Archaeologists have unearthed a 3,300-year-old clay tablet depicting a catastrophic foreign invasion of the Hittite Empire in Büklükale, about 100 km from Turkey’s capital Ankara.
A translation of the tablet’s cuneiform text indicates that the invasion occurred during a Hittite civil war, presumably in an attempt to support one of the fighting factions.
Previously, only broken clay tablets had been found in the excavations at Büklükale, but this one is in almost perfect condition.
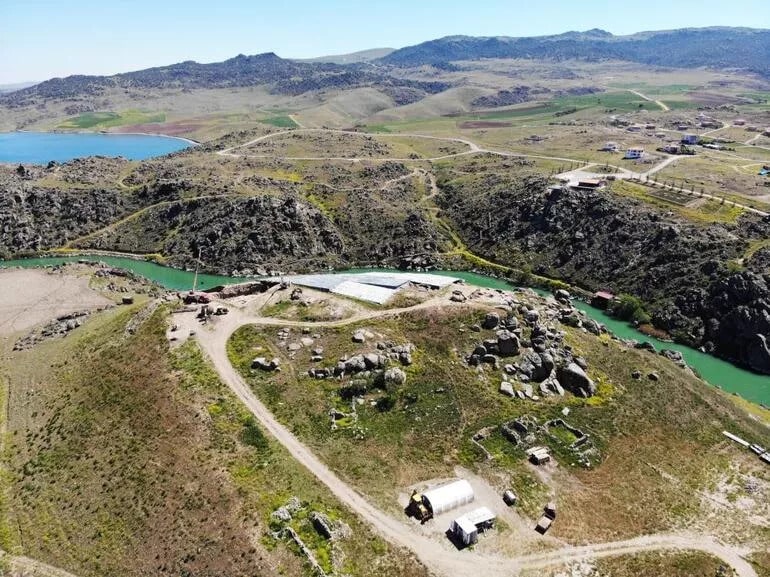
Based on the typology and distribution of the collected pottery shards, Büklükale is thought to be a single-period city belonging to the Hittite Empire Period and having a diameter of 500 m.
The palm-size tablet was found in May 2023 by Kimiyoshi Matsumura, an archaeologist at the Japanese Institute of Anatolian Archaeology, amid the Hittite ruins at Büklükale.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Hittites used the Hurrian language for religious ceremonies, Matsumura told Live Science, and it appears that the tablet is a record of a sacred ritual performed by the Hittite king.
“The find of the Hurrian tablet means that the religious ritual at Büklükale was performed by the Hittite king,” Matsumura told Live Science in an mail. “It indicates that, at the least, the Hittite king came to Büklükale … and performed the ritual.”
According to a translation by Mark Weeden, an associate professor of ancient Middle Eastern languages at University College London, the first six lines of cuneiform text on the tablet say, in the Hittite language, that “four cities, including the capital, Hattusa, are in disaster, ” while the remaining 64 lines are a prayer in the Hurrian language asking for victory.

The Hurrian language, which was spoken from the last centuries of the third millennium BCE until the Hittite empire’s final years (c. 1400–c. 1190 BCE), is now extinct and is not related to either the Indo-European or Semitic languages. Hurrian was originally the language of the region’s Mitanni kingdom, which later became a Hittite vassal state.
The language is still poorly understood, and experts have spent several months trying to learn the inscription’s meaning, Matsumura said.
It turns out, the Hurrian writing is a prayer addressed to Teššob (also spelled Teshub), the Hurrian name of the storm god who was the head of both the Hittite and Hurrian pantheons.
“It praises the god and his divine ancestors, and it repeatedly mentions communication problems between the gods and humans. The prayer then lists several individuals who seem to have been enemy kings and concludes with a plea for divine advice,” Matsumura said.
The Hittite Empire collapsed in the early 12th century for a variety of reasons, including civil war, climate change, and invaders such as the Sea Peoples, Kaskis, Phrygians, and Mycenaean Greeks pushing the borders of Hatti.
But it seems that the invasion indicated by the tablet has nothing to do with the end of the Hittite Empire. Matsumura said the tablet dates to the reign of the Hittite king Tudhaliya II, between about 1380 to 1370 B.C. — roughly 200 years before the Late Bronze Age collapse.
The tablet “seems to come from a period of civil war which we know about from other [Hittite] texts,” he said. “During this time, the Hittite heartland was invaded from many different directions at once … and many cities were temporarily destroyed.”
Although the Hittite Civil War is known as a period of civil war that destabilized the Hittite Empire in the last decades of its existence, it is understood that this problem has been ongoing since the past.
Cover Photo: The ancient tablet is inscribed with cuneiform text in both the Hittite and Hurrian languages. The Hittite inscription describes the outbreak of war, and the Hurrian inscription is a prayer for victory. Image credit: Kimiyoshi Matsumura, Japanese Institute of Anatolian Archaeology