Researchers from the University of Reading’s Department of Archaeology have found new evidence that Anglo-Saxon monastic communities were more resistant to Viking raids than previously believed.
Lyminge, a monastery in Kent, was on the front line of long-running Viking hostility which ended in the victories of Alfred the Great. The monastery endured repeated attacks, but resisted collapse for almost a century, through effective defensive strategies put in place by ecclesiastical and secular rulers of Kent, University of Reading archaeologists say.
The new evidence is presented after a detailed examination of archaeological and historical evidence by Dr. Gabor Thomas, from the Department of Archaeology at the University of Reading.
“The image of ruthless Viking raiders slaughtering helpless monks and nuns is based on written records, but a re-examination of the evidence show the monasteries had more resilience than we might expect,” Dr. Thomas said.
Despite being located in a region of Kent that bore the full brunt of Viking raids in the later 8th and early 9th centuries, the evidence suggests that the monastic community at Lyminge not only survived these attacks but recovered more completely than historians previously thought, Dr. Thomas concludes in research, published today (30 January 2023) in the journal Archaeologia.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
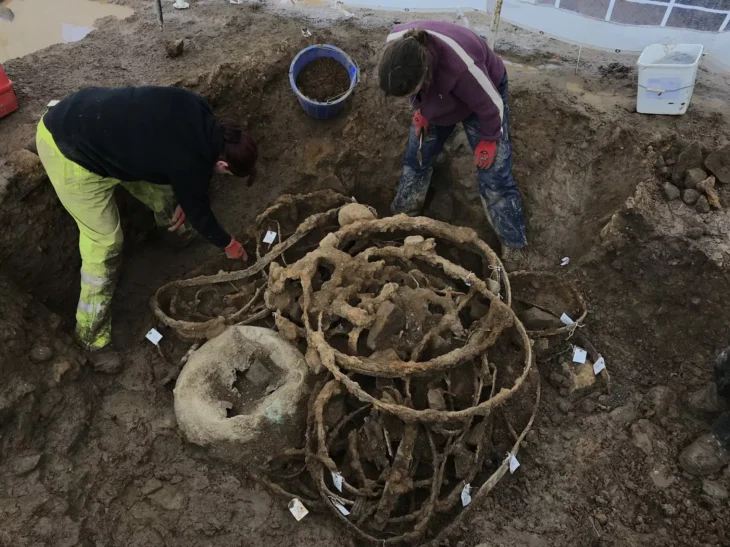
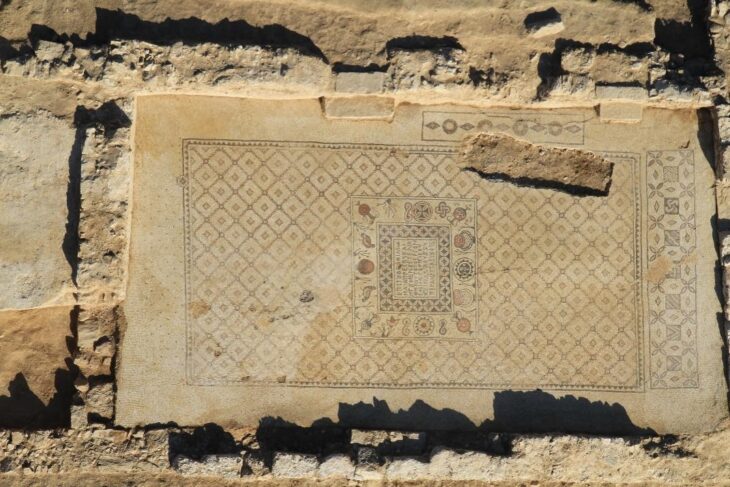
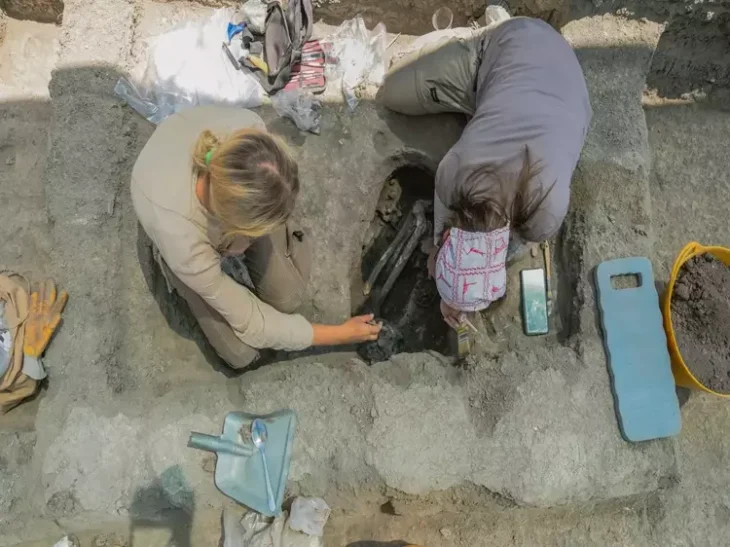
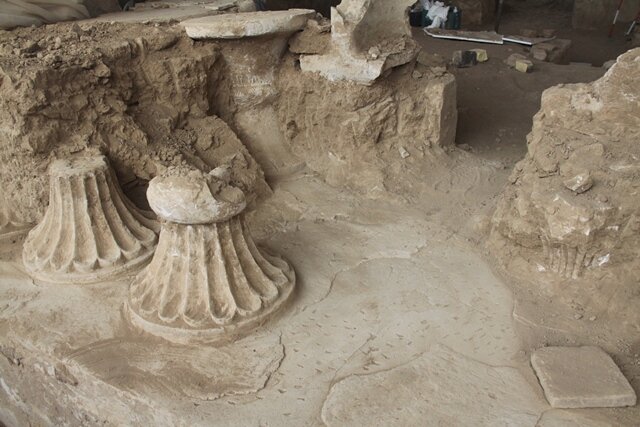
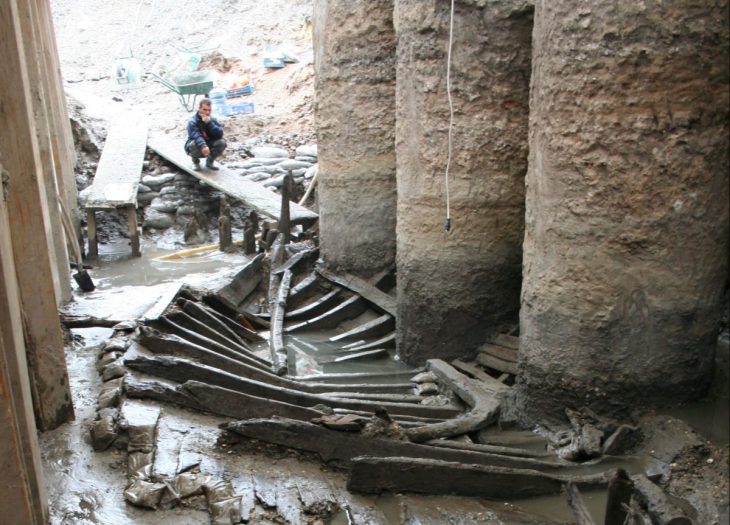
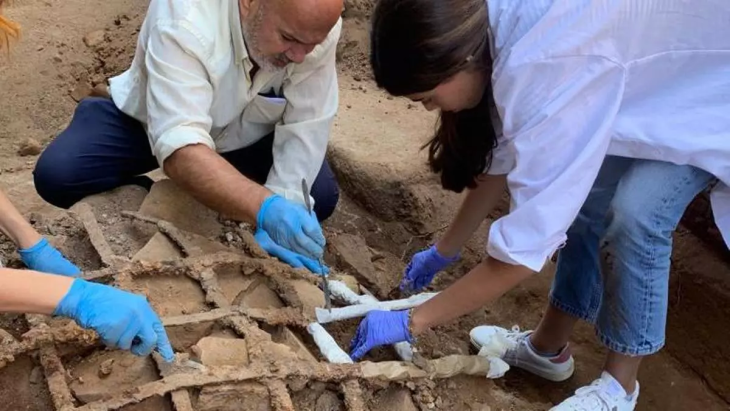
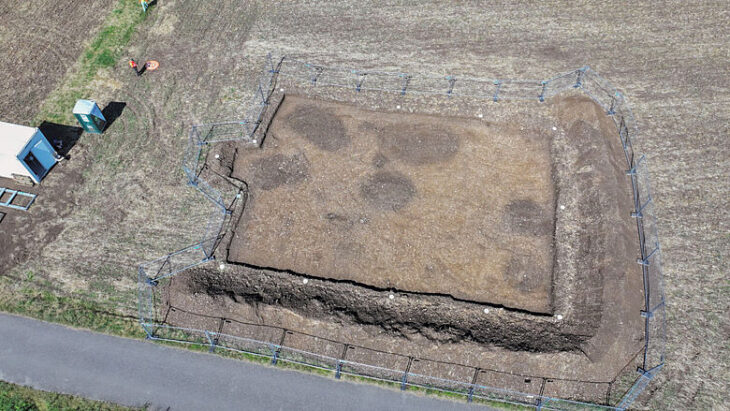
During archaeological excavations between 2007-15 and 2019, archaeologists uncovered the main elements of the monastery, including the stone chapel at its heart surrounded by a wide swathe of wooden buildings and other structures where the monastic brethren and their dependents lived out their daily lives. Radiocarbon dating of butchered animal bones discarded as rubbish indicates that this occupation persisted for nearly two centuries following the monastery’s establishment in the second half of the 7th century.
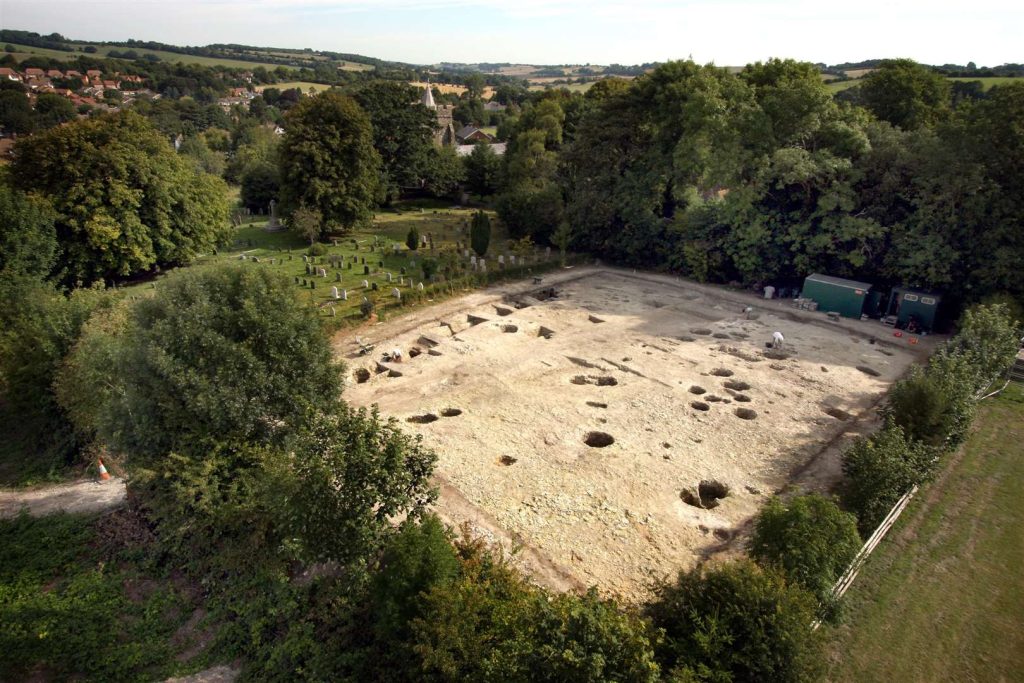

Historical records held at nearby Canterbury Cathedral show that after a raid in 804 CE, the monastic community at Lyminge was granted asylum within the relative safety of the walled refuge of Canterbury, a former Roman town and the administrative and ecclesiastical capital of Anglo-Saxon Kent.
But evidence from Dr Thomas’s dig shows the monks not only returned to re-establish their settlement at Lyminge, but continued living and building for several decades over the course of the 9th century. Dateable artefacts such as silver coins discovered at the site provided Dr Thomas with an insight into the re-establishment of the monastic community.
Dr Thomas said: “This research paints a more complex picture of the experience of monasteries during these troubled times, they were more resilient than the ‘sitting duck’ image portrayed in popular accounts of Viking raiding based on recorded historical events such as the iconic Viking raid on the island monastery of Lindisfarne in AD 793.
“However, the resilience of the monastery was subsequently stretched beyond breaking point.
“By the end of the 9th century, at a time when Anglo-Saxon king Alfred the Great was engaged in a widescale conflict with invading Viking armies, the site of the monastery appears to have been completely abandoned.
“This was most likely due to sustained long-term pressure from Viking armies who are known to have been active in south-eastern Kent in the 880s and 890s.
“Settled life was only eventually restored in Lyminge during the 10th century, but under the authority of the Archbishops of Canterbury who had acquired the lands formerly belonging to the monastery.”
The latest research article is based on the results of over a decade of archaeological research at Lyminge, directed by Dr. Thomas. The village was first established by Anglo-Saxons in the 5th century.