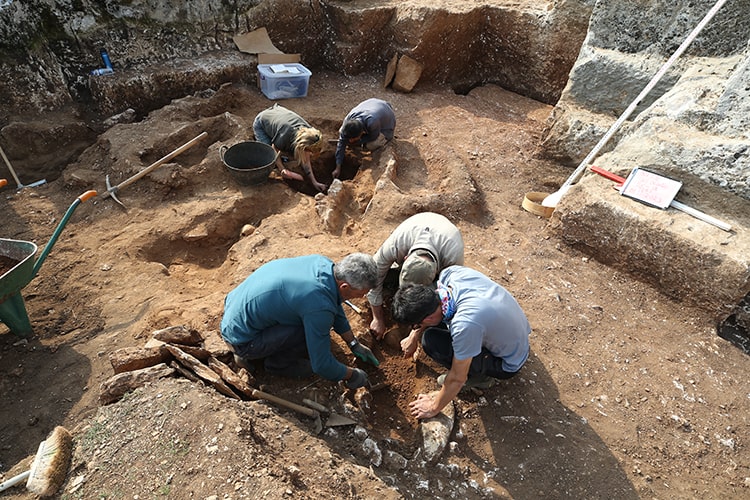
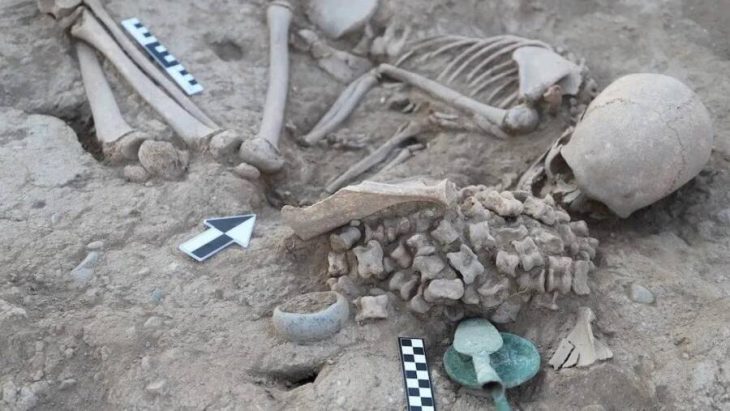
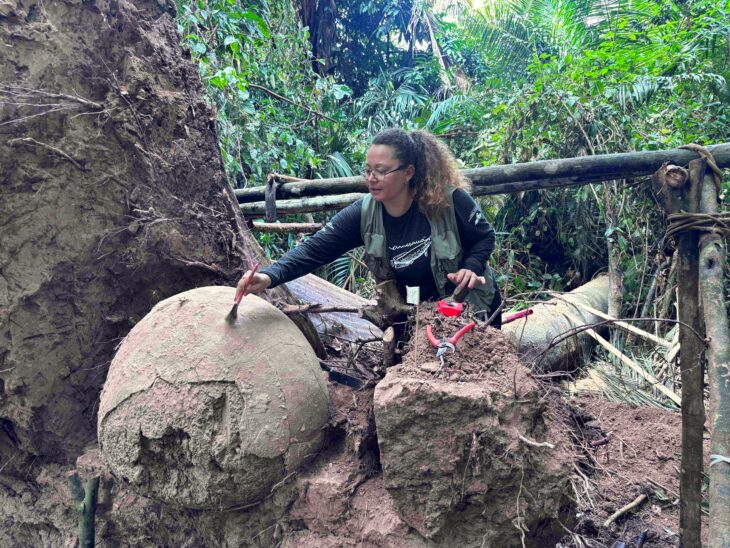
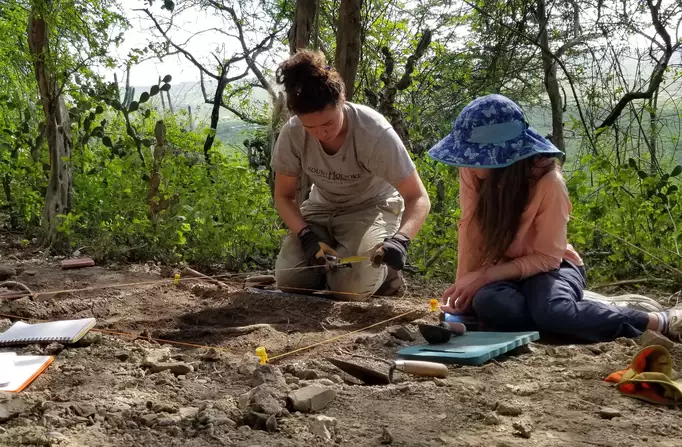
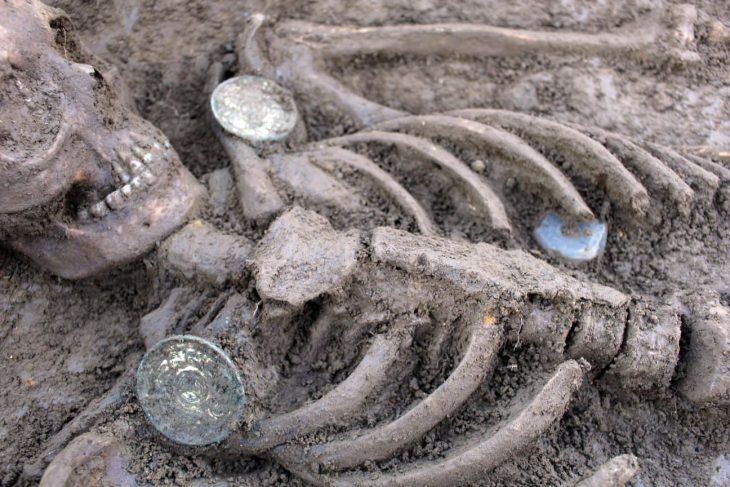
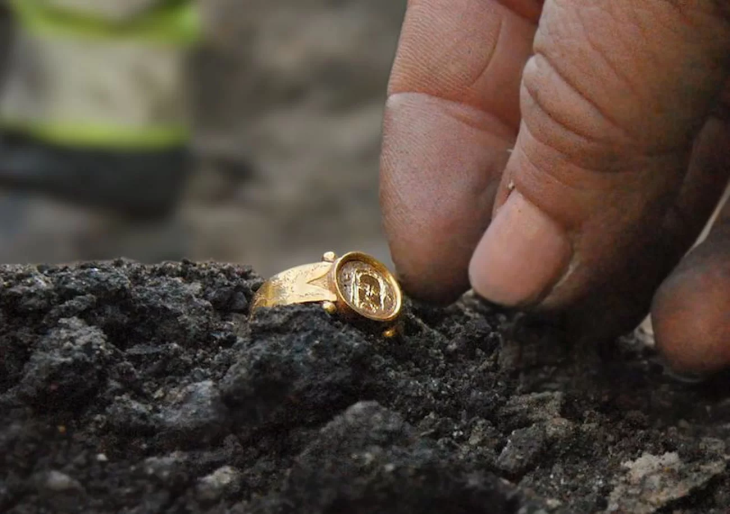
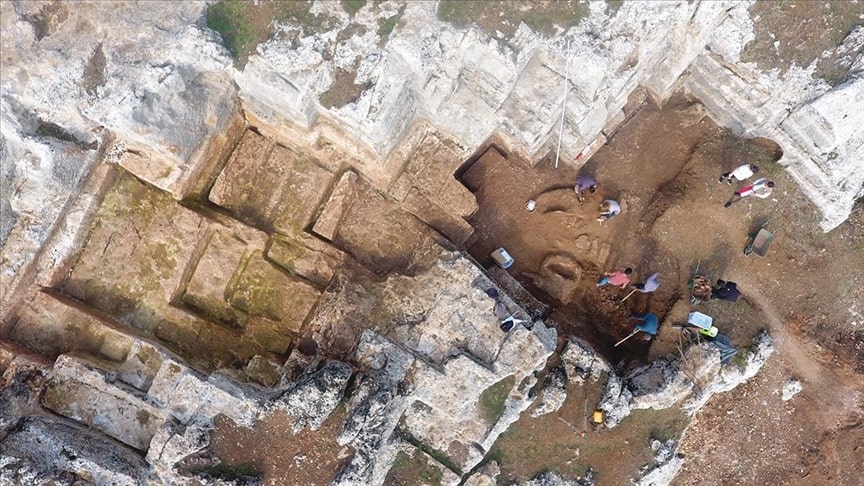
During the archaeological excavation carried out in the area considered to be an old quarry in the Kulp district of Diyarbakır in southeastern Turkey, a cemetery where 54 children between the ages of 0-6 were buried was unearthed.
Following the discovery of coins belonging to the Byzantine Emperor Anastasius I in the surface survey conducted in different areas in İnkaya Neighborhood, the excavations started by the Diyarbakır Museum Directorate in 2021 in the region continue with a team of 35 people, 15 of whom are experts.
After the discovery of the remains of a 1500-year-old church last year, excavation works commenced in the area considered to be an ancient quarry. The teams encountering the children’s graves during the excavations intensified their efforts in this area.
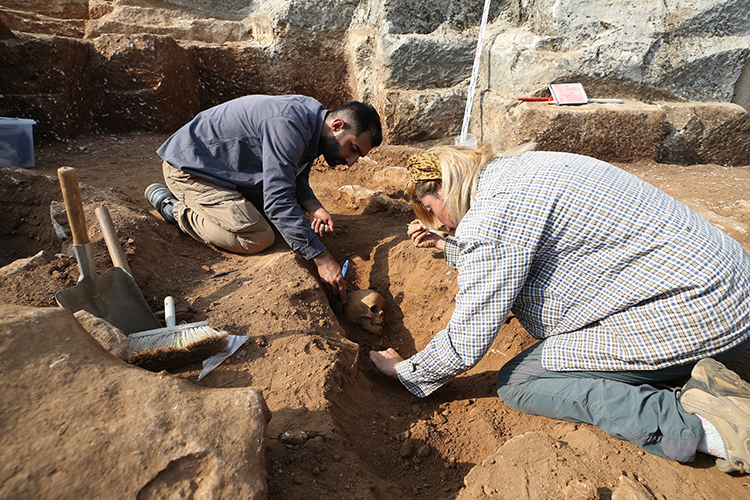
Diyarbakır Museum Acting Director Müjdat Gizligöl told Anadolu Agency (state-run news agency) correspondent, ‘So far, we have found 50 graves in the excavation works here. Today, we reached 4 more graves. The excavation process is currently ongoing. Therefore, we know there are a total of 54 graves. This is a very interesting result for us.”

“Probably after this place was used as a quarry, it was turned into a necropolis (a cemetery, belonging to an ancient city), and only children were buried here.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Stating that they found that more than one child was buried in some graves, Gizligöl said, “A limestone cist was formed around the graves and closed with limestone. The graves are in the east-west direction, there is no random burial.”
A burial site where all of the bones belong to children is not a common occurrence. For this reason, a detailed study will be carried out on the age, sex, and cause of death of the collected bones.

Dr Nazlı Akbaş, a research assistant and anthropologist at Gaziantep University Social Sciences Institute, also reminded that church ruins were found in previous excavations in the area and stated that the church dates to the early Byzantine Period and approximately 1500 years ago.
Akbaş said the following about the detection of graves in the church: “Since there was a ‘saint’ and ‘martyr’ culture in early Byzantium, in-settlement burials can occur in churches. In this area, which we call the quarry, only graves belonging to infants and children between the ages of 0 and 6 were found.”
Stating that, based on the preliminary examination, they do not think that the babies and children died due to any epidemic, Akbaş stated that a detailed skeletal study has not been carried out yet.
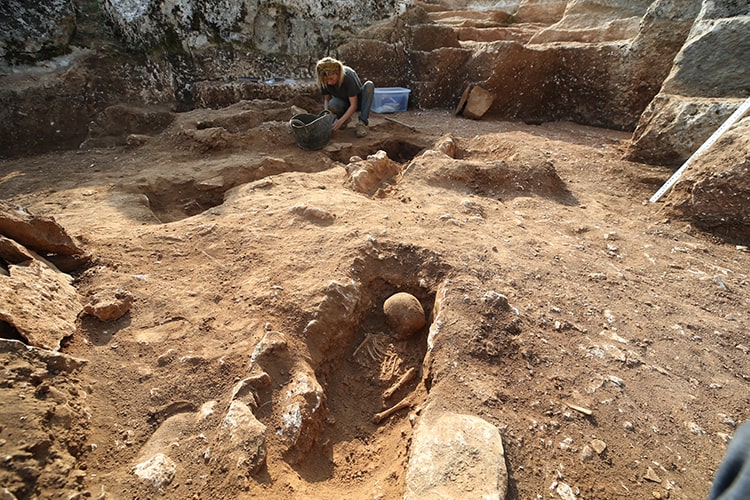

“We think that the burial of babies in the area in question is related to the baptismal culture of Christianity in the early Byzantine period. In the early Christian period, those who were baptized were generally adults. After the 10th century, it became legal that children should be baptized. We think that these belong to the early Christian period. Therefore, babies and children who have not been baptized, that is, who are not yet Christians. Since he was not baptized, we are considering the possibility of him being buried outside the church rather than inside it.”
The researcher drew attention to an example of a grave in which only children were buried in the Amorium excavations in Afyonkarahisar. He said that during the Amorium excavations, it was revealed that only babies and children were buried in a certain area of the cemetery dating back to the 10th and 11th centuries, and a baptistery was detected near the cemetery, but no baptistery was found yet in the excavations in Kulp.
Cover Photo: Bestami Bodruk/AA