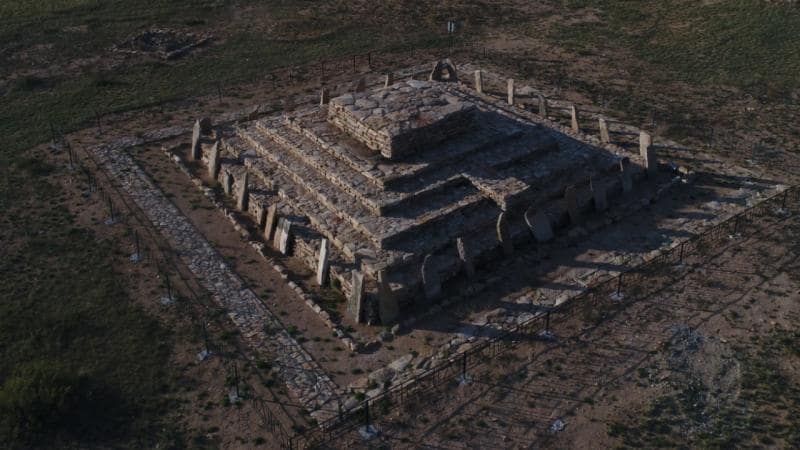
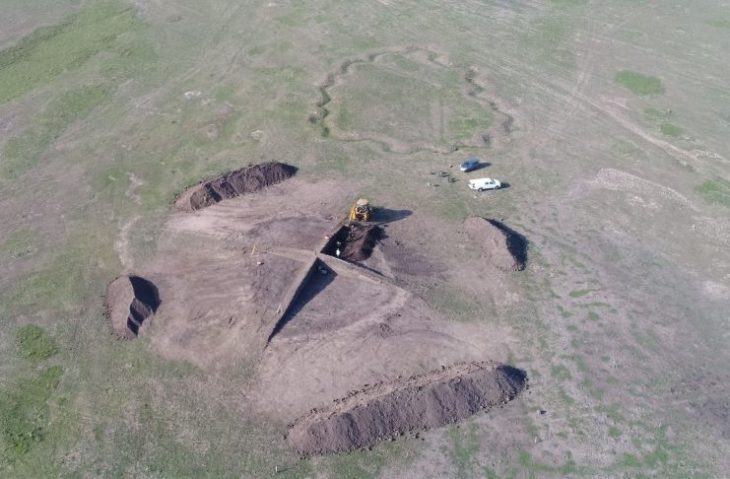
A pyramid belonging to the Scythian-Saka period was found in the Karaganda region of Kazakhstan.
Experts announced that the Karajartas mausoleum belongs to a ruler from the Begazı Dandibay period, which was the last phase of the Andronovo period.
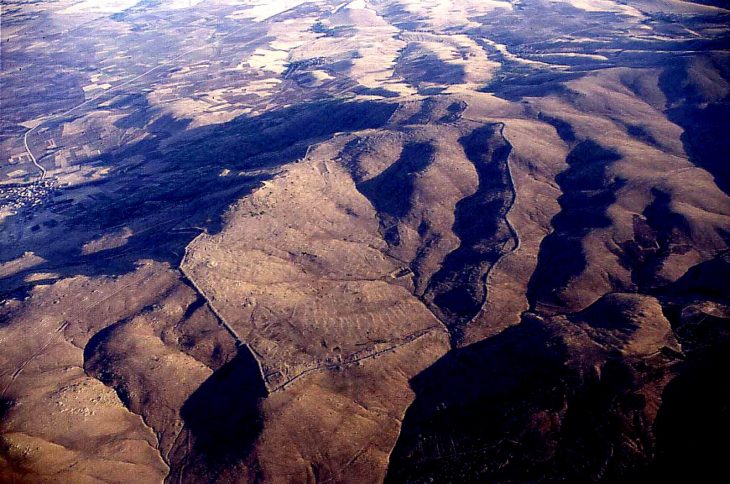
The pyramid, which was excavated over the course of four excavation seasons by archaeologists from Karaganda University, is situated atop a hill overlooking the Taldy River in the Shet district of Karaganda.
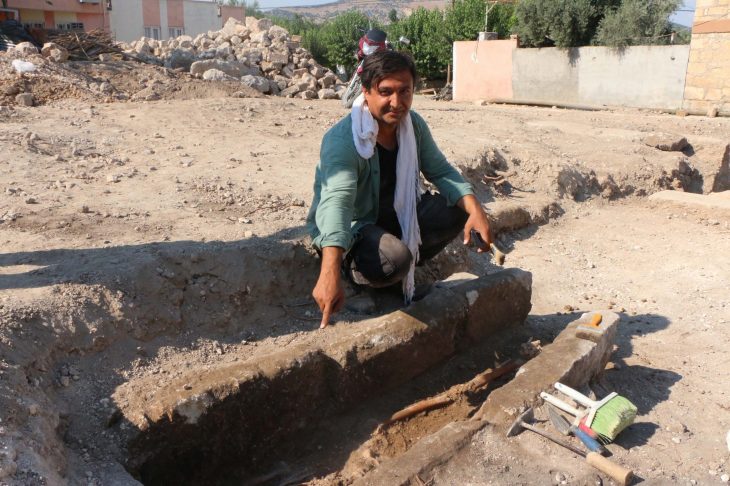
From the National Museum of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Dr. Aibar Kassenali made the first evaluation of the discovered pyramid to TRT Haber.
Dr. Aibar Kassenali announced that according to the results of carbon 14 analyses carried out on the finds, the pyramid structure was dated between the 14th and 12th centuries before Christ (BC).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Kassenali explains the meaning of this dating: “The presence of multiple pyramidal stepped mausoleums detected in the region shows that the Taldı River valley, located in the Sari Arka steppes, was used by the Andronovo communities in the Bronze Age as the valley of kings where their great leaders were buried, like the Nile Valley in Egypt. ” he explained with his words.
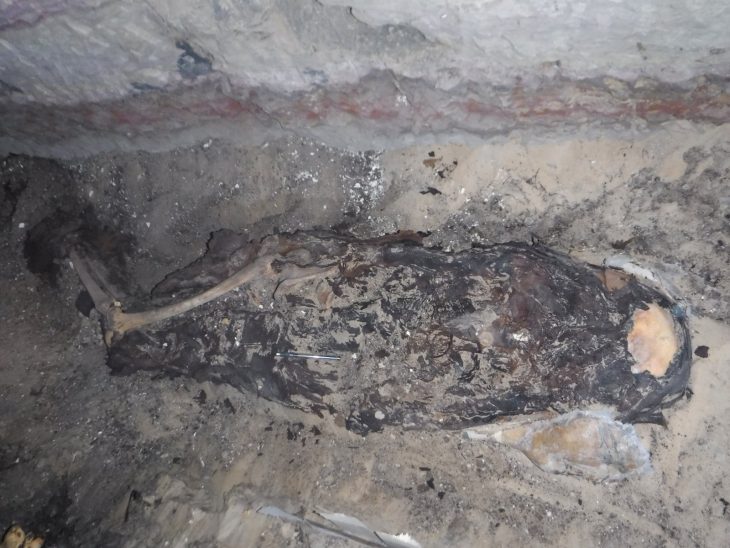
Dr Aibar Kassenali said that when the findings in the burial chamber were examined, the steppe pyramid may have been built on behalf of a local ruler who ruled the Kazakh steppes during the Andronovo period.
Dr. Aibar Kassenali said, “Looking at the cut stones found in the pyramid, the size of the mausoleum, and the fact that such a huge structure was built in the Bronze Age in a very arid region such as the steppe is an indication of the high understanding of art and rich spiritual beliefs that the Begazi Dandibay communities have reached.”
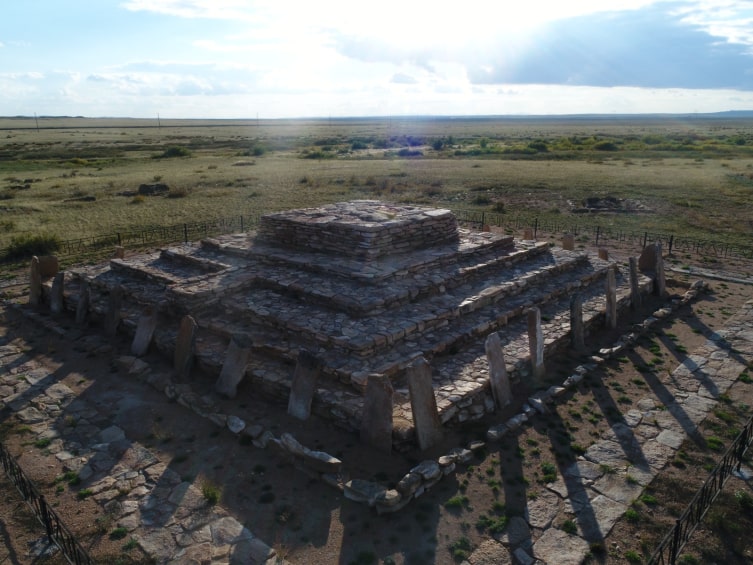

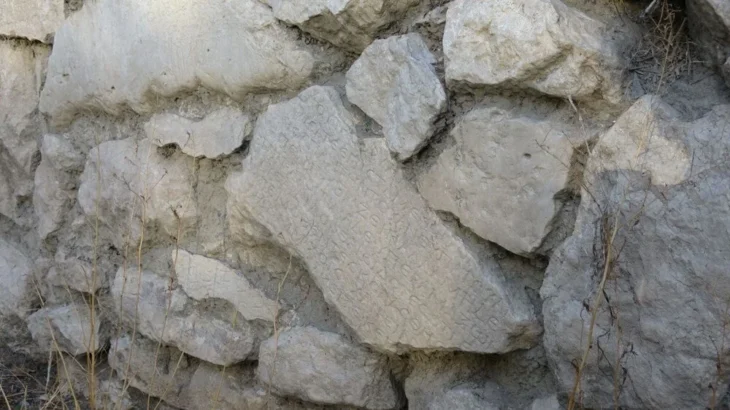
Dr. Serhan Çınar noted that there is information about pyramid-shaped tomb structures in ancient historical sources related to the Scythian-Saka and the early periods of the Begazı Dandibay communities. Dr. Çınar emphasized that the step-like pyramidal monumental tombs identified in Karajartas may be early versions of burial structures from the Scythian period mentioned in historical records.
Excavations in the region have also uncovered a proto-city settlement also belonging to a Begazı Dandibay community.
Dr. Çınar said, “This settlement, which extends over an area of 15 hectares, existed chronologically in the same historical period as Troy 4 in Asia Minor, the Early Mycenaean period in mainland Greece, and the advanced period of the Middle Kingdom in Egypt. The settlement has a series of walls, a planned street network, and water collection systems.”
The researchers believe that the Begazı Dandibay communities demonstrate a close relationship with the Proto-Turkish culture, which is derived from the Karasuk culture of Southern Siberia. As a manifestation of traditional Turkish religious belief, the corridors leading to the burial chamber, particularly in the mausoleums of the Begazı Dandibay phase, always open towards the direction of sunrise.
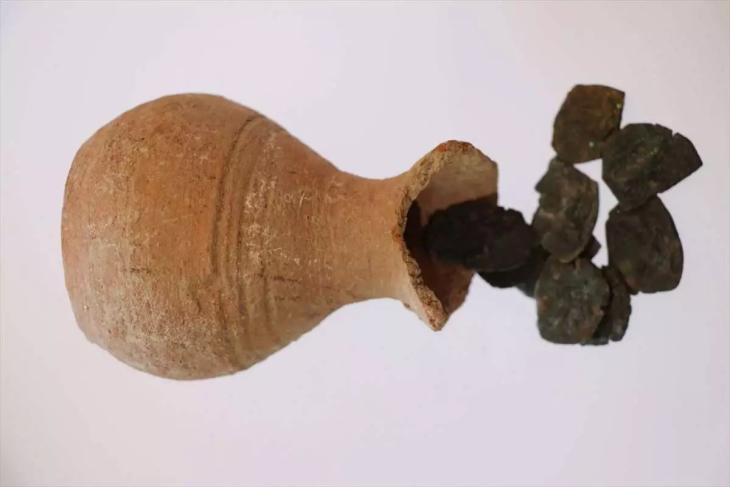
The round-shaped ceramic vessels found in the graves from this period symbolize a cultural continuity in the steppe environment. They represent ritual vessels from the Scythian-Saka period, and in later periods, they evolved into the archaic versions of traditional cauldrons commonly seen among Turkic tribes from the time of the Asian Huns onwards.
It is known that among the Turkic runic script characters from the Göktürk period, there are many tamga pictograms associated with the Andronovo and Begazı Dandibay phases.
Furthermore, the geometric decorations and tamga-type characters (A tamga or tamgha was an abstract seal or stamp used by Eurasian nomads and by cultures influenced by them) found in burial sites are present in the art of medieval Turkic tribes, indicating ethnographic and historical continuity.
Cover Photo: Dr. Aibar Kassenali