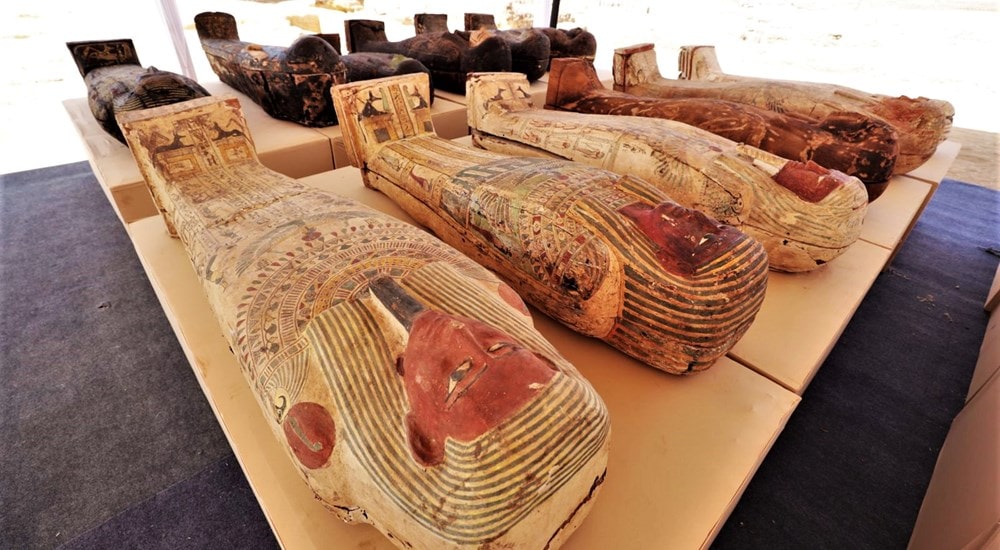
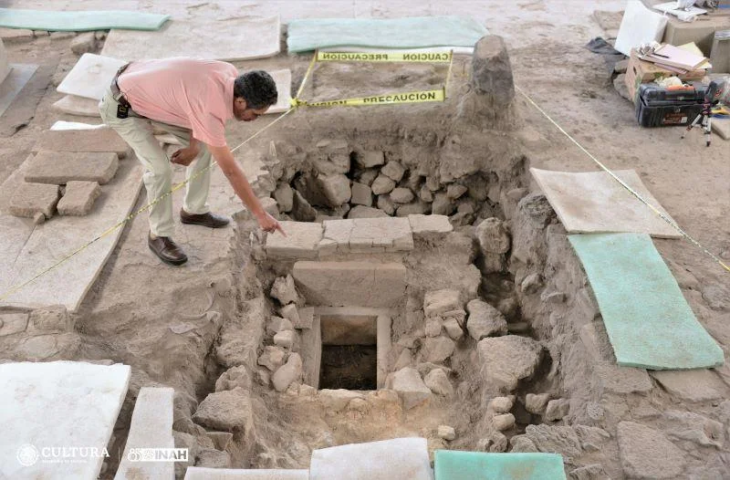
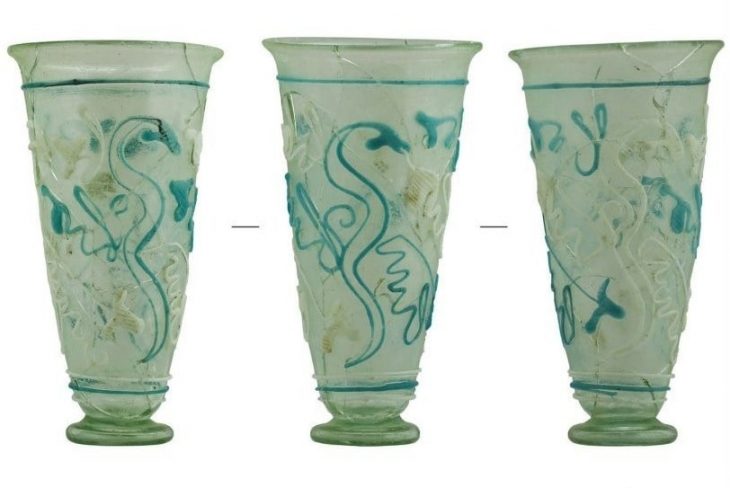
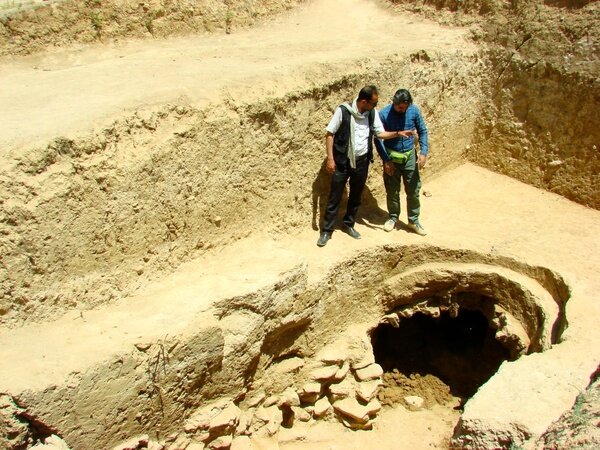
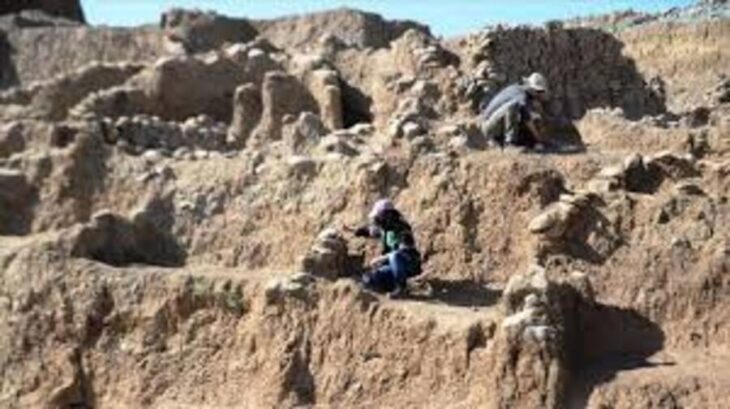
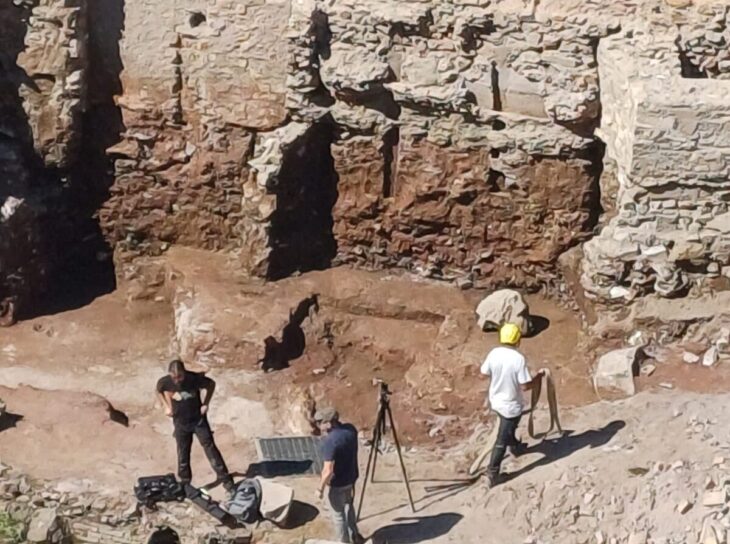
Archaeologists at the necropolis of Saqqara, near Cairo, have discovered a cache of 250 complete mummies in painted wooden sarcophagi and the largest caches of bronze statues -150 in total- ever found at the site.
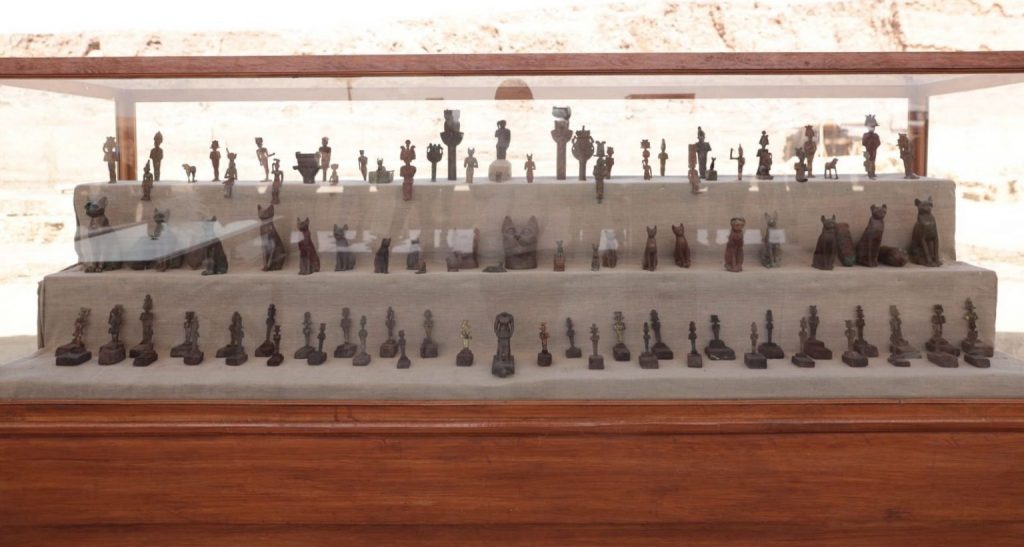
The discovered statues of the gods Anubis, Amun, Min, Osiris, Isis, Nefertum, Bastet, and Hathor along with a headless statue of the architect Imhotep, who built the Saqqara pyramid, Egypt’s ministry of tourism and antiquities said recently.
They were accompanied by a musical instrument known as a sistrum and a collection of bronze vessels used in rituals for the worship of the goddess Isis.
The ministry said that 250 sarcophagi and 150 bronze statues were dated to the Late Period, around 500 BC. Excavations have been ongoing since 2018, where previously the team discovered 100 wooden coffins back in 2020.

The antiquities were the fifth and latest major find from an archaeological mission at Saqqara’s Cemetery of Sacred Animals that began in 2018 and are expected to continue for years to come. So far only a quarter has been excavated.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The trove was found at Saqqara’s “Cemetery of Ancient Animals,” a temple complex outside Cairo once dubbed “Bubasteion” — a reference to the ancient Egyptian goddess Bast or Bastet, who was worshiped there in the form of a cat, CBS News reported. The complex was renamed in 2019, however, after archaeologists discovered other types of mummified animals and statues of different Egyptian gods there.
“Today’s discovery confirms that the temple wasn’t exclusively for cats, but for other Egyptian deities too,” Mohamed Al Saidi, the mission’s director, told CBS News.
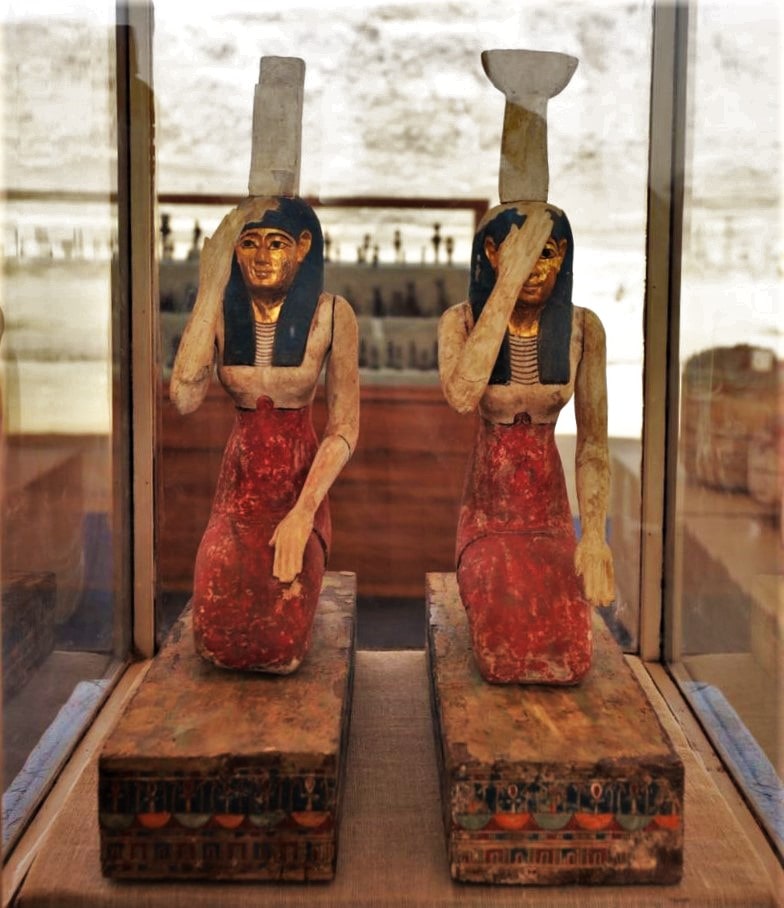

The mission also found two colored wooden statues of the goddesses Isis and Nephthys posed as mourners, and a burial well from around 1500 BC with adornments such as necklaces, bracelets, earrings, and even a bronze mirror.
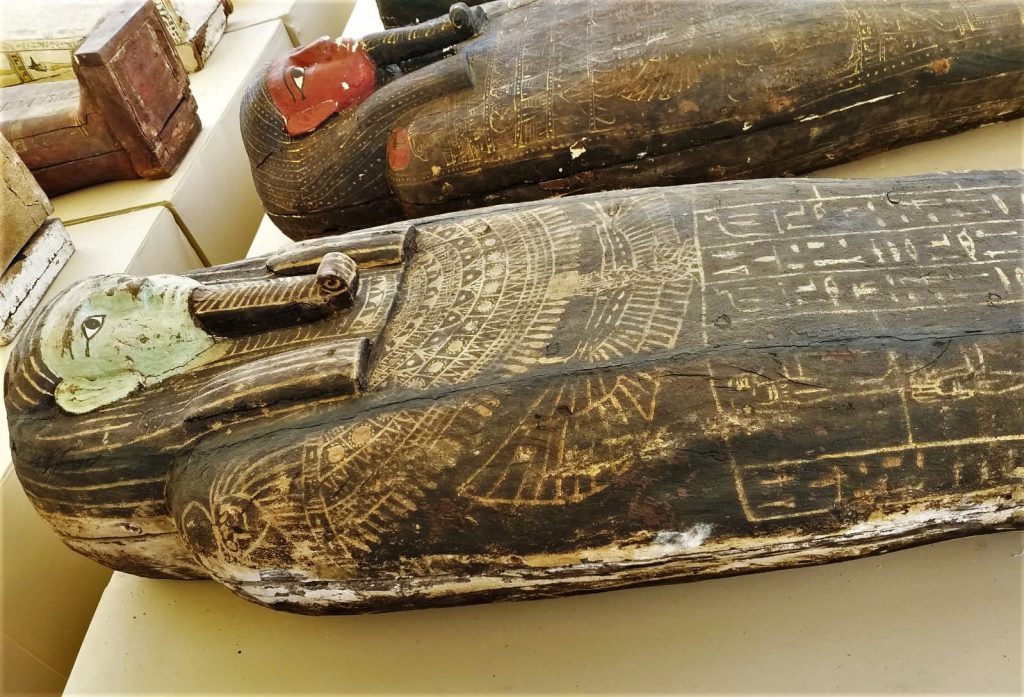
Excavations identified a series of burial wells, in which colored wooden sarcophagi were recovered. The sarcophagi appear to have remained undisturbed by tomb robbers and still contain burials and various ornaments.
One sarcophagus contained a well-preserved papyrus written in hieroglyphs, perhaps verses of the Book of the Dead, and was sent to the Egyptian Museum in Cairo laboratory for study, said Mostafa Waziri, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities.

A collection of cosmetics was found, including kohl containers, as well as bracelets and earrings.
The sarcophagi will be transferred for display at the Grand Egyptian Museum under construction near the Great Pyramids of Giza and are due to open later this year.
Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Photo: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities