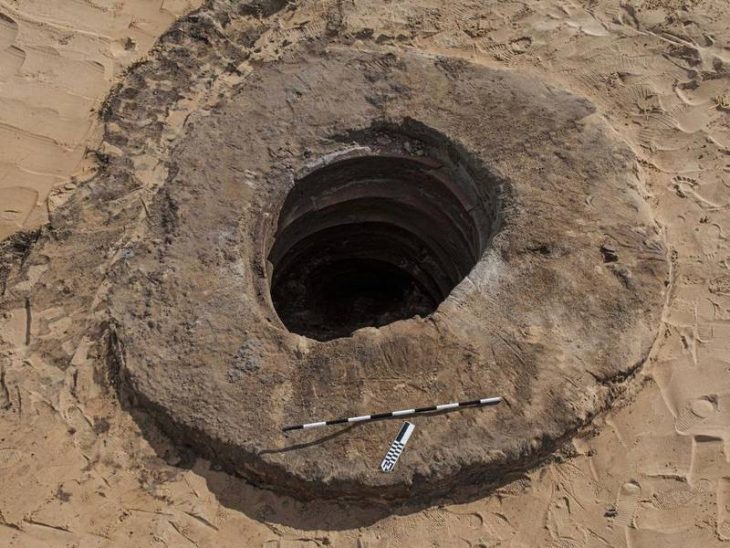
The interior patio where rituals took place is about four meters (13 feet) below ground level, according to a team of archaeologists who spent three months analyzing the site.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
They found various layers of what had been home over the centuries, the statement said, along with 13 incense burners, five bowls, a cup, a plate, and a pot with cremated skeletal remains.
The house surrounding the altar was made up of a large room that was connected by a corridor to five smaller rooms, one of which is believed to be a kitchen.
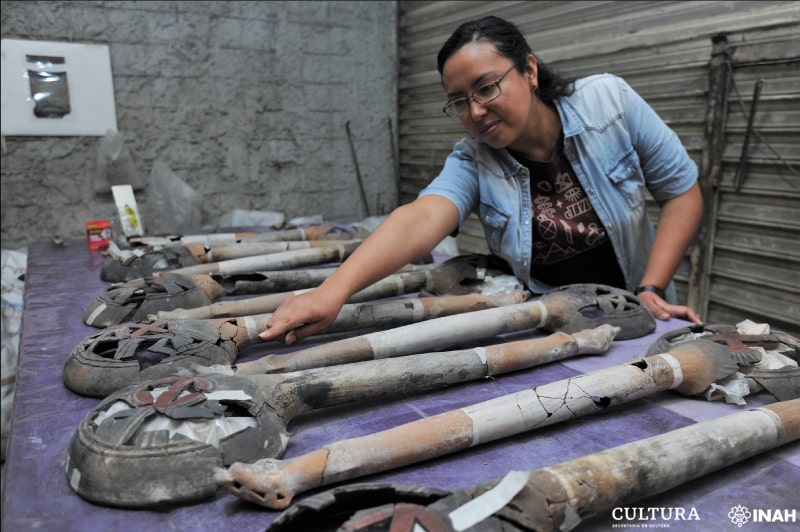

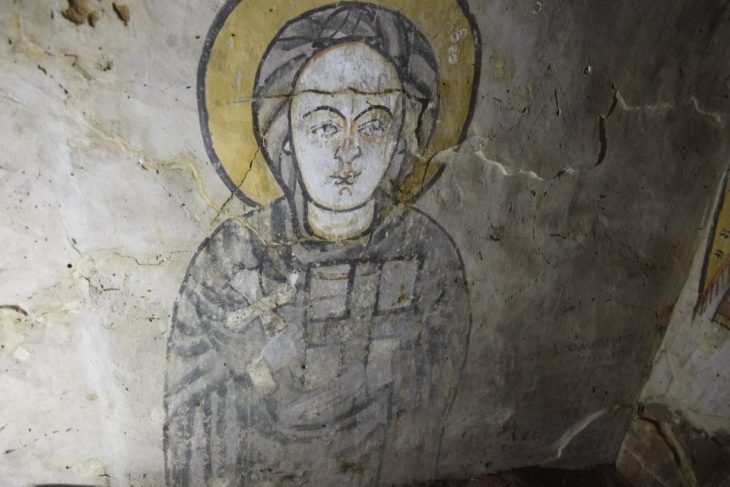
Archaeologist Mara Becerra states that this residence was the cause of spatial and architectural changes in at least two stages: in the Late Postclassical period between AD 1325 and 1521, and during the Spanish occupation between AD 1521 and 1610. Material evidence such as omichicahuaztlis (musical instruments made of worked bone), flute, and ocarina indicate that various rituals took place here.
According to Ms. Becerra, the inhabitants of the house wanted to hide it from the prying eyes of the Spanish conquistadors.
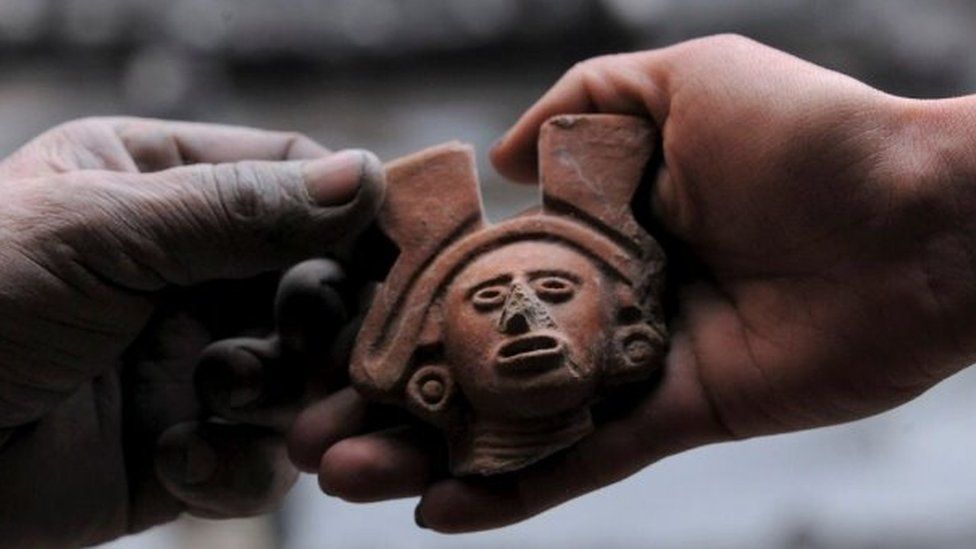

She believes they were Mexica, the indigenous people who lived in the Valley of Mexico and who founded the Aztec empire.
This discovery is the result of permanent works carried out by the INAH Directorate of Archaeological Rescue, whose specialists monitor the research, conservation, preservation, and dissemination of the cultural heritage of Mexico’s paleontological, anthropological, archaeological, and historical nature.
Cover Photo: The altar was found underneath a modern home near Plaza Garibaldi in Mexico City. Photograph by Mauricio Marat. INAH