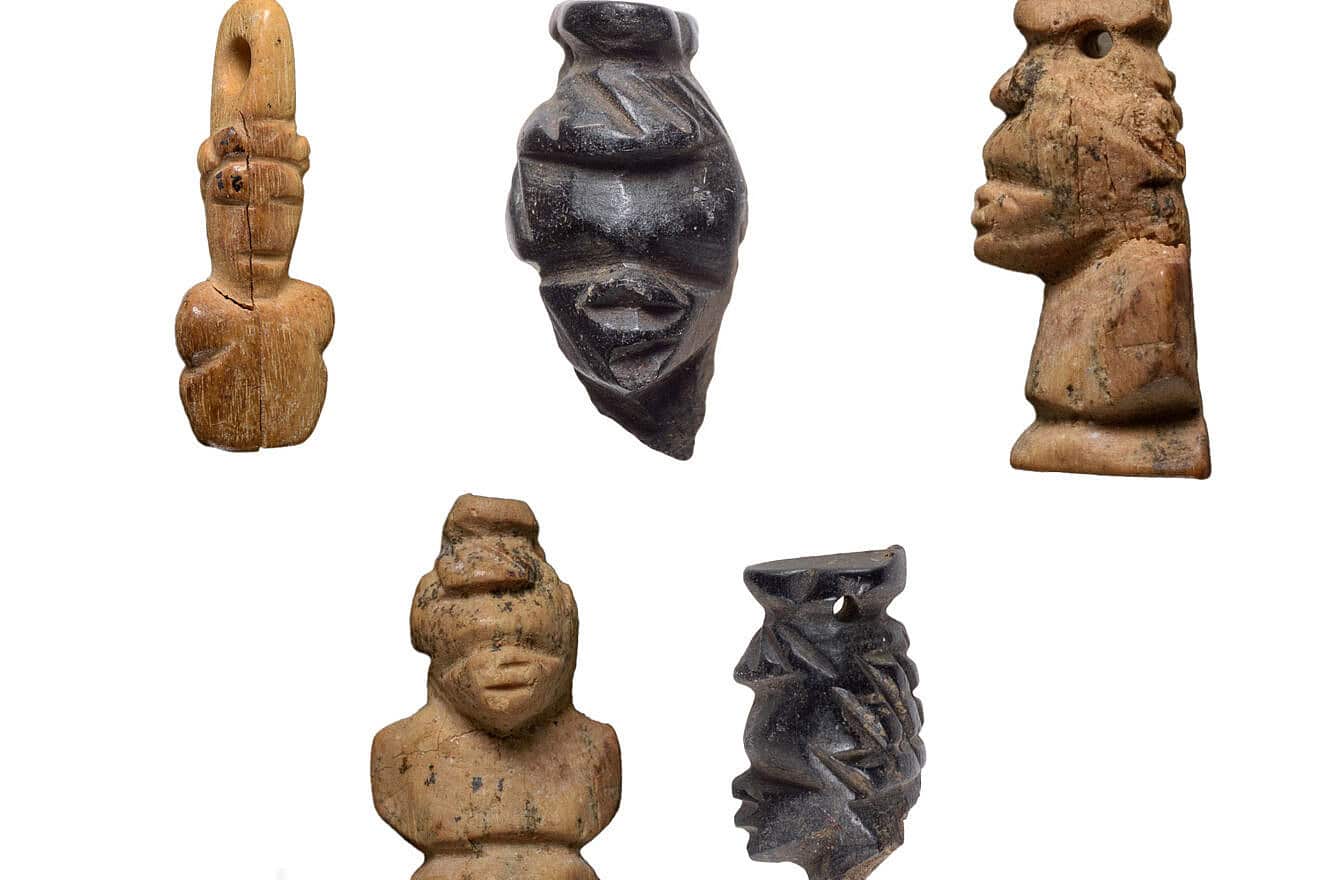
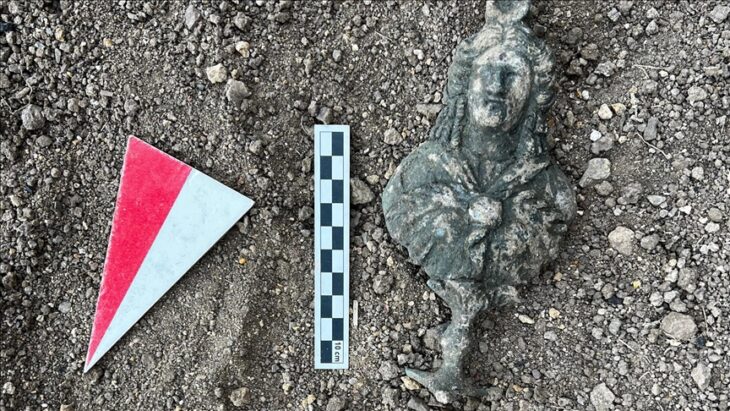
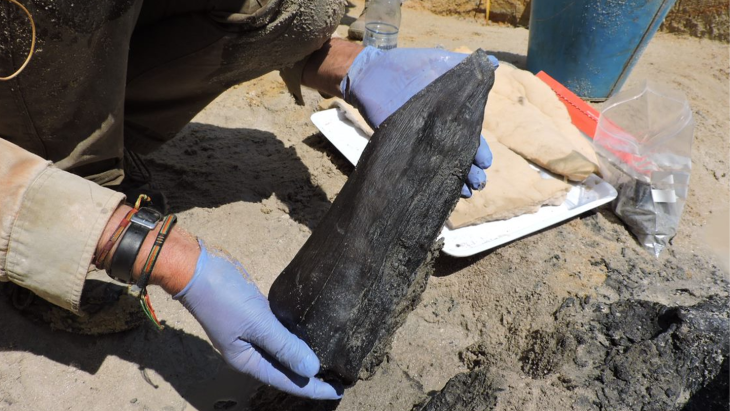
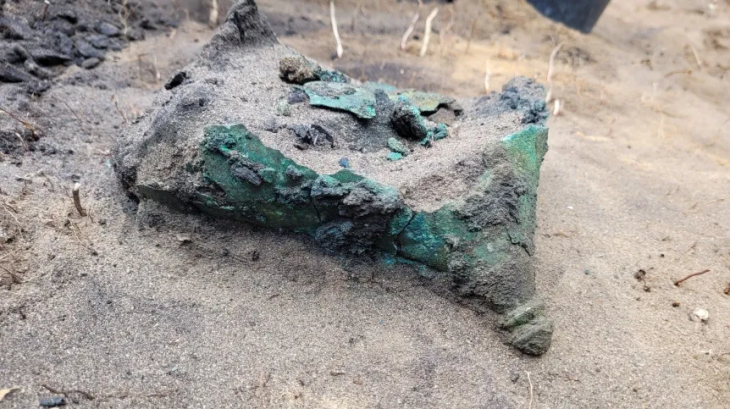
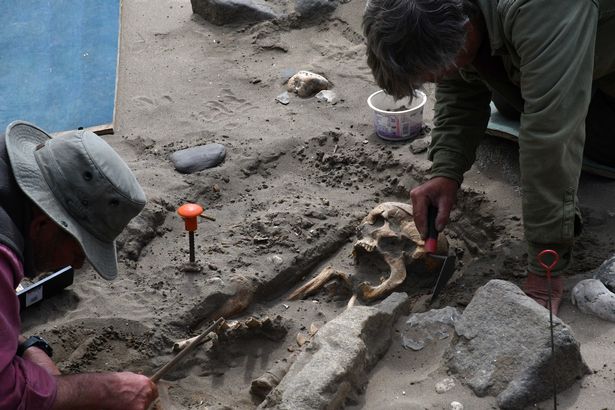
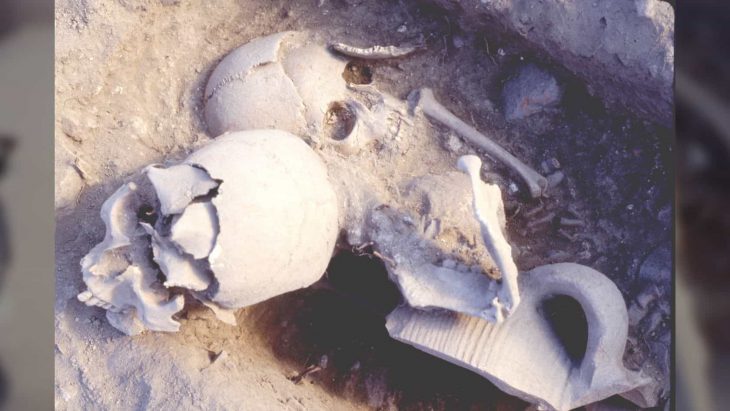
Researchers have uncovered five miniature figurines, including intricately carved African heads, in 1,500-year-old graves in Israel’s Negev Desert. These rare artifacts—found in Christian burial sites at Tel Malḥata—are shedding new light on the region’s unexpected cultural diversity during the Byzantine period.
The statuettes were discovered in 2017 during an excavation at Tel Malhata in the Arad Valley, in graves belonging to women and children.
The discovery, made during excavations by the Israel Antiquities Authority in collaboration with the University of Cologne, is detailed in the latest issue of ʻAtiqot, the Authority’s academic journal. The findings provide evidence of long-distance trade, religious transformation, and African influence in the southern Levant.
Ancient Symbols of Identity and Belief
The figurines, made of bone and ebony wood—a luxury material imported from southern India and Sri Lanka—were found in tombs of women and children. Each figurine features distinct African facial characteristics and is designed with a hole, suggesting it was worn as a pendant or personal amulet.
According to lead researcher Dr. Noé D. Michael, “These figurines may have served not only as ornaments but also as deeply personal items, embodying identity, memory, and ancestral heritage—even after the community had adopted Christianity.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
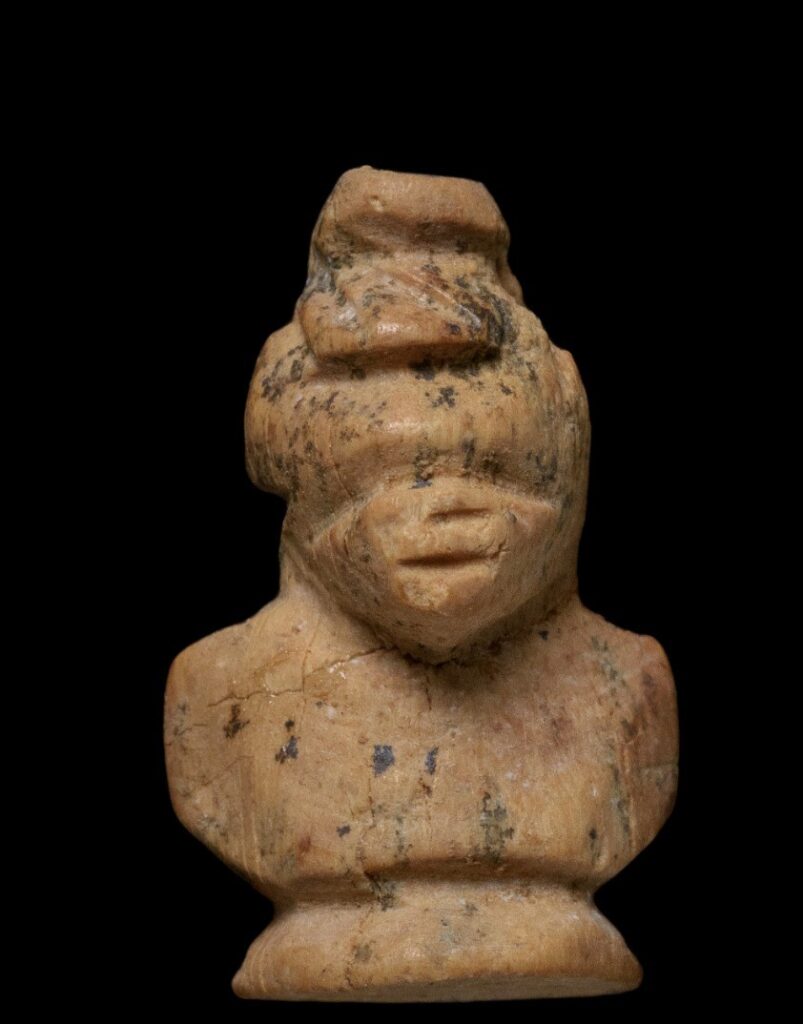

A Crossroads of Trade and Tradition
During the Roman-Byzantine era, Tel Malḥata functioned as a vital trade hub, connecting Africa, Arabia, and South Asia. The presence of African figurines in Christian burial contexts is exceptionally rare and offers compelling evidence of the cultural mosaic that existed in the Negev around the 6th–7th centuries CE.
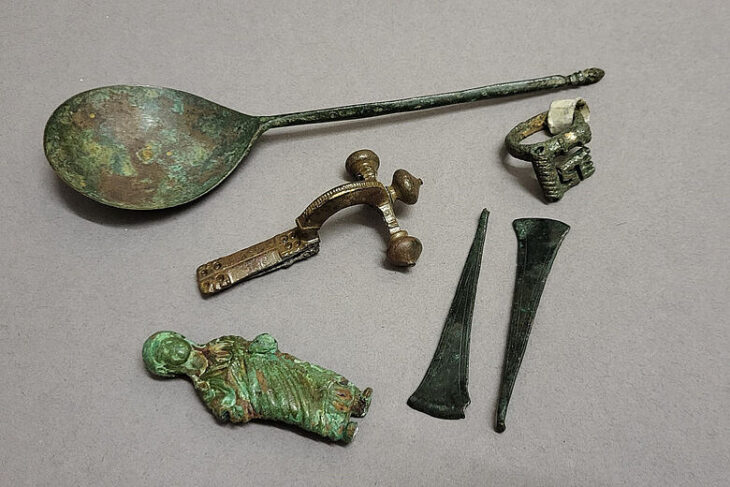
In addition to the figurines, the graves contained glassware, stone and alabaster jewelry, and bronze bracelets, further highlighting the area’s multicultural character.
Family, Faith, and Forgotten Stories
One grave held the remains of a woman and a child buried side by side—possibly a mother and son—alongside two figurines, suggesting intimate familial connections and possibly shared spiritual beliefs. These burial practices demonstrate how personal traditions were preserved even within a Christian religious framework.
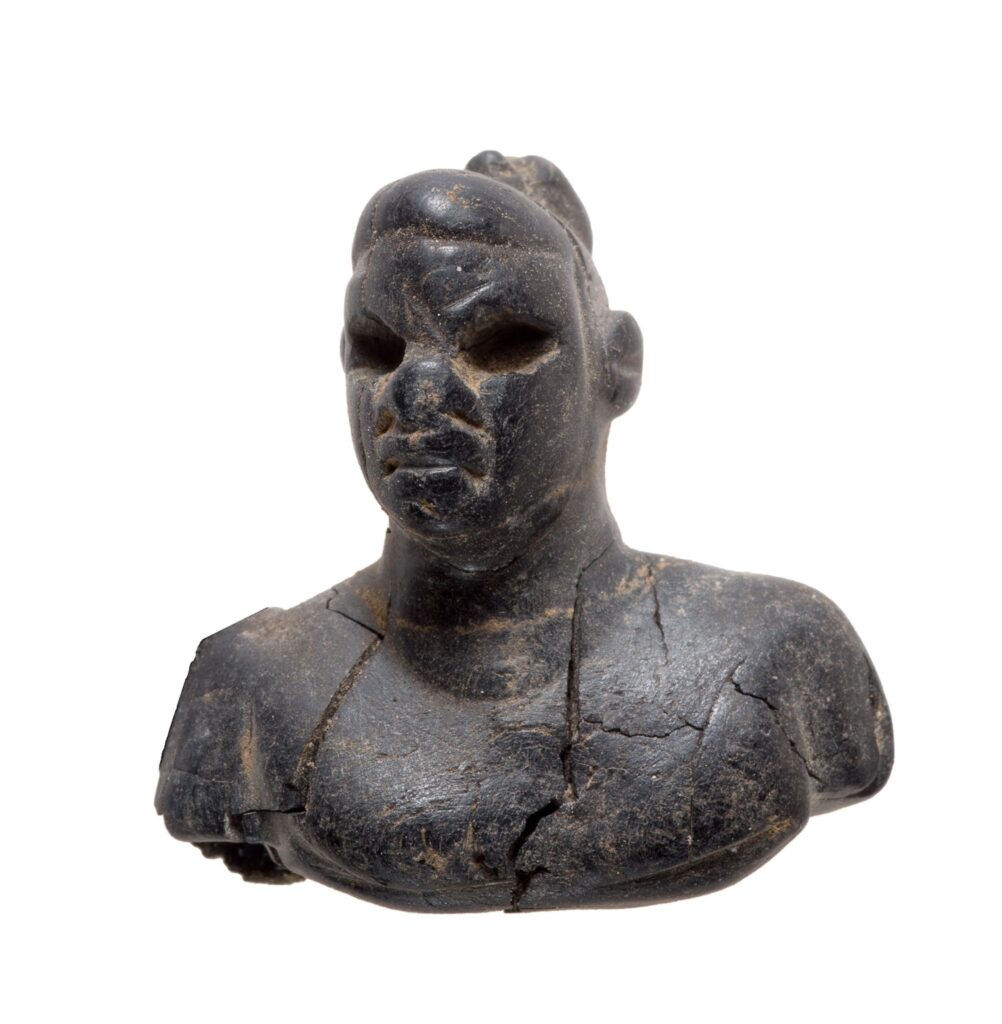

A Window into the Past
Eli Escusido, Director of the Israel Antiquities Authority, emphasized the emotional and scholarly significance of the find: “These artifacts are a poignant reminder that the Land of Israel has always been a crossroads of civilizations. The people who lived here came from afar, settled, and brought with them the stories, customs, and memories of distant homelands.”
The discovery of these figurines at Tel Malḥata offers far more than a glimpse into ancient burial customs—it reveals a rich and complex web of intercultural relationships, spiritual continuity, and global connections in a region often viewed through a narrow historical lens. The presence of African-inspired artifacts, made from materials sourced from South Asia, in the graves of early Christian communities speaks volumes about the cosmopolitan character of the Negev 1,500 years ago.
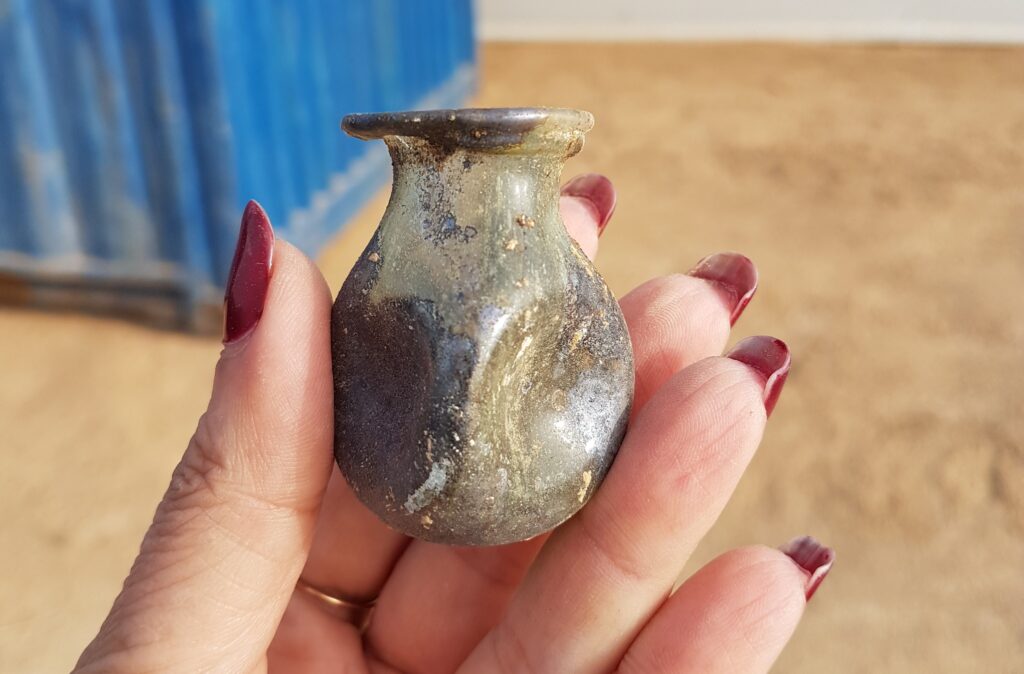

Such findings challenge the conventional understanding of ancient societies as isolated or homogenous. Instead, they highlight how even in remote desert settlements, people maintained ties—through trade, belief, or heritage—with distant parts of the world. These figurines serve not only as archaeological treasures but also as timeless symbols of how identity, faith, and culture travel across borders and endure through generations.
Cover Image Credit: Dafna Gazit, Israel Antiquities Authority