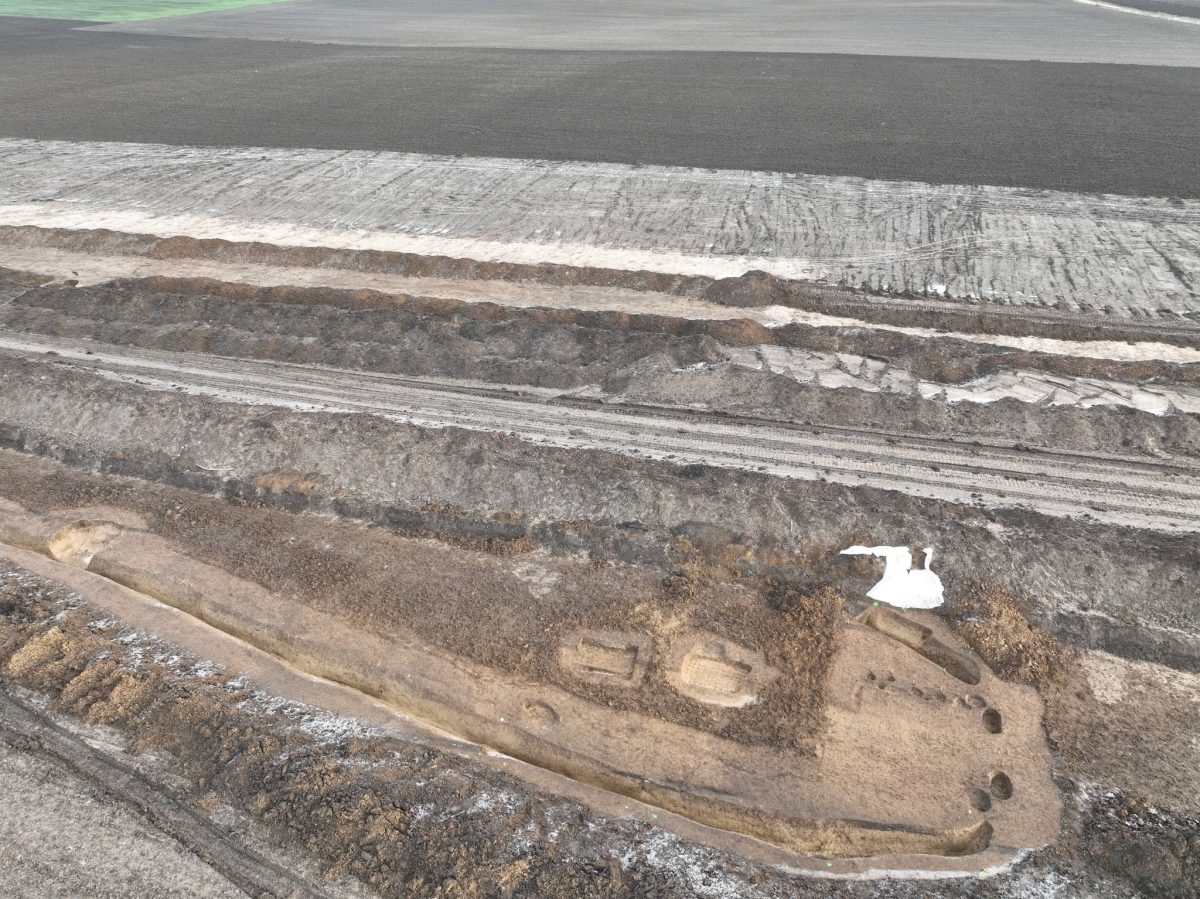
Czech archaeologists in the Hradec Králové area in East Bohemia have discovered what is probably the longest prehistoric mound in Europe.
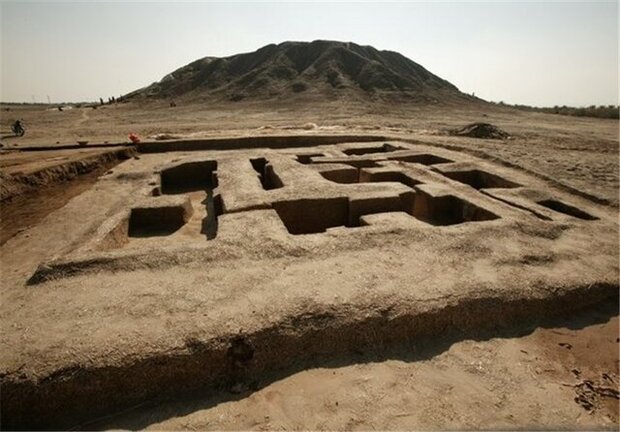
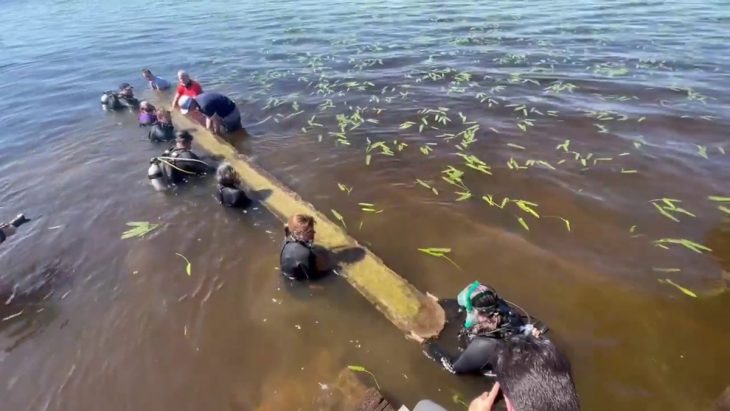
Archaeologists first uncovered an “elongated trapezoidal gutter” during road work between Dlouhé Dvory and Lípa, the Department of Archaeology at the University of Hradec Králové said in a June 19 Facebook post. The gutter was identified as a “typical” structure for an ancient burial mound known as a long barrow.
The mound, which was found along the route of a future motorway near the village of Dohalice, is about 190 meters in length and has a maximum width of 15 meters. The length of this gutter, and of the mound in general, is 190 m, making it one of the longest monuments of its kind in the whole of Central Europe.
Mound date back to the Eneolithic period, the Funnel-Beaker culture (3800-3350 BC), and it is in this period that burial complexes, of which the mounds are a part, first appear in this territory.
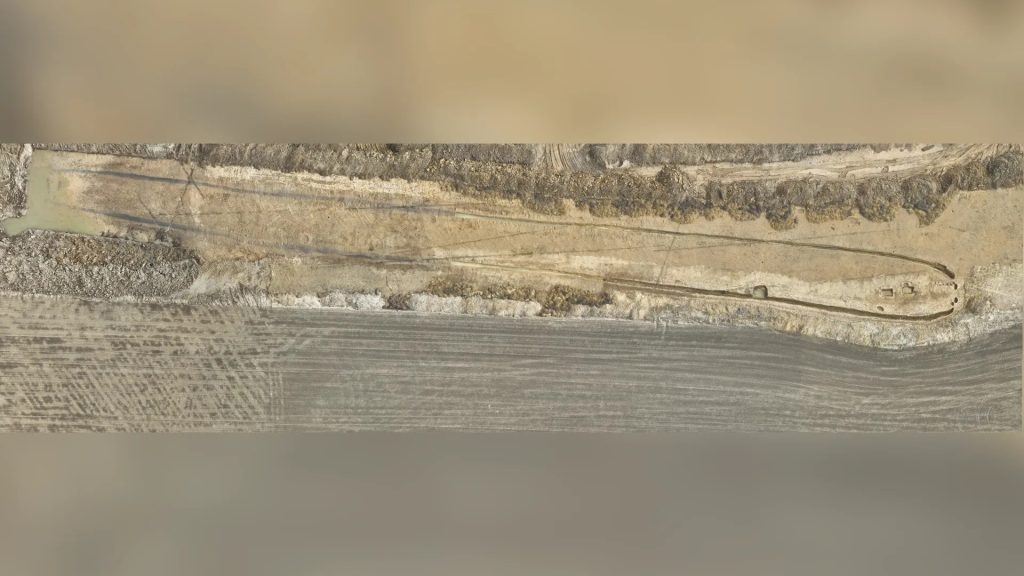

The above-ground portion of the ancient mound was gone, likely destroyed by agricultural work, the department said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
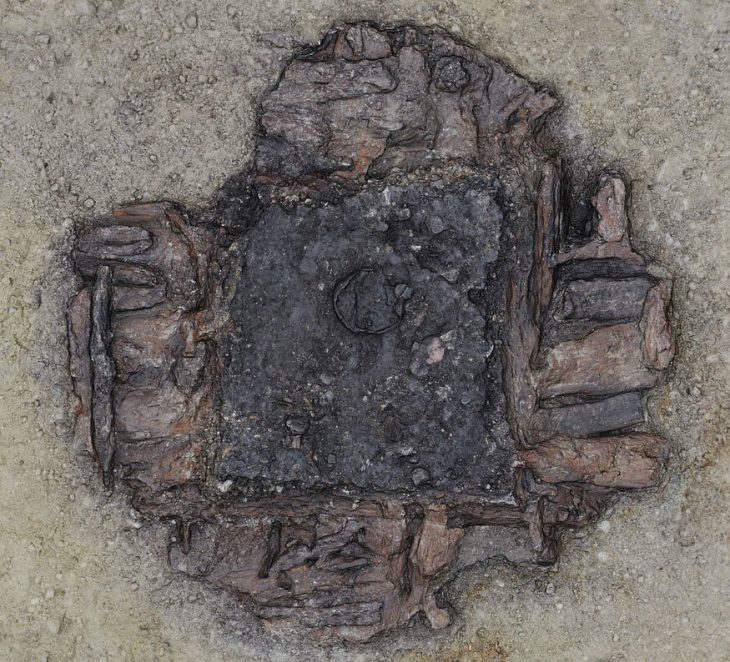
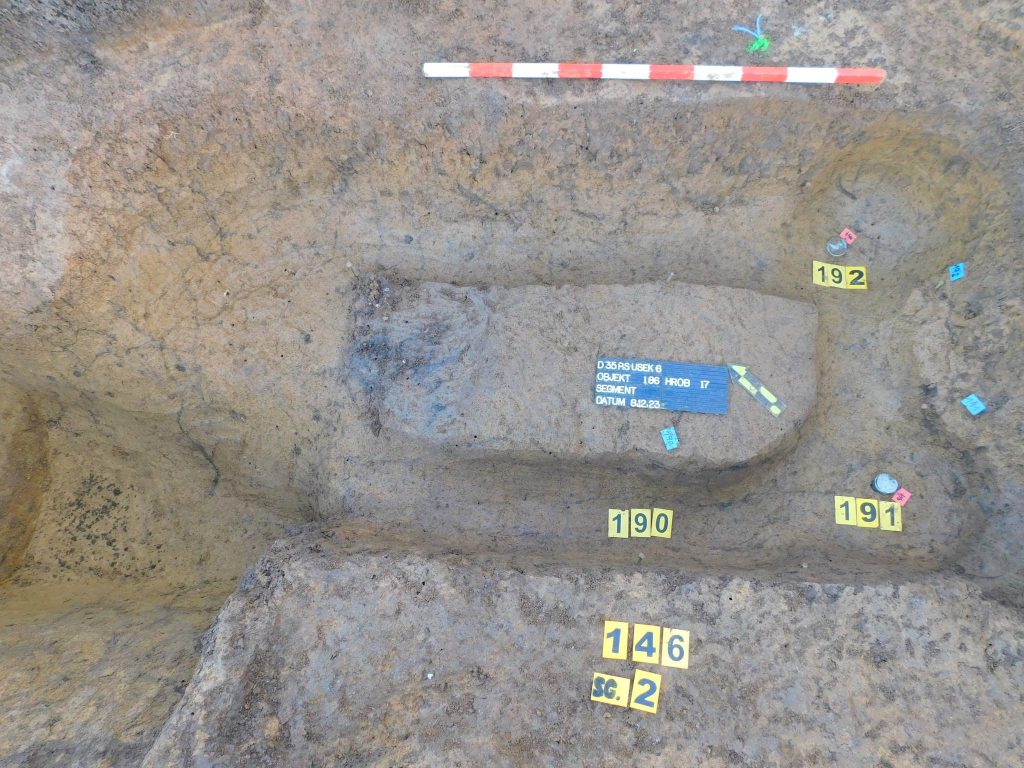
The team has also managed to excavate the entrance to the barrow, which is preserved in the form of a posthole and a gutter.
Archaeologists discovered two central burials, which contained the individuals for whom the mound was most likely built, as well as 28 additional burials. The graves, like the surrounding mound, are likely to be at least 5,300 years old. More precise ages will be obtained from the burials through laboratory analysis.

In the statement, archaeologists said: “The burial mounds were built as monumental funerary objects and as such they contain graves, we call them central burials and assume that they are the burials of the individuals for whom the mound was built. In our case, two central burials were recorded.”
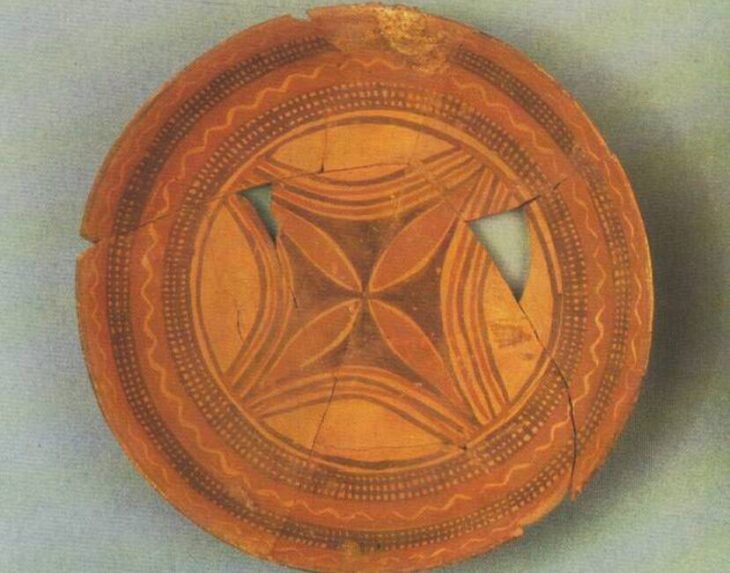
“The first central burial – a grave with an internal pit construction consisting of gutters on the longer sides and post holes at the corners, the grave offering was a ceramic vessel, the body lying on its left side facing north. The second central burial – the grave was without an internal structure, the body was also lying on the left side.”
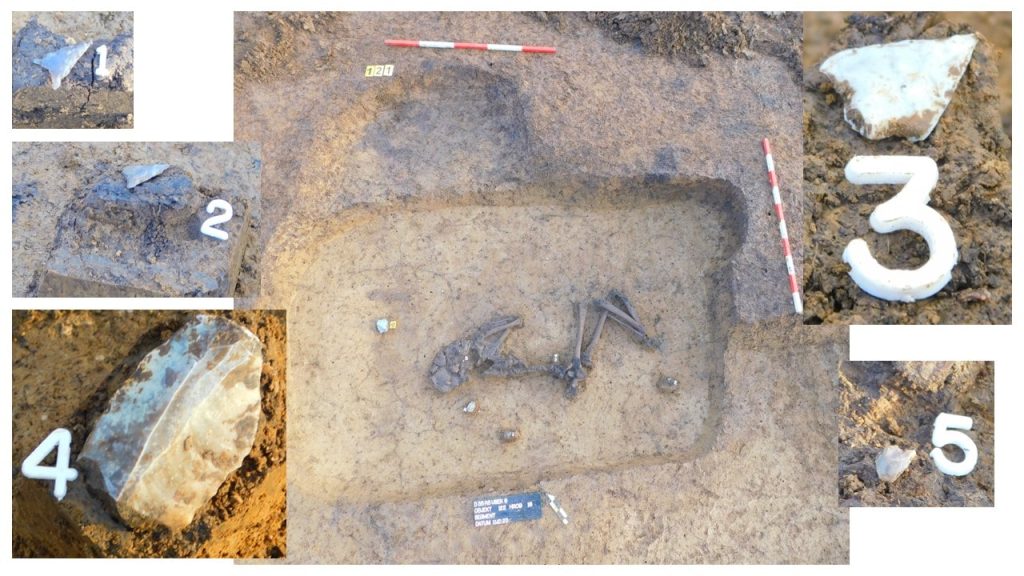

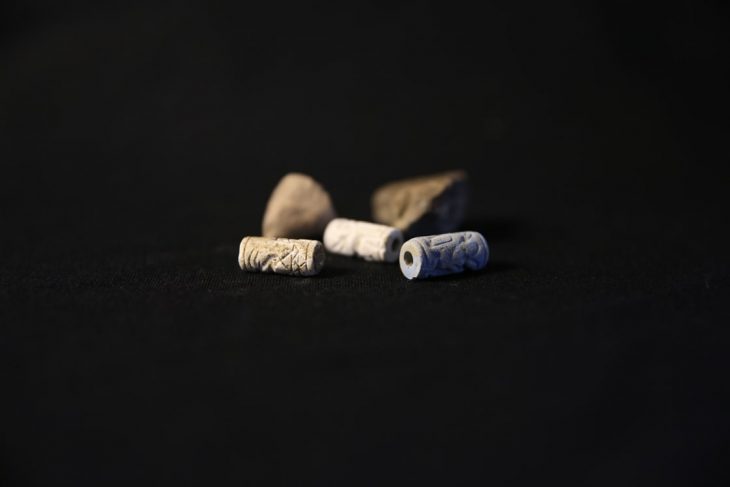
Archaeologists discovered several objects deposited as offerings near the central burials. Pottery fragments were found in one grave, and four flint arrowheads and a flint blade were found in another.
The grave inventory of the central burials is consistent with analogous sites in Czechia and Poland.
Cover Photo: Detail of the entrance to the barrow. Department of Archaeology at the University of Hradec Králové