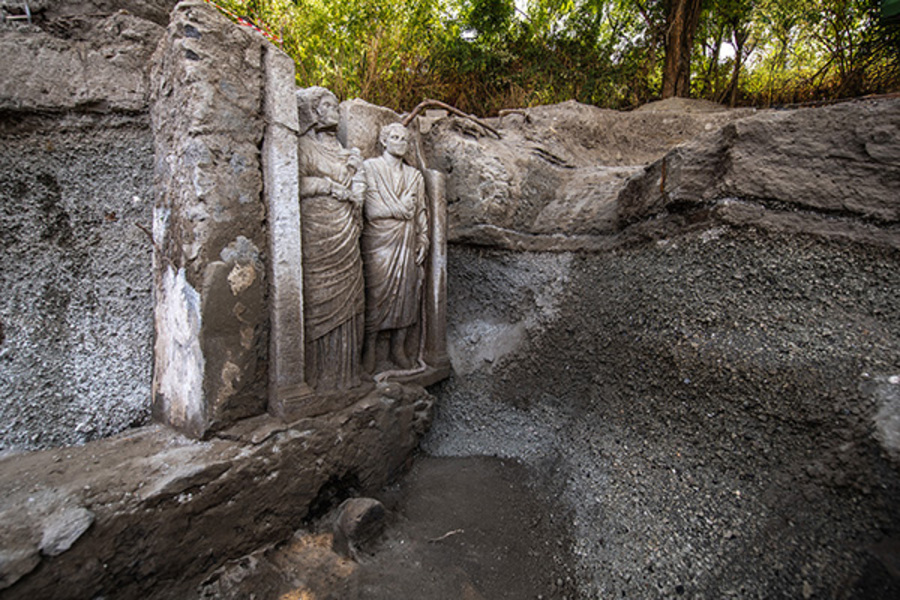
A research project titled “Investigating the Archaeology of Death in Pompeii,” developed by the Universitat de València in collaboration with the Pompeii Archaeological Park, has led to a groundbreaking discovery in the Porta Sarno necropolis of Pompeii, unearthing a remarkable funerary relief depicting a couple—almost life-size—that sheds light on the funerary practices and social dynamics of this ancient city.
Led by Professor Llorenç Alapont, the project aims to deepen our understanding of the social identity of the deceased in a city famously buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. The high-relief figures, which have been transferred to the Palaestra Grande for meticulous restoration, will be featured in the upcoming exhibition “Being a Woman in Ancient Pompeii,” set to open on April 16, 2025. Visitors will have the unique opportunity to observe the restoration process as it unfolds within the exhibition space.
The excavation of the area began in July 2024, although it had previously been explored during the 1990s when a second track for the Circumvesuviana railway was installed. Notably, a 1998 excavation campaign documented over 50 cremation burials marked by stelae and monumental structures, including a large funerary arch.
Recent investigations have revealed a monumental tomb characterized by a large wall with several niches, at the top of which the newly discovered relief of a man and woman is sculpted. This suggests that the couple may have held a significant social presence in Pompeian society. Intriguingly, the symbolism surrounding the female figure indicates she may have been a priestess of the goddess Ceres, highlighting her involvement in the city’s religious life.
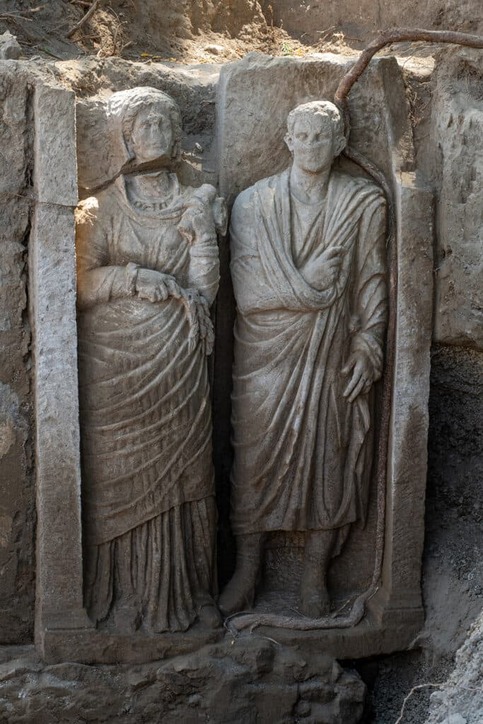

The artistic quality and stylistic features of the relief date it to the late Republican period, a time when local elites reinforced their identities through imposing funerary monuments. The director of the Pompeii Archaeological Park, Gabriel Zuchtriegel, emphasized the project’s potential to expand knowledge about life in Pompeii’s extramural areas, noting past collaborations with the Universitat de València that led to significant discoveries, such as the tomb of Marcus Venerius Secundio.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The multidisciplinary team, comprising archaeologists, architects, restorers, and anthropologists, has meticulously recovered and analyzed the remains found in the Porta Sarno necropolis. Initial analyses and conclusions have been published in the E-Journal of the Excavations of Pompeii, where the team presents hypotheses regarding the identity of the figures in the relief and the funerary context of their discovery.
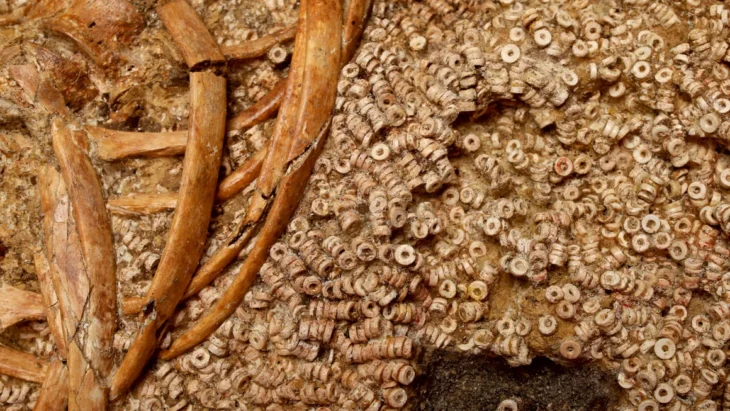
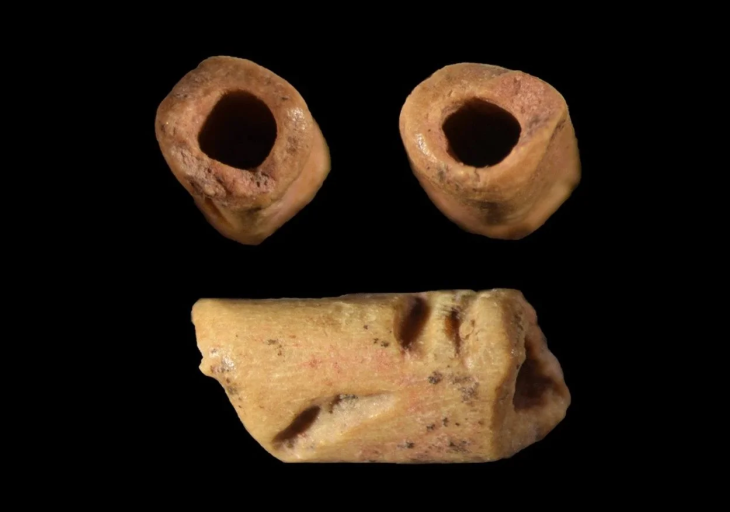
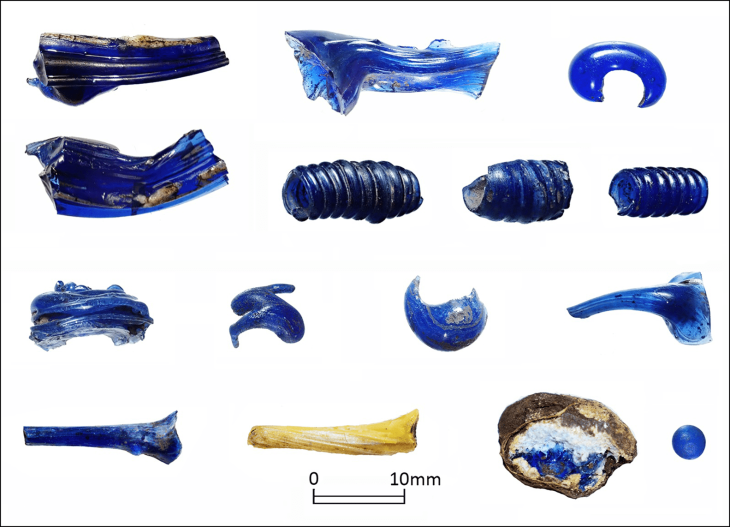
In addition to the relief, the excavations have uncovered evidence of funerary rituals, including ceramic remains and glass ointment jars, likely used in libation ceremonies. These rituals, which involved pouring perfumed oils, were essential for creating a multisensory atmosphere during funerals, counteracting the unpleasant odors associated with death.
As excavations continue, the findings from the Porta Sarno funerary area promise to reshape our understanding of Pompeii’s social and religious landscape. The discoveries not only highlight the complexity of funerary customs but also underscore the active participation of women in religious practices, challenging previous assumptions about gender roles in ancient Roman society.
The ongoing research emphasizes the need for further documentation and exploration of this significant archaeological site, as it continues to reveal the rich tapestry of life and death in ancient Pompeii.
Archaeological Park of Pompeii
Cover Image Credit: Alfio Giannotti / Parco archeologico di Pompei (Archaeological Park of Pompeii )