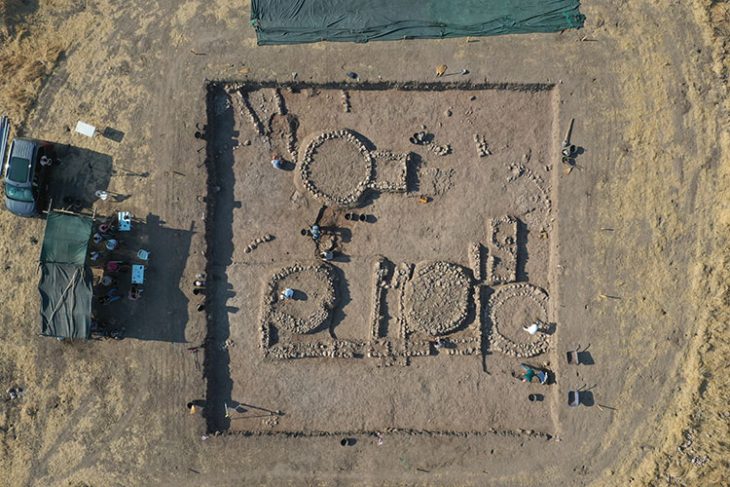The Polytechnic University of Madrid announced the discovery of a Roman camp and the Celtiberian city of Titiakos in the province of Soria, in the north of Spain.
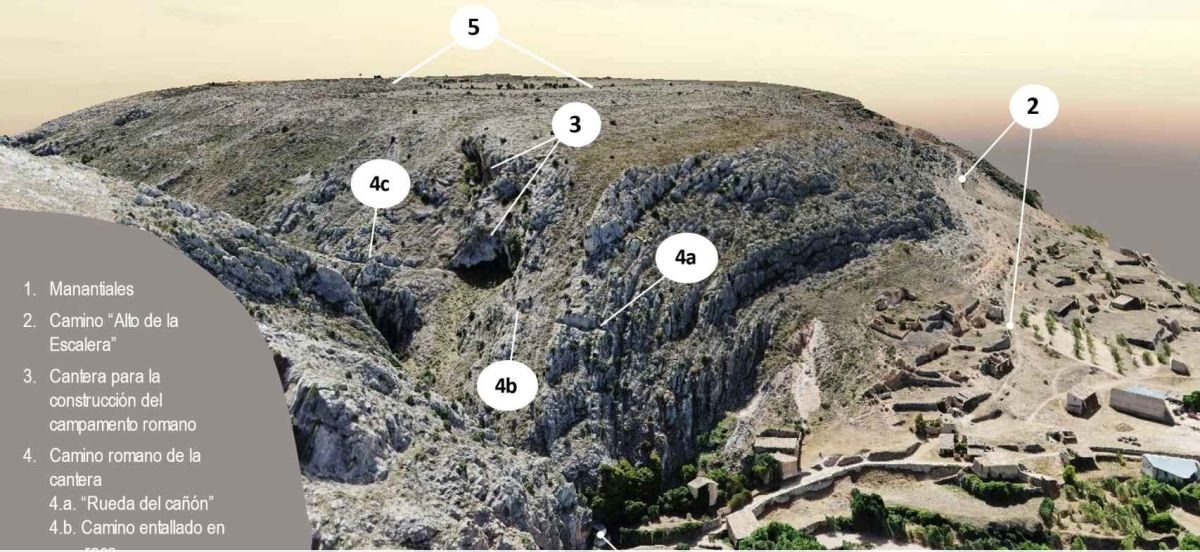
In addition, a limestone quarry was found, which is thought to have been used for the construction of this large military camp, according to a statement from the university.
Celtiberia is a region in modern-day north-central Spain that was inhabited starting in the third century BC by tribes thought to be of mixed Celtic and Iberian ancestry. The majority of the current province of Soria as well as a sizable portion of the neighboring provinces of Guadalajara and Teruel were inhabited by these Celtiberians, who lived in the hill country between the sources of the Tagus (Tajo) and Iberus (Ebro) rivers.
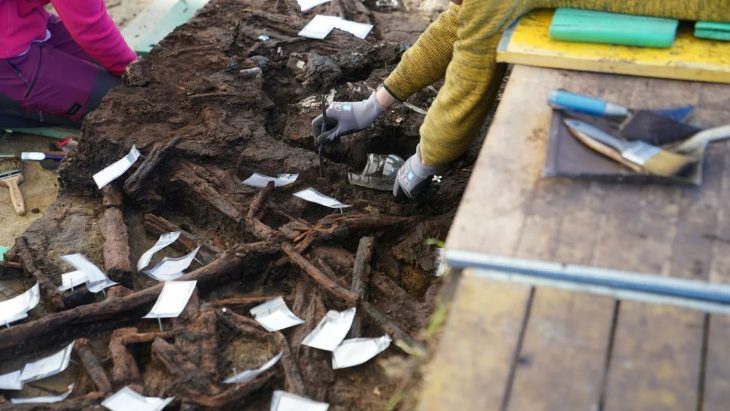
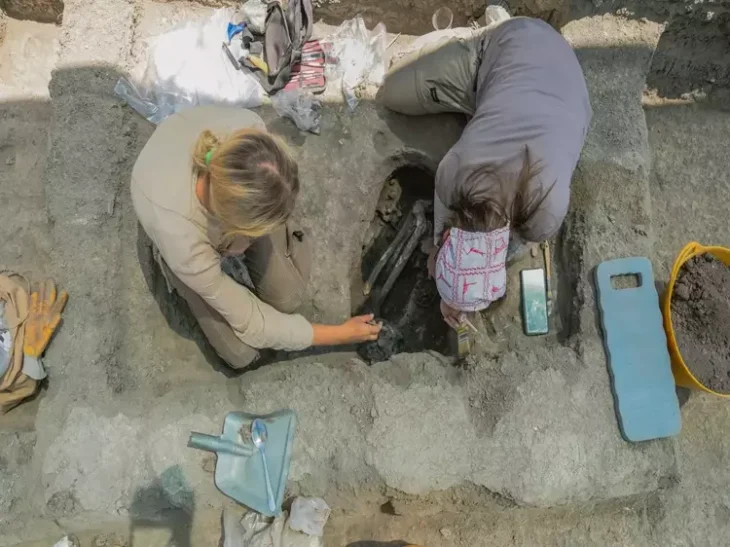
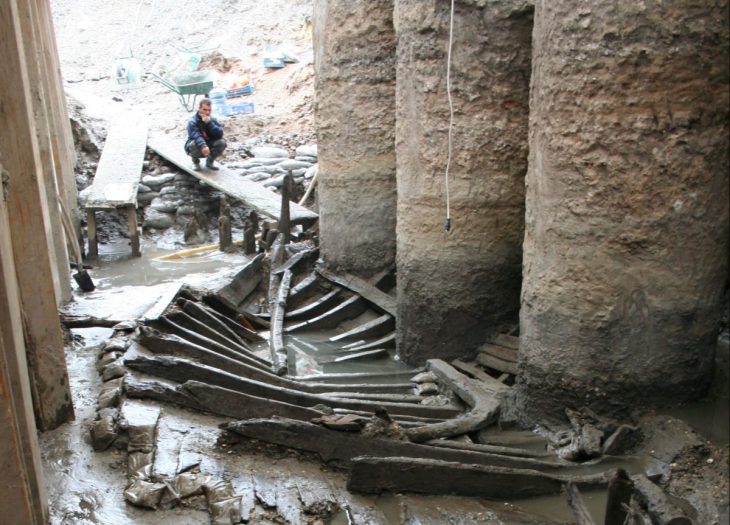
The remains of a Celtoiberian city that existed more than 2,000 years ago have been discovered by excavations carried out by the Polytechnic University of Madrid (UPM). The site could be the lost city of Titiakos, a Celtoiberian stronghold from the Sertorian War, according to the researchers.
The Sertorian War (80-72 BC) was the last stand of the Marian faction after their defeat in Italy during Sulla’s Second Civil War and saw Quintus Sertorius hold out in Spain for over a decade before finally being defeated by Pompey and Metellus Pius.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The research, recently published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, was conducted in the locality of Deza after archaeological sites were detected through aerial photographs. These photographs revealed sections of a rock-cut road with wheel ruts caused by the passage of carts.
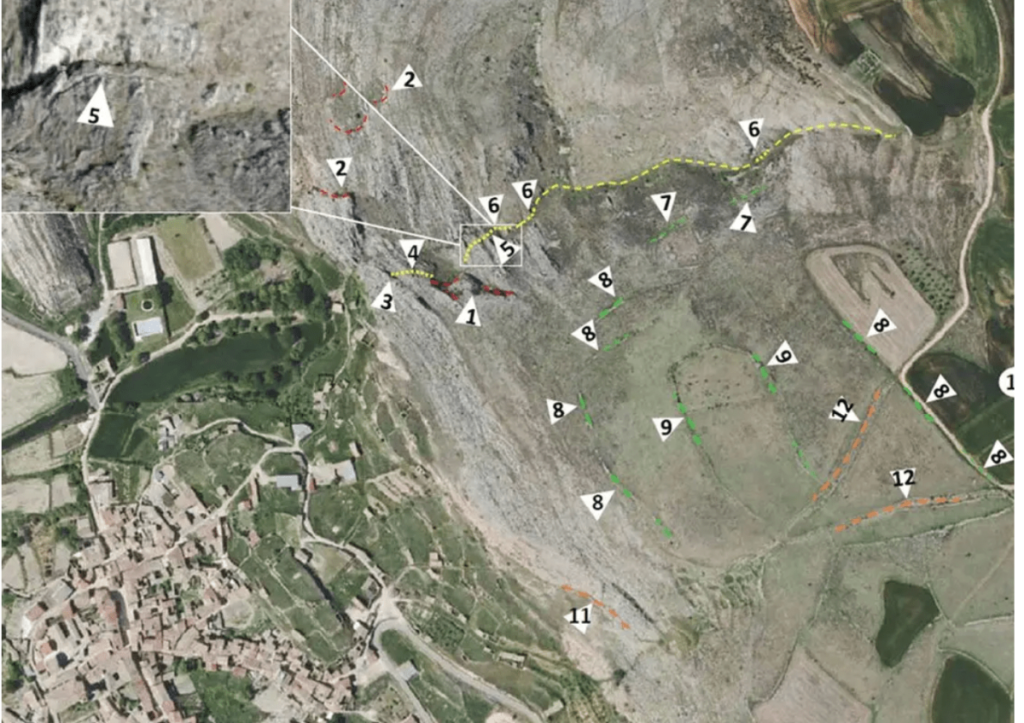
“Despite its relevance, this site has never been studied and has remained ignored. To date no systematic study has been carried out that has tried to discover its historical importance”, says Vicente Alejandre, mayor of Deza.
These sections end at a precipice where there is a large 2.5-tonne block of stone, “shrouded in mystery since it was not understood why it had been built,” according to the statement.
The professor who led this investigation, Eugenio Sanz, explains that it went “totally unnoticed” because the place and the rock “are naturalized in such a way that, after more than 2,000 years, the quarry fronts were considered natural accidents of the terrain “.
This military camp presumably had the purpose of protecting the Celtiberian-Roman city from its “most vulnerable” side, Sanz adds, with a construction that was “very well made.”
Sanz concludes that approximately 12,000 cubic meters of limestone were extracted from this quarry, which corresponds to the volume and type of rock found in the remaining walls and the reused stone boundaries in the surrounding agricultural estates.
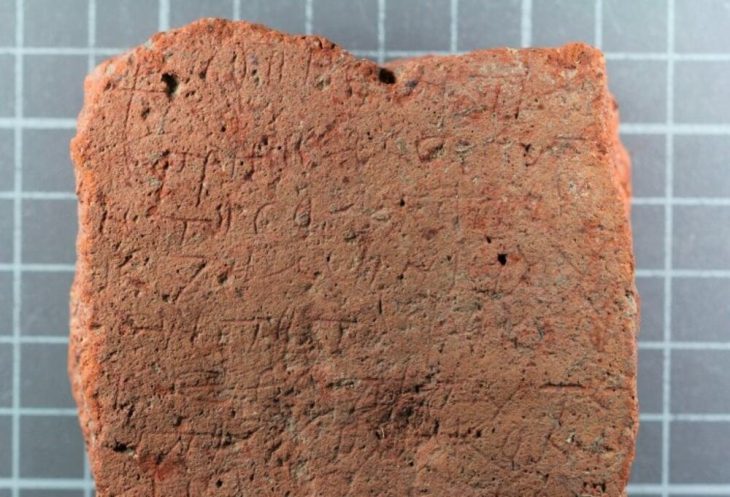
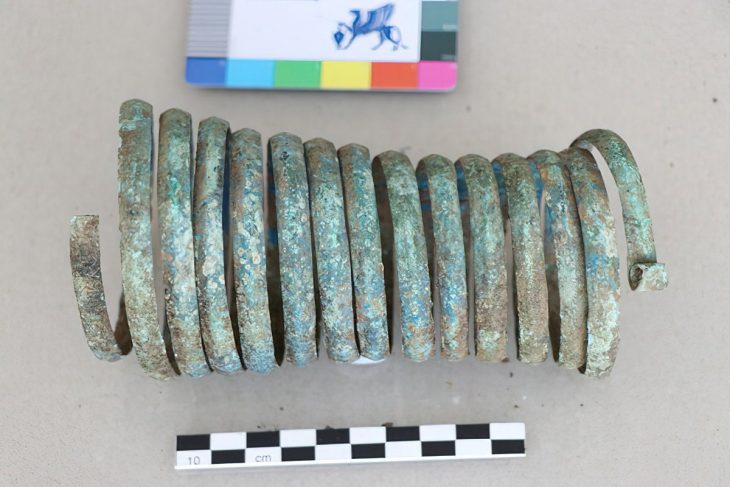
The team suggest that the fort was likely built to protect the city mint by allied Sertorians, as excavations have revealed warlike elements and evidence of conflict such as projectiles, and also coins that came from the mint.
Cover Photo: UPM