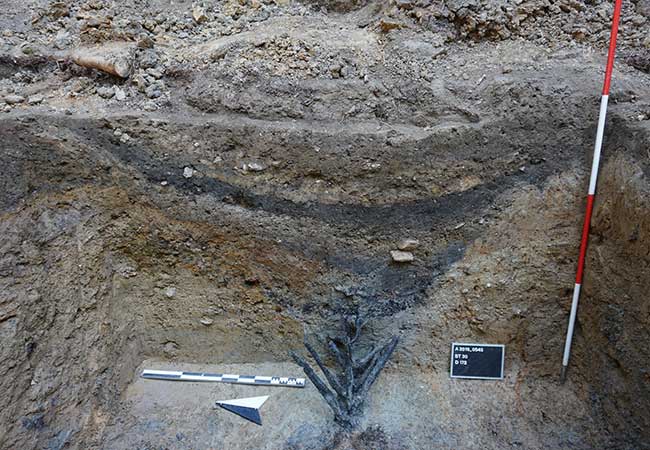
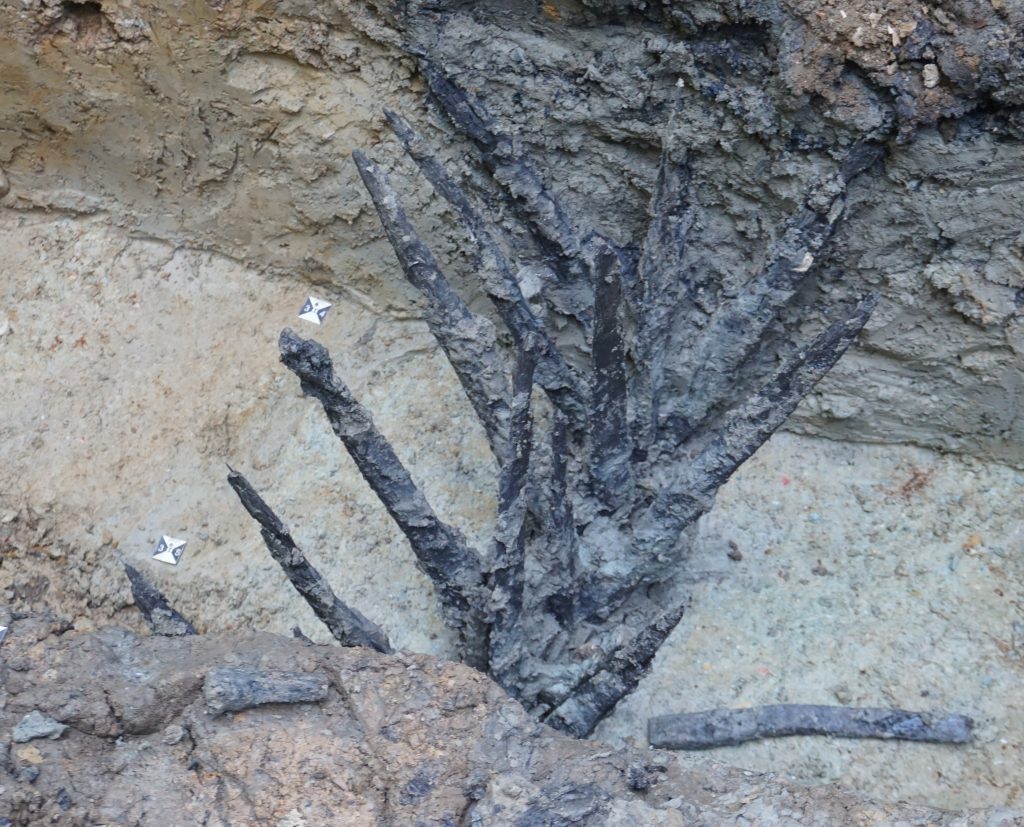
Archaeologists have discovered wooden defenses surrounding an ancient Roman military base for the first time in Bad Ems, western Germany. The fence, which is topped with sharpened wooden stakes similar to barbed wire, is the type of fortification mentioned in ancient writings, including by Caesar, but no surviving examples had previously been discovered.
The spikes were mounted in a v shape onto a central post and were preserved in the water-logged soil of Blöskopf hill. Enemies who fell into the defensive ditch would come face to face with the business ends of this razor-sharp structure.
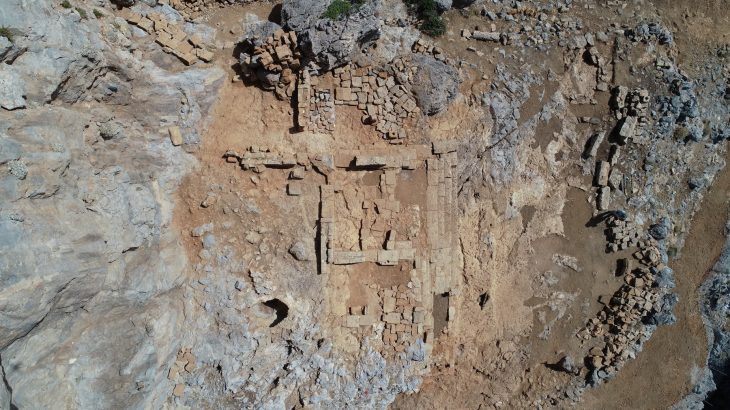
The work of the Frankfurt archaeologists and Dr. Peter Henrich of the General Directorate for Cultural Heritage of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate uncovered two previously unknown military camps in the vicinity of Bad Ems, situated on both sides of the Emsbach valley.
The excavations were triggered by observations made by a hunter who, from his raised hide, spotted color differences in the grain field, indicating the existence of sub-surface structures. Drone photography and geomagnetic scans confirmed the presence of large double ditches beneath the grain, which formed the defensive perimeter of a Roman camp. It would have been a massive Roman camp: eight hectares with 40 wooden towers — much larger than the known Bad Ems camp. It was supposed to be permanent, but it was never finished. Only a warehouse was built in the end, and the camp was burned down a few years later.
A second, much smaller camp, was unearthed a mile away. The stake structure was part of the defenses of this second camp.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

It appears that the ancient Romans were tunneling into the earth in search of silver deposits. Archaeologists initially thought that fire remains and melted slag proved that the Romans had established smelting works to process silver ore.
The Roman governor Curtius Rufus attempted to mine silver in the region in the year 47 A.D., but his efforts were unsuccessful, according to the writings of the ancient historian Tacitus. The Romans had built a heavily fortified base with a military presence because they anticipated untold riches; this accounts for the defenses that resemble barbed wire and were intended to thwart sudden raids.
Unfortunately for them, it would take millennia for archaeological excavations in 1897 to find a rich vein of the precious metal in the region. If the Romans had only kept digging, they could have kept mining for two centuries because there was enough silver there. It appears that the ancient fire’s remnants came from a watch tower rather than a successful smelting operation.
Excavations and research are set to continue, led by Markus Scholz, a professor of archaeology and ancient Roman history at Goethe University; archaeologist Daniel Burger-Völlmecke; and Peter Henrich of Rhineland-General Palatinate’s Directorate for Cultural Heritage.
The ancient wooden spikes are now at the Römisch-Germanisches Zentralmuseum in Mainz.
Frederick Auth, who has been in charge of the excavations since 2019, won first place for his description of the history of the site at the 2022 Wiesbaden Science Slam. These futile ancient efforts make for a fascinating story.