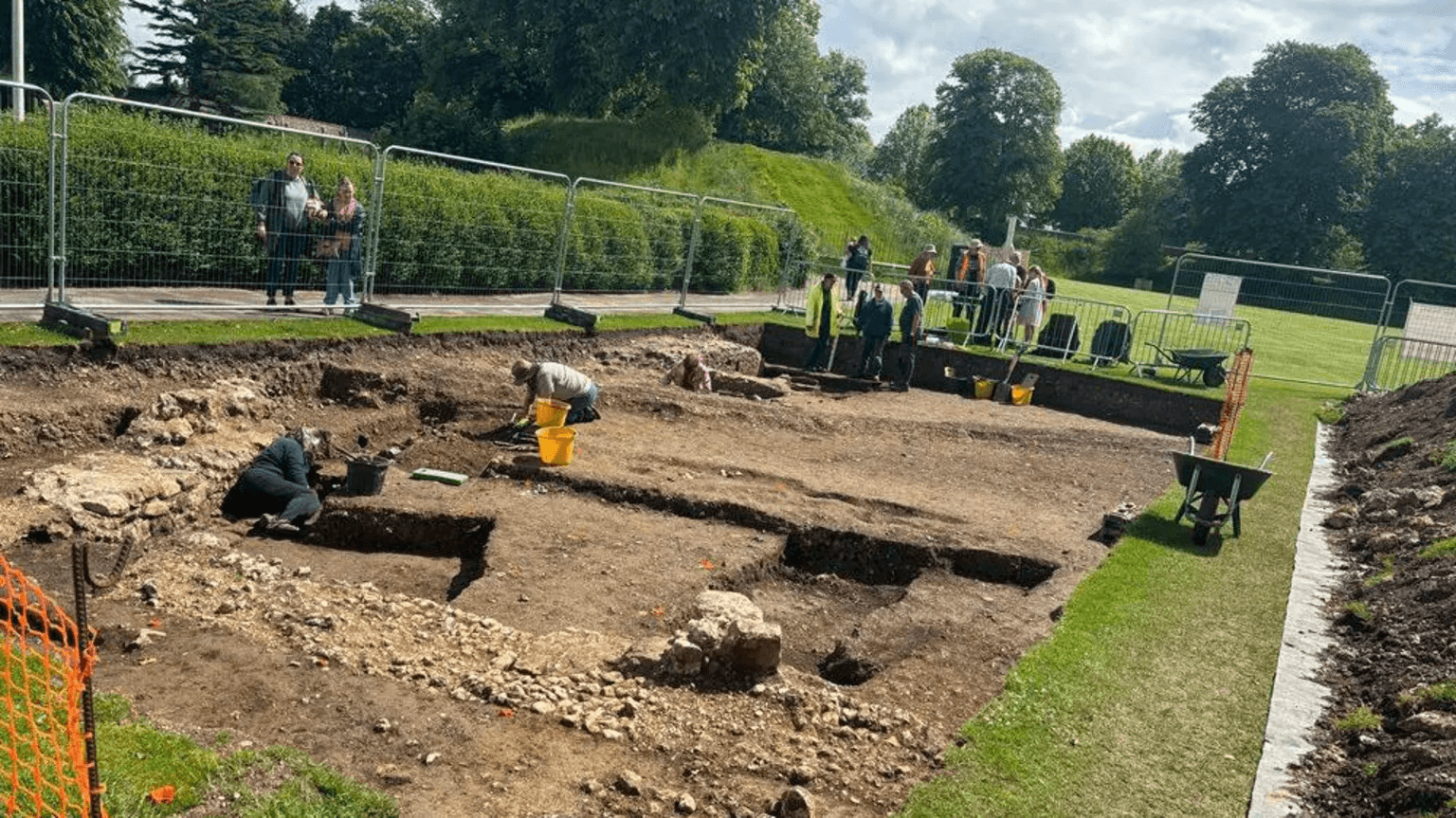
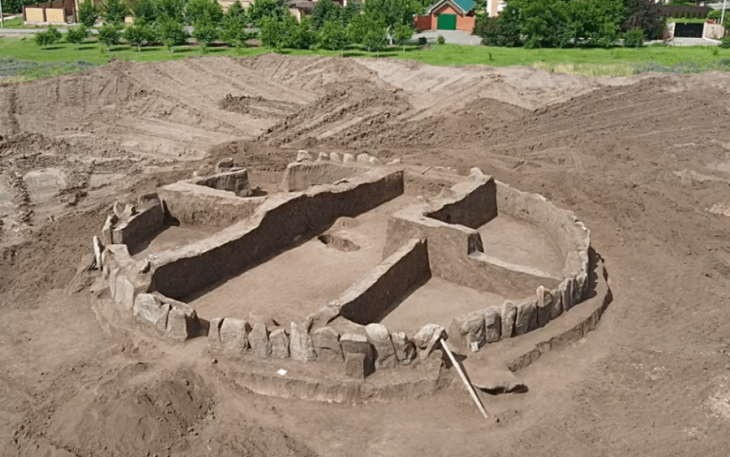
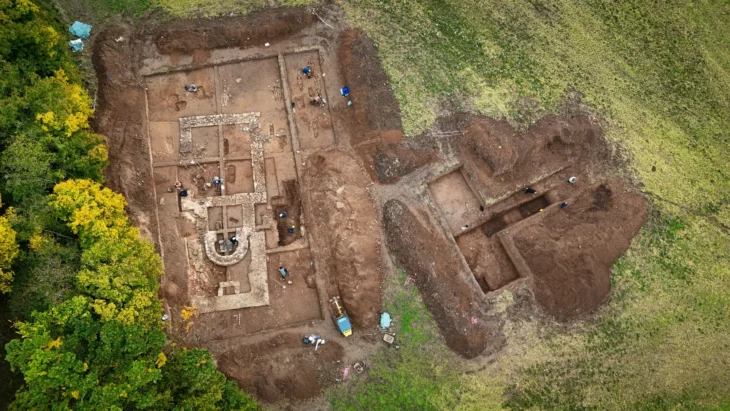
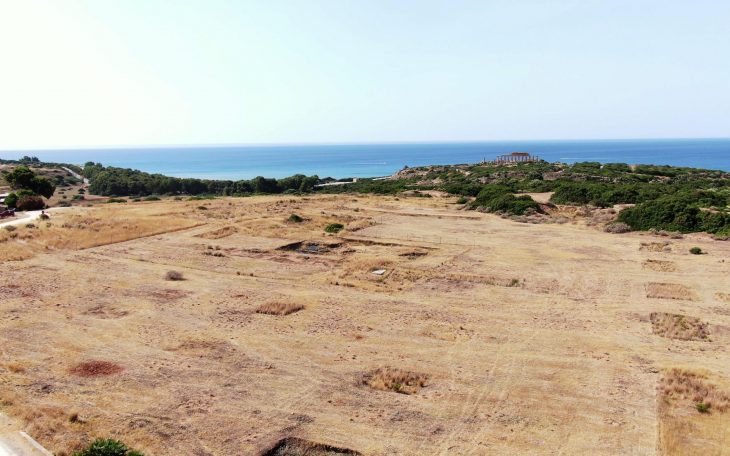
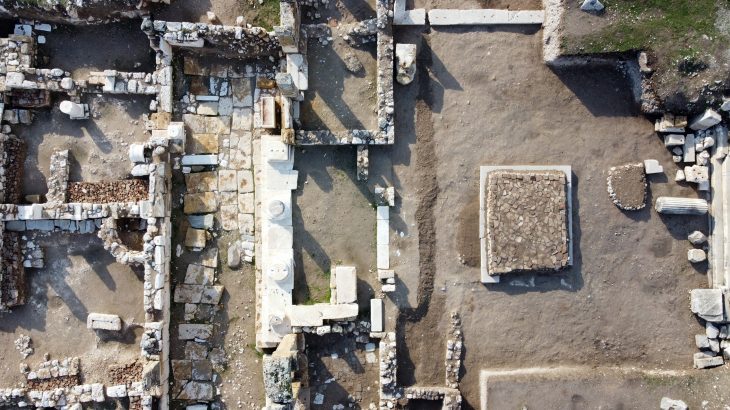
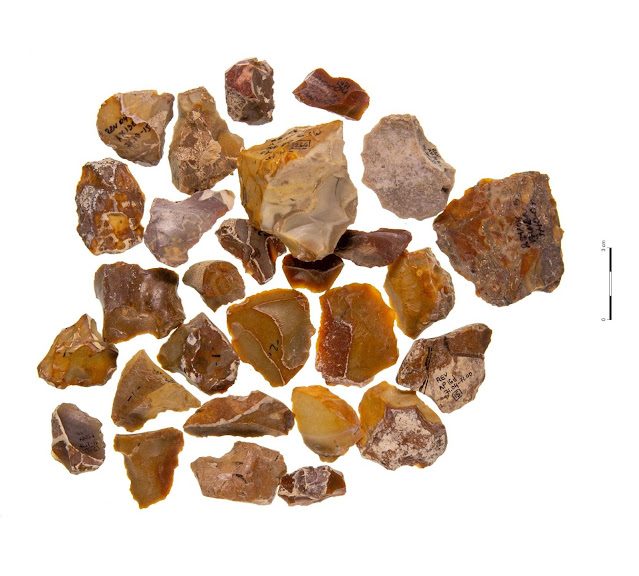
During an excavation in West Sussex, England, archaeologists uncovered the remains of a military causeway, or bridge, that led to the city’s 11th-century Norman castle.
The Chichester and District Archaeology Society team, led by Chichester District Council’s archaeologist James Kenny, found the Norman military structure during their current excavation in Priory Park, Chichester.
The dig began on May 21 and is set to end on Monday. It is the seventh dig to take place at the site, with last year’s dig uncovering the remains of a ditch and the foundations of a building that was part of a medieval Franciscan Friary.
Other discoveries include fragments of decorative floor tiles from the late medieval period and roofing materials and other floor tile remains believed to be from the Tudor period.
“We have been continuing the work that we did last year, focusing on the park’s Norman history, and we’ve been fortunate enough to uncover the structure of a bridge that would have spanned the ditch surrounding the central mound, or ‘motte’,” explains Chichester District Council’s archaeologist, James Kenny.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“This is an exciting discovery because this is the first time since the Middle Ages that people have been able to view what would have been a very impressive military defensive system.”
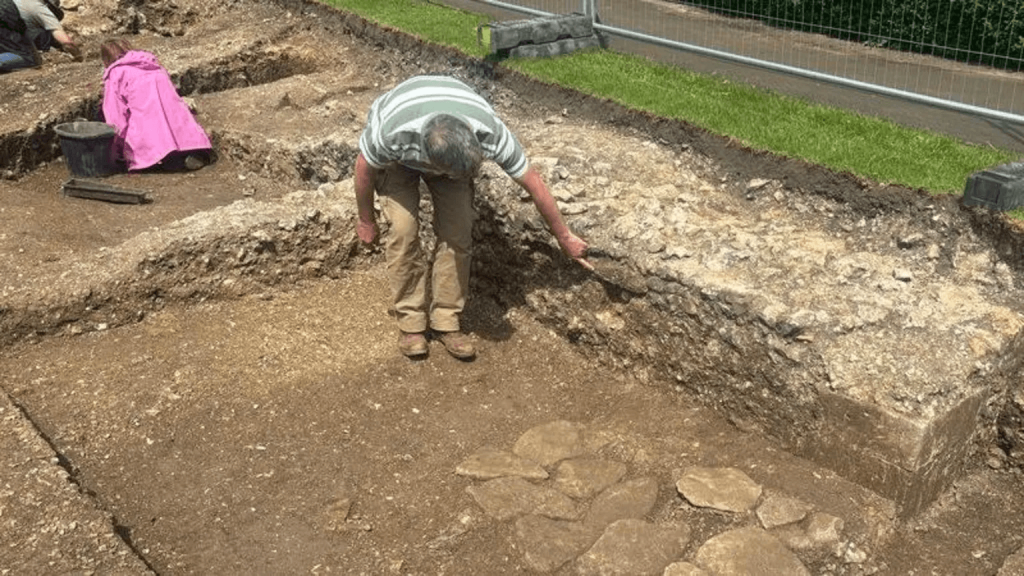

The archaeologists’ work this year was informed by a series of geophysics and ground-penetrating radar scans.
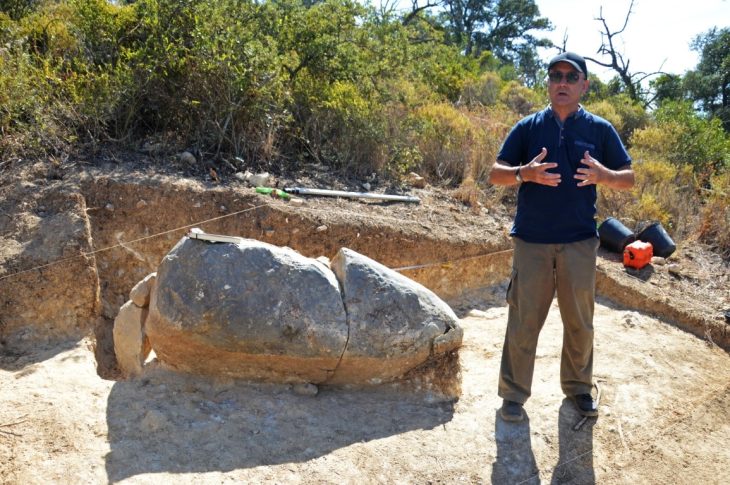
“As part of the excavation, we have found key architecture that would have formed the structure of the bridge, including a robust corner block — or ‘quoin’ — made of limestone, which would have been imported for the purpose. We have also discovered putlog holes, which are holes that oak beams would have been inserted into to help form a scaffolding system that would have been used while building the structure. The level of the putlog holes indicate that the ground level at the time would have been at least six feet lower, but could have been much deeper.”
“The structure is extremely impressive and solidly constructed. Norman soldiers would have used this bridge as a means of protecting the city’s castle. They would have crossed the bridge on wooden beams over the masonry — on foot, by horse, or with carts — and then removed the beams after use so that invaders wouldn’t be able to cross to the motte. Our finds indicate that the bridge may have been constructed in phases as the Normans settled and the castle was used on a more permanent basis,” Mr Kenny continued.
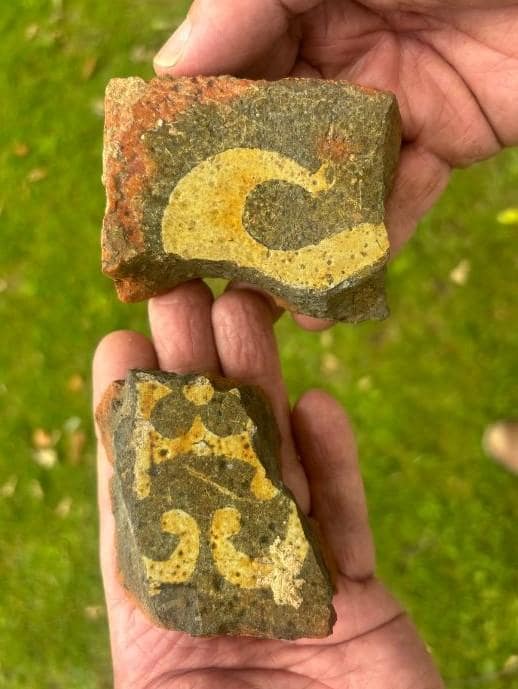

The motte and bailey castle was probably built directly after the Norman Invasion in 1067 or 1068 by Earl Roger Montgomery. Controlling most of what would become West Sussex, he was one of the most influential Norman barons.
The motte was once a major structure, four or five times larger than it is now, and most likely comparable in size to the one at Arundel Castle. Today, only a small portion of the motte remains. The purpose of Chichester’s castle was to terrify the urban English populace and discourage them from rising up against their new Norman overlords.
Cover Photo: Chichester District Council